Журнал высшей нервной деятельности им. И.П. Павлова, 2022, T. 72, № 3, стр. 405-420
Дефицит гиппокамп-зависимого обучения не коррелирует с подавлением долговременной посттетанической потенциации при системной блокаде НМДА-рецепторов
В. А. Коршунов 1, *, **, Ш. С. Узаков 1
1 Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки
Институт высшей нервной деятельности и нейрофизиологии РАН
Москва, Россия
* E-mail: korav-md@mail.ru
** E-mail: vkorshunov@ihna.ru
Поступила в редакцию 07.08.2021
После доработки 17.11.2021
Принята к публикации 20.12.2021
- EDN: GOFCQP
- DOI: 10.31857/S0044467722030054
Аннотация
Обучение и поведение более чувствительны к блокаде НМДА-рецепторов (НМДАр), чем ДПП-подобная пластичность. Интраперитонеальные и интравентрикулярные инъекции низких, нетоксичных доз неконкурентного антагониста НМДАр MK-801 не блокируют ДПП в гиппокампе, но нарушают гиппокамп-зависимые формы обучения и пространственного поведения как в алло-, так и в эгоцентрической координатных системах и препятствуют воспроизведению ранее выработанных реакций у хорошо обученных животных. Наши результаты не подтверждают связь ДПП-подобной пластичности с пространственным обучением.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Долговременная посттетаническая потенциация (ДПП) в гиппокампе рассматривается как синаптическая модель обучения и памяти (Bliss, Collingridge, 1993; Whitlock et al., 2006). Антагонисты N-метил-D-аспартатных (НМДА) рецепторов блокируют как индукцию ДПП, так и пространственное обучение (Morris, 1989). Дозы, блокирующие ДПП, всегда влияют на пространственное обучение (Butcher et al., 1990). Эти данные легли в основу предположения о связи ДПП-подобной пластичности и обучения. Тем не менее результаты подобных экспериментов свидетельствуют лишь о том, что НМДАр участвуют в пространственном обучении (Morris et al., 2013) и, в ряде случаев, в реконсолидации пространственной памяти (Зайченко и др. 2018), в то время как роль ДПП-подобной пластичности остается неочевидной (Saucier, Cain, 1995; Bannerman et al., 1997; Jeffery, 1997; Holscher, 1999; Kikusui et al., 2000; Александров, 2005). НМДАр присутствуют во многих структурах мозга (Monaghan, Cotman, 1985), и любое системное (интраперитонеальное или интравентрикулярное) введение блокаторов может нарушить много процессов в мозге, помимо блокады ДПП (Keith, Rudy, 1990), например, блокировать пачечную активность пирамид гиппокампа (Peet et al., 1987; Abraham, Kairiss, 1988), связанную с пространственным обучением (Christian, Deadwyler, 1986). Антагонисты НМДАр нарушают тета-ритм в гиппокампе (Leung, Desborough, 1988), в то время как тета-осцилляции необходимы для пространственного обучения (McNaughton et al., 2006). Эти данные говорят о роли НМДАр в динамических процессах, происходящих в нейронной сети. К сожалению, большинство современных исследований ограничивается лишь участием НМДАр в синаптической пластичности (Cercato et al., 2014, 2017; Sengar et al., 2019). Действительно ли причина дефицитов обучения связана с блокадой ДПП-подобной пластичности, или мы имеем дело с другими нарушениями? Если представить, что механизмы обучения более чувствительны к блокаде НМДАр, чем ДПП, то мы получим ложную корреляцию между ДПП и обучением. В этом случае нарушения обучения будут наблюдаться уже при низких дозах антагониста НМДАр, а чтобы заблокировать ДПП, придется увеличить концентрацию антагониста, при которой обучение будет нарушено a priory. Следовательно, дозы, блокирующие ДПП, неадекватны для выявления корреляции между ДПП и пространственным обучением (Коршунов, 2012). В этой работе мы исследовали пространственное и непространственное обучение у крыс при низких дозах антагонистов НМДАр, не блокирующих ДПП.
МЕТОДИКА
Четырнадцать взрослых крыс самцов линии Long-Evans (ИПРАН) весом 300–520 г было использовано в экспериментах. Крысы этой линии имеют хорошее зрение по сравнению с альбиносами, вследствие нормально пигментированной радужной оболочки (Prusky et al., 2002), а визуальные стимулы играют основную роль в пространственных задачах в бассейне Морриса (Whishaw, 2004). Крысы содержались индивидуально при естественном суточном цикле и имели свободный доступ к воде и пище. Все процедуры выполняли в соответствии с международными этическими нормами (EU Directive 2010/63/EU) и положением Института ВНД и НФ о работе с животными.
Животные псевдослучайно были разделены на 3 группы: экспериментальную (6 крыс) и 2 контрольные (5 и 3 крысы соответственно).
Операция
Крыс анестезировали золетилом (Zoletil 100, VIRBAC S.A., Франция, 35 мг/кг) или хлоралгидратом 400 мг/кг внутрибрюшинно. Скальпирование проводили под дополнительной новокаиновой блокадой. Трепанационные отверстия сверлили согласно координатам атласа (Paxinos, Watson, 1998). Отрезок инъекционной иглы (Рекорд 1A1-06x25-1 15, ОСТ 64-1-102-73, Россия) использовали в качестве направляющей для интравентрикулярных инъекций и имплантировали в левый латеральный желудочек мозга (AP = –0.8; L= = 1.4; H = 3.8). В направляющую вставляли стерильный мандрен, во избежание загрязнений. Биполярные стимулирующие электроды делали из 80 мкм нихромовой проволоки в эмалевой изоляции (ПЕТНХ-155, ТУ16-505810-75, Россия). Электроды скручивали вместе, припаивали к индивидуальным контактам и вживляли в перфорантный путь (ПП) (левое полушарие, AP = –6.8; L = 3.4; H = 3.5 от кости) и в вентральную гиппокампальную комиссуру (ВГК) (правое полушарие, AP = –1.3; L = 1.0; H = 4.0 от bregma). Электроды фиксировали к кости зуботехнической пластмассой. Регистрирующие электроды вживляли в дорсальную зубчатую фасцию (ДЗФ) (левое полушарие, AP = –3.1; L = = 1.8; H = 3.5 от кости) и в поле СА1 дорсального гиппокампа (правое полушарие, AP = –3.8; L = 2.8; H = 2.2–2.5 от поверхности мозга). Эти структуры были выбраны, поскольку ДПП в них НМДАр-зависимая. Для регистрации использовали 25 мкм платино-иридиевую проволоку в эмалевой изоляции (CFW, USA) или высокоимпедансные (1–3 MΩ при 1600 Гц) электроды, изготовленные из 100–130 мкм вольфрамовой проволоки, электролитически заточенной и изолированной винифлексовым лаком или стеклом. Микропроволочные электроды вставляли в микроманипулятор и имплантировали под физиологическим контролем (подробности см. Korshunov, 2012). Для высокоимпедансных электродов использовали съемный микроманипулятор, для чего на голове животного во время операции фиксировали только “гнездо”, манипулятор устанавливали и погружали электроды непосредственно перед экспериментом (подробности см. Korshunov, Averkin, 2007).
Электрофизиология
Эксперименты начинали через 3–8 дней после операции. Процедура экспериментов была одинаковой для всех 3 групп. Все эксперименты начинали вечером, когда крысы наиболее активны. Животное находилось в домашней клетке. Стимулирующие и регистрирующие электроды подключались соответственно к стимулирующей приставке (DL360, NBLab, Россия) и усилителям (U7-1, Россия) с помощью гибкого кабеля с миниатюрным многоканальным предусилителем (Korshunov, 2012). Выход усилителя и входы стимулятора соединяли соответственно с аналого-цифровым и цифро-аналоговым преобразователями (L-203, L-CARD, Россия), управление экспериментом осуществлял компьютер PC AT-386. Для стимуляции и регистрации вызванных потенциалов (ВП) использовали ранее опубликованный протокол (Ezrokhi et al., 1999). Для стимуляции использовали прямоугольные импульсы тока (50–200 мкс, 60–350 мкА для ПП и 50–100 мкс, 60–124 мкА для ВГК). Перед началом эксперимента для каждого животного подбирали стимуляцию, вызывающую в соответствующей области гиппокампа ВП 30–50% от максимума. В дальнейшем эта стимуляция использовалась в качестве тестирующей. Каждое тестирование состояло из 10 предъявлений импульсов тока, с псевдослучайным интервалом 25–35 с. Полученные ВП усредняли и записывали на диск с 12-битным разрешением. Интервал между тестами составлял от нескольких минут до нескольких часов. Для получения базовой линии использовали усреднение по 3–5 тестам, результат усреднения принимали за 100%. Для ДПП использовали высокочастотную стимуляцию 200 имп/с для ПП и 100 имп/с для ВГК. Продолжительность стимуляции 1 с, амплитуда и длительность импульсов была равна тестирующим стимулам. ВП после тетанизирующей стимуляции оценивали в процентах от базовой линии. После эксперимента положение электродов проверяли гистологически.
Введение препарата
Мы использовали неконкурентный антагонист НМДАр (+)-МК-801 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). Выбор последнего был обусловлен тем, что он наиболее эффективен среди селективных антагонистов НМДАр (Tricklebank et al., 1989) и длительно действует. Таким образом, отсутствует необходимость в довведении препарата, и конечная доза точно известна. Во избежание токсичного воздействия на нейроны мы использовали дозы вдвое меньшие нижней границы токсичности для МК-801 (см. Olney et al., 1993). Предварительные эксперименты (Коршунов, 2012) показали, что эти дозы не влияют на индукцию ДПП в ДЗФ и поле СА1 гиппокампа. MK-801 растворяли в изотоническом р-ре NaCl и вводили интраперитонеально (0.05–0.1 мг/кг, 1 мл на крысу) или интравентрикулярно (12–20 мкг, 5 мкл на крысу, 1 мкл/мин) с помощью прецизионной помпы (Stoelting, USA). Для этого изымали мандрен из направляющей и вставляли в нее отрезок инъекционной иглы 0.3 мм диаметром, соединенный с помпой тонкой силиконовой трубкой. Контрольные инъекции (изотонический р-р NaCl) делали в тех же объемах: 1 мл интраперитонеально и 5 мкл интравентрикулярно.
Поведение
Для анализа поведения использовали аллоцентрическую (гиппокамп-зависимую) и эгоцентрическую задачи в бассейне Морриса. Бассейн диаметром 150 см и глубиной 50 см был заполнен теплой (24–27°С) водой. Уровень воды – 25 см. Невидимая платформа диаметром 10 см располагалась на 1 см ниже уровня воды для аллоцентрической задачи. Для эгоцентрической задачи на платформу ставили черный цилиндр, возвышавшийся над водой на 2 см. Согласно данным (Lamberty, Gower, 1991) упрощение среды улучшает пространственное поведение; также показано (Nakazawa et al., 2002), что пространственные тесты в обедненной среде более чувствительны к нарушениям поведения, поэтому мы сознательно сократили количество визуальных стимулов. Бассейн стоял в углу заземленной комнаты и был отгорожен с двух сторон черными занавесками, таким образом, крыса могла видеть только две светлые и две темные стены. Крысам давали 3–5 попыток в день, чтобы найти платформу, с 10–30-минутными интервалами между попытками для отдыха и еды. Поведение записывали на веб-камеру (LG, Korea) и анализировали с помощью программы трекинга с поправкой перспективных искажений (Коршунов, 2014).
Анализ поведения
Традиционные методы оценки поведения в бассейне Морриса включают время нахождения платформы, длину траектории, скорость плавания и процент времени пребывания в квадрантах и зонах. Поскольку МК-801 влияет на двигательную активность (Tricklebank et al., 1989; Ahlander et al., 1999), мерить время бесполезно (Коршунов, 2014). Предварительный анализ (Коршунов, 2012) показал, что выбор правильного направления – наиболее адекватный параметр для оценки пространственного поведения в аллоцентрических задачах. Мы использовали три индекса оценки поведения: w/m, w/d и w/c, где w – длина траектории плавания; m – кратчайшее расстояние между платформой и исходным положением крысы в бассейне; d – диаметр бассейна; c = π × d – длина стенки бассейна. Аллоцентрическая задача сводится к выбору правильного направления, и если выбор верен, то w близка к m и индекс w/m стремится к 1, или 100% (см. Коршунов, 2014). Если животное использует дирекциональную или фокальную стратегию поиска, то w не может быть больше d; следовательно, w/d < 1. Таким образом, если крыса использует пространственную стратегию, w/d < 1< w/m. Если животное ошиблось в выборе направления или использует непространственные стратегии поиска, длина траектории растет и w/c < 1 < < w/d. Наивные животные обычно плавают вдоль стен бассейна, совершая несколько полных кругов, что отражается на индексе w/c > 1. Эмпирически мы нашли, что, когда индекс w/c становится меньше 1, крыса меняет escape-реакцию на целенаправленный поиск платформы (Коршунов, 2012). Попытка, когда это случилось, может быть использована как точка синхронизации для сравнения различных животных. Индексы не зависят от физического состояния животных и их двигательной активности. Кроме того, будучи пропорциями, эти индексы позволяют сравнивать между собой различные попытки разных животных независимо от места запуска в бассейн, без каких-либо дополнительных расчетов (Коршунов, 2019).
Протокол экспериментов
Отсутствие ДПП на фоне антагониста еще не означает успешной блокады рецепторов, поскольку тот же эффект будет и без блокатора, при ошибочной установке электродов или неудачных параметрах тетанизирующей стимуляции. Для нахождения оптимальных параметров индукции ДПП индивидуально для каждой крысы мы предварительно потенцировали ПП и ВГК на фоне инъекции изотонического р-ра NaCl. Эксперименты начинали через несколько дней после полного угашения предварительной ДПП. Предварительное плавание наивного животного использовали для оценки исходного физического состояния (средняя и максимальная скорость плавания). ВП в ответ на стимуляцию соответствующих входов регистрировали в течение всего эксперимента, до и после введения антагониста. Тетанизирующую стимуляцию с ранее найденными параметрами предъявляли через 20–50 мин после инъекции антагониста, когда наблюдались наиболее выраженные поведенческие изменения, что свидетельствовало, что препарат действует на ЦНС. Каждой крысе давали столько попыток, сколько необходимо, чтобы найти подводную или видимую платформу после инъекции препарата (экспериментальные крысы) или изотонического раствора (контрольные животные). При тестировании после обучения всем крысам давали одну попытку найти подводную платформу.
Статистический анализ
Если данные имели нормальное распределение (тесты Колмогорова–Смирнова и Шапиро–Уилка), использовали двусторонний критерий Стьюдента (число степеней свободы: df = n1 + n2 – 2). В случае ненормального распределения использовали тест Манна–Уитни. Для данных с биномиальным распределением использовали точный тест Фишера. Различия p < 0.05 принимались как достоверные во всех тестах. Для обработки данных использовали программы Statistica10 и SPSS17.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ
Препарат протестировали до экспериментов. Большая доза МК-801 (1 мг/кг) полностью блокировала индукцию ДПП (рис. 1, первая инъекция). Напротив, низкие, нетоксичные дозы (0.08–0.1 мг/кг) препарата не препятствовали индукции ДПП (рис. 1 (а), вторая инъекция). Результаты представлены на рис. 1 (б). Поскольку NaCl вводили и контрольным, и экспериментальным животным, группы объединили (11 крыс, 8 потенциаций в ДЗФ, 10 в СА1); МК-801вводили только экспериментальной группе (6 крыс, 8 потенциаций в ДЗФ, 6 в СА1). ДПП после инъекции изотонического р-ра NaCl и после интраперитонеальных и интравентрикулярных введений МК-801 достоверно не отличались в ДЗФ (тест Манна–Уитни, для ВПСПz = = 1.636181, p > 0.1; для ПСz = –0.806179, p > > 0.4) после тетанизирующей стимуляции ПП. В СА1 потенциация ПС на фоне МК-801 была даже выше, чем после инъекции изотонического р-ра у тех же крыс (+17.7% в среднем, z = –4.29132, p < 0.001); достоверных различий в потенциации ВПСП не выявлено (z = –0.297012, p > 0.76). Низкие дозы препарата вызывали гиперактивность у крыс в домашней клетке, сопровождаемую вестибулярными и моторными нарушениями как после интраперитонеальных, так и после интравентрикулярных инъеций (рис. 1 (в)). Изменения поведения начинались через 26–61 мин после инъекции, что соответствует ранее опубликованным результатам (Tricklebank et al., 1989; Adams et al., 2013). Введенные дозы не блокировали индукцию ДПП ни в ДЗФ, ни в поле СА1 гиппокампа после тетанизации соответственно ПП и ВГК. Тем не менее как интраперитонеальные, так и интравентрикулярные инъекции низких доз МК-801 драматически нарушали поведение как в аллоцентрических, так и в эгоцентрических пространственных задачах. Экспериментальной группе крыс было сделано 11 интравентрикулярных инъекций низких доз МК-801 (0.08–0.1 мг/кг). Ни одно из шести экспериментальных животных под действием антагониста НМДАр не смогло выучить не только аллоцентрическую, но даже эгоцентрическую пространственную задачу. Типичный пример показан на рис. 2. У этой крысы было 8 попыток на фоне интраперитонеальной инъекции препарата. Два первых эксперимента были с невидимой платформой. До инъекции наивное животное сначала плавает вдоль стен бассейна, потом пересекает его по хордам (рис. 2 (а), траектория 0t01). Напротив, под воздействием МК-801 животные вращаются на месте или кружатся в воде, иногда погружаясь под воду (рис. 2 (а), траектория 0t02). Плавание начинает возвращаться к норме только через 3 часа после инъекции (рис. 2 (а), траектория 0t04). ДПП в СА1 была вызвана тетанизирующей стимуляцией ВГК, на пике действия препарата (через 24 мин после введения), когда животное было не в состоянии решить пространственную задачу. После короткой депрессии (1 тест, сразу после тетанизации, см. рис. 2 (а)), амплитуда ПС достоверно увеличилась по сравнению с фоном (нормальное распределение, тест Стьюдента, t108 = –16.2841, p < 0.001). ДПП сохранялась более суток (t78 = = –2.67815, p < 0.05). Когда ДПП полностью угасла, эксперимент повторили. ВГК потенцировали через 50 мин после интраперитонеальной инъекции МК-801, стимуляция снова вызвала достоверное возрастание ПС (t108 = –15.9573, p < 0.001), при грубых нарушениях поведения (рис. 2 (б), траектория 0t05). Эта крыса нашла платформу один раз с 6-й попытки, но не забралась на нее и не запомнила ее позиции, что выяснилось при тестировании. В третьем эксперименте выяснилось, что крыса после интраперитонеальной инъекции МК-801 не смогла решить даже эгоцентрическую задачу с видимой платформой (рис. 2 (в), траектории 0t07-9). Для сравнения, контрольная крыса выучила ту же задачу за 2 попытки (рис. 2 (г)).
Рис. 1.
(а) Предварительное тестирование доз блокатора. ПС регистрировали в ДЗФ. МК-801 интраперитонеально в дозе 1 мг/кг блокирует ДПП в ДЗФ после тетанизирующей стимуляции ПП. Два дня спустя эксперимент повторили с низкой (0.1 мг/кг) дозой блокатора. Стимуляция с теми же параметрами через те же электроды легко вызывала ДПП в ДЗФ. Стимуляция предъявлялась на пике поведенческих изменений в обоих экспериментах. При большей дозе препарата пик активности начинается раньше. (б) ДПП после инъекций изотонического р-ра NaCl (белые столбики) и низких доз МК-801 (темные столбики). Гистограмма показывает суммарный результат, полученный на всех экспериментальных крысах. ДПП ВПСП и ПС показаны отдельно. Пунктир – базовая линия до тетанизации (100%). Остальные детали в тексте. (в) – Сравнение между интравентрикулярным и интраперитонеальным введением низких доз МК‑801. Сходный эффект (гиперактивность с сенсомоторными дефицитами) наблюдали в обоих случаях. Каждый прямоугольник показывает траекторию крысы в домашней клетке за 1 мин, сверху от прямоугольника – время после инъекции, снизу – средняя скорость перемещений. Верхний ряд – контрольная инъекция NaCl. Второй ряд – МК-801 интравентрикулярно (ИВИ) (20 мкг на крысу, 5 мкл, 1 мкл/мин) 18 дней спустя. Третий ряд – МК-801 интраперитонеально(ИПИ) (0.1 мг/кг) 6 дней спустя после предыдущей инъекции.
Fig. 1. (а) Preliminary test of the drug. PS was recorded in DDG. Intraperitoneal injection of high (1 mg/kg) dose of MK-801 blocks LTP induction in DDG after tetanic stimulation of PP. Two days later the experiment was repeated with low (0.1 mg/kg) dose of the drug. Tetanic stimulation with the same parameters via the same electrodes easily induced LTP in DDG. Stimulation was presented at the peak of behavioral changes after both doses. When the dose was higher, the peak of hyperactivity began earlier (note the time difference between the injections and tetanic stimulations in experiments). (б) LTP after saline injections and under the low dose of the drug. Histograms show the summary results obtained from all experimental rats. Potentiation of EPSP and PS in both fields are shown separately. Dotted horizontal line – normalized background before tetanisation (100%). White columns – LTP after saline injections, dark columns – after injections of low dozes of MK-801. For more details see the text. (в) Comparison between intraventricular and intraperitoneal injections of low non-toxic doses of MK-801. Similar effects (hyperactivity with motor and sensor deficits) were observed in both cases. These data were obtained from the same rat. iv, ip – intraventricular and intraperitoneal injections of the drug, respectively. Each panel shows trajectory of the animal in the home cage per minute, time after injection (above the panel) and average velocity of movements (below the panel). The first row – control injection of isotonic solution of NaCl; second row – intraventricular injection of MK-801 (20 μg in 5 μL per rat, 1 μL/min) 18 days later; third row – intraperitoneal injection of MK-801 (0.1 mg/kg in 1 mL) 6 days after the previous injection.
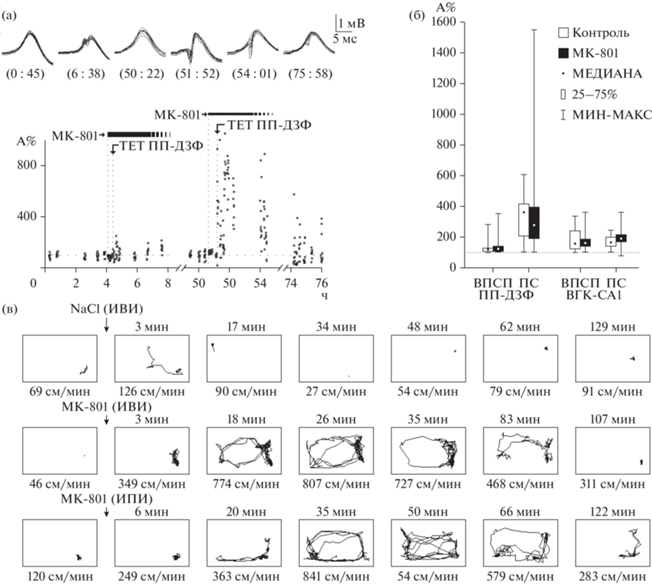
Рис. 2.
Влияние интраперитонеальной инъекции МК-801 на индукцию ДПП и пространственное поведение. Низкие дозы антагониста НМДА-рецепторов не блокируют индукцию ДПП, но драматически нарушают поведение как в алло-, так и в эгоцентрических пространственных задачах. Сверху – вызванные ответы в СА1 гиппокампа при стимуляции ВГК до и после ТЕТ. В скобках – время на общей временной шкале. На графиках ниже – амплитуды ПС до и после ТЕТ, нормированные по амплитуде фона. Ниже показаны траектории животного в бассейне при отдельных попытках. Время после инъекции указано в правом верхнем углу. Светлый круг – подводная платформа, темный – видимая платформа. Время каждой попытки относительно общей временной шкалы показано под траекторией. min – минимальное расстояние между платформой и исходной позицией крысы в бассейне; way – длина траектории в воде; w/m, w/d, w/c – индексы выполнения. В первых двух экспериментах ТЕТ ВГК легко вызывает ДПП через 24 (а) и 50 мин (б) после инъекции МК-801 на фоне грубых нарушений аллоцентрического пространственного поведения в бассейне Морриса. В третьем эксперименте крыса не может решить эгоцентрическую задачу с видимой платформой на фоне МК-801 (в). Для сравнения, контрольной крысе (инъекция изотонического р-ра) потребовалось всего две попытки для решения той же задачи (г).
Fig. 2. Effect of intraperitoneal injections of MK-801 on induction of LTP and behavior. Low doses of NMDAr antagonist MK-801 do not block induction of LTP, but dramatically impair spatial learning in both, allocentric (submerged platform) and egocentric (visible platform) tasks. The panels show the trajectories of the animal in the water maze in each trial; times after injections are shown in the right upper corners of each panel; light circle – submerged platform, dark circle – visible platform; the time of each trial according to the common time scale is shown below the panel; min – the minimal distance between the platform and initial position of the animal; way – the length of the animal trajectory in the water; w/m, w/d, w/c – indices of performance. Graphics and waveforms above the panels illustrate the changes of the field potentials recorded in CA1 field of hippocampus before and after tetanic stimulation of VHC. Data were obtained in the same rat with 2 days interval between experiments. Swimming pattern was dramatically changed after the injection of the drug in all tasks in comparison with swimming after a control saline injection. Intraperitoneal injection of 0.1 mg/kg of MK-801 did not prevent LTP induction. Tetanic stimulation of VHC easily induced LTP in CA1 hippocampal field after 24 min (а) and 50 min (б) of the drug injection exactly during the period of time when the animal could not learn the task due to impairments of behavior. In the third experiment the rat could not find even the visible platform under the drug (в). For comparison, it takes 2 trials for control rat to learn the same egocentric task (г).
При интравентрикулярных инъекциях низких доз МК-801 (20 мкг на крысу) результаты не отличались от интраперитонеальных введений. В экспериментальной группе крыс было сделано 9 интравентрикулярных инъекций. Ни одно животное не обучилось под действием препарата. Типичный пример показан на рис. 3 (а). Тетанизирующая стимуляция ПП легко вызвала ДПП в ДЗФ на фоне гиперактивности животного, вызванной низкой дозой МК-801 (тест Манна–Уитни, z = –8.94836, p < 0.001). Крыса не смогла найти даже видимой платформы, несмотря на интактность индукции ДПП. ДПП длилась более 3 суток (тест Манна–Уитни, z = –2.08272, p < 0.05 на третий день). Три инъекции с интервалом в неделю были сделаны этому животному, все попытки обучиться были безуспешными.
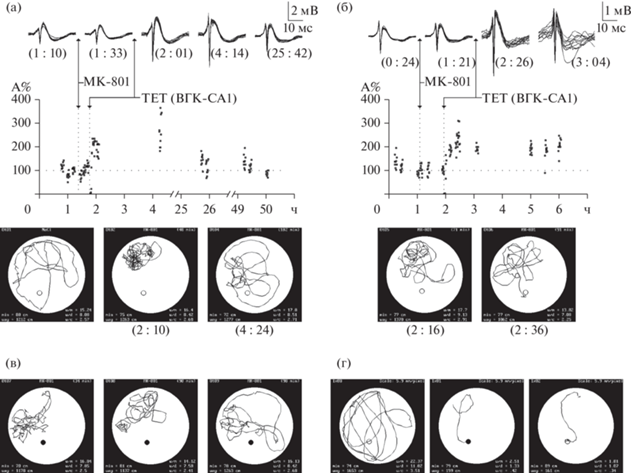
Рис. 3.
Влияние интравентрикулярой инъекции МК-801 на индукцию ДПП и пространственное поведение. (а) МК-801(20 мкг на крысу) не блокирует индукцию ДПП, но нарушает поведение даже в эгоцентрических задачах с видимой платформой. На графике ВП в ДЗФ и ДПП ПС после ТЕТ ПП на фоне антагониста НМДАр. ТЕТ предъявили через 49 мин после инъекции, на пике гиперактивности, когда животное не могло решить задачу (6е02–6е04). ДПП длилась трое суток. В первой попытке на фоне антагониста (6е02) крыса коснулась платформы, но не залезла и не запомнила ее позицию. Эксперимент повторили трижды с недельным интервалом, все попытки на фоне МК-801 были неудачными. После отмены антагониста та же крыса легко решила как эго-, так и аллоцентрическую задачи. (б) Все обозначения как на рис. 2.
Fig. 3. (а) Intraventricular injections of MK-801 (20 μg per rat, 5 μL, 1 μL per minute) do not block LTP induction, but impair spatial learning even in egocentric task (visible platform). All the symbols on the plates have the same meaning as they do in Fig. 2. The graphic and the waveforms show LTP in DDG after tetanic stimulation of PP. Stimulation was presented 49 min after drug injection during the period of time when the animal could not learn the task. LTP lasted for 3 days. In the first trial under the drug the animal touched the platform, but did not remember the position and could not find the platform in the next trials. Three drug injections with one week intervals were made in this particular animal, all the trials under the drug were not successful. (б) Two weeks after the last drug injection this rat could easily learn the task with both, visible and submerged platforms; thus, the dozes used in our experiments were not toxic for the brain.
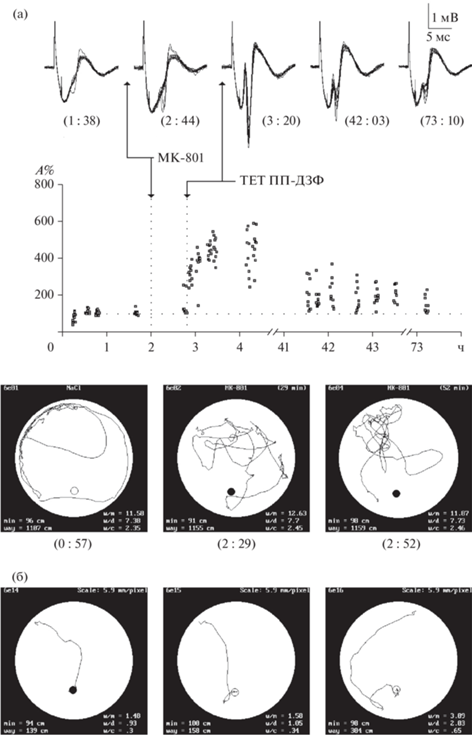
Использованные нами дозы не были токсичны для мозга. Через несколько дней после последней инъекции экспериментальные крысы легко обучались. Типичный пример показан на рис. 3 (б). В первой же попытке крыса сразу нашла видимую платформу, в последующих 2 попытках крыса нашла невидимую платформу с разных исходных позиций.
Низкие дозы МК-801 нарушали поведение даже у хорошо обученных животных (рис. 4). Эксперименты проведены на трех крысах второй контрольной группы после обучения в аллоцентрической задаче. Все 44 попытки до применения препарата были успешны у всех крыс. Половины низких доз (0.05 мг/кг интраперитонеально и 12 мкг на крысу интравентрикулярно) не влияли на поведение; все 9 попыток были успешны. При полных низких дозах поведение драматически нарушалось у всех крыс (только 2 успешные попытки из 17, точный тест Фишера, p < 0.001). Крысы 10 раз случайно (индексы дирекциональности w/m и выполнения w/c достоверно возрастали до уровня попыток наивных животных: тест Манна–Уитни, z = –3.88057, p < < 0.001; z = –3.826673, p < 0.001 соответственно) натыкались на платформу, но в 8 случаях даже не пытались на нее забраться. Для дополнительной проверки одну из крыс дважды потенцировали на фоне МК-801, когда крыса не могла найти платформу. При этом ДПП в ДЗФ была интактна: ПС достоверно возрастал после стимуляции ПП как на фоне интраперитонеальной (z = –9.48424, p < 0.001), так и на фоне интравентрикулярной инъекций (z = –7.63068, p < 0.001) низких доз МК-801. ДПП длилась 3 дня минимум в обоих случаях (z = –7.44223, p < 0.001; z = –5.43591, p < 0.001 на третий день). Обученные крысы под действием блокатора смогли найти только видимую платформу, невидимую находили случайно. Этот эксперимент показал, что блокатор мешает животным воспроизвести ранее выученное поведение. Может быть, крысы все-таки учатся под действием МК-801, но препарат мешает им выполнить выученное поведение? Чтобы проанализировать возможность отставленного или “молчащего” обучения (Rossato et al., 2018), мы исследовали выполнение задачи у экспериментальных животных после отмены МК-801. Если антагонист не влияет на обучение, а только мешает воспроизвести выученное поведение, то после отмены препарата экспериментальные животные должны находить платформу лучше, чем в наивных попытках. Одна крыса из экспериментальной группы была исключена из анализа, поскольку ни разу не нашла платформу, следовательно, не могла обучиться пространственной задаче. Поведение остальных 5 крыс после обучения на фоне МК-801 не отличалось от наивных попыток. Таким образом, низкие дозы МК-801 нарушают обучение, не блокируя ДПП-подобной пластичности. Типичные траектории контрольных и экспериментальных крыс показаны на рис. 5 (а). Индекс дирекциональности w/m достоверно падает у крыс контрольной группы после обучения (рис. 5 (а), К1), чего не наблюдается в экспериментальной группе (рис. 5 (а), Э), несмотря на большее число попыток. Животные не могли решить ни пространственной аллоцентрической задачи (подводная платформа), ни эгоцентрической (видимая платформа) под действием МК-801. В то же время контрольное животное легко решает эгоцентрическую задачу (рис. 5 (а), К2), после чего сразу находит невидимую платформу при тестировании.
Рис. 4.
(а) Низкие дозы МК-801 как при интраперитонеальных (ИПИ), так и при интравентрикулярных инъекциях (ИВИ) нарушают поведение у хорошо обученных животных как в аллоцентрических, так и в эгоцентрических задачах. Траектории под действием антагониста показаны в пунктирных прямоугольниках. Без блокатора индекс w/m близок к 1, на фоне МК-801 он достоверно возрастает до показателей наивного плавания. Только через 5 часов после интравентрикулярой инъекции (198 ч на временной шкале) крыса смогла найти платформу. Белые кружки – невидимая платформа, черные – видимая, “–” в кружке – крыса не нашла платформу. (б) Гистограммы показывают статистически обработанные результаты второй контрольной группы, включающие в себя вероятность нахождения платформы (Р), индексы дирекциональности – w/m и выполнения – w/c. Инъекции половинных доз не влияют на поведение, полные низкие дозы нарушают поведение у хорошо обученных животных без блокады ДПП.
Fig. 4. (а) Low doses of MK-801 after both, intraperitoneal (ip – 0.1 mg/kg, 1 mL) and intraventricular (iv – 20 μg in 5 μL per rat, 1 μL/min) injections impaired behavior even in well-trained animals. Panels with trajectories and graphic below show the results obtained in a particular well-trained control rat. Trajectories under the drug are shown in dotted rectangles. White circles on graphic mean submerged platform, dark – visible platform. Symbol “–“ in the circle indicates that the animal could not find the platform. Without the drug index of directionality w/m was close to 1, but under the drug this parameter significantly increased in all trials. Only five hours after iv – injection (198 h at the total scale) behavior became better and the animal could find submerged platform. (б) Histograms show the statistical analysis of summary results in control group, including probability of finding the platform and indices of directionality w/m and performance w/c. Injections of isotonic solution or a half of low dose of MK-801 did not impair behavior. The whole low dose dramatically impaired behavior even in well-trained rats without blockade of LTP.
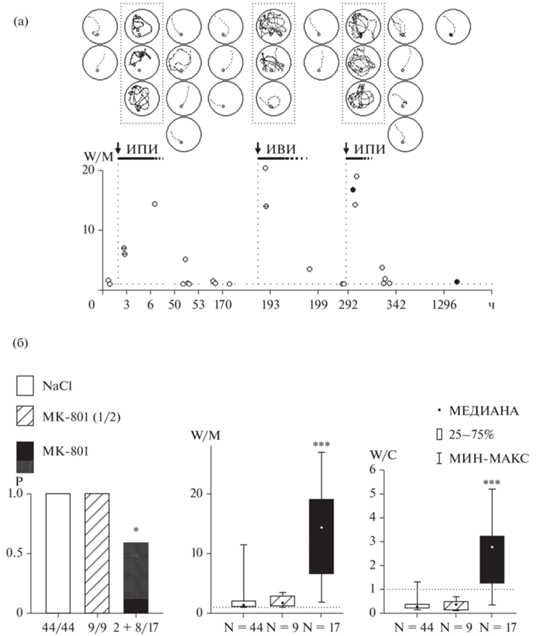
Рис. 5.
Суммарные результаты. (а) Типичные траектории контрольных и экспериментальных крыс. К1 – контроль с подводной платформой, К2 – контроль с видимой платформой, Э – экспериментальная крыса. w/m – индексы показаны под каждой попыткой. В прямоугольнике показаны попытки под влиянием МК-801. В тесте экспериментальные крысы показывают тот же результат, что и в наивной попытке (НП). (б) Кривые обучения. Слева контрольные крысы, справа – экспериментальные. Белые кружки – невидимая платформа, темные – видимая. Символ “–” в кружке – крыса не нашла платформу. Данные контрольных крыс синхронизированы относительно попытки с индексом w/c < 1 (0 на графике). Ни одна из экспериментальных крыс не достигла подобного показателя. Все контрольные крысы показали при тестировании достоверно лучший результат, чем экспериментальные. (в) Гистограммы показывают количество попыток (Q) до первого попадания на платформу, вероятность (P) нахождения платформы и индекс дирекциональности (w/m) до, во время и после обучения, X – число попыток, X/N – соотношение числа успехов X и общего числа попыток N. Остальные объяснения в тексте.
Fig. 5. Summary results. (а) Typical trajectories of control and experimental rats. First row – control with the submerged platform; second row – control with the visible platform; third row – a typical trajectory example of an experimental rat. Visible platform is shown as a black circle, submerged platform – as a white circle. Rectangle marks trials under the drug. w/m – indices are shown under each trial. Experimental rats showed the same task performance as they did in naive trials (НП). (б) Learning curves. Left graph – control rats, right graph – experimental rats. White circles – submerged platform, black circles – visible platform. Symbol “–” inside a circle indicates that the animal did not find the platform in this particular trial. Results obtained from control rats are synchronized relative to the trials with w/c ≤ 1 (see “0” point on the x-axis). None of the experimental rats achieved this index of performance. Experimental rats after learning under the drug showed the same performance as they did in naive trials. Control rats showed significantly better results in the test. (в) Histograms show the number of trials before a rat found the platform the first time, the probability of finding the platform before, during and after learning. N – number of trials, X/N – number of successful trials X out of total N. For more details see the text.
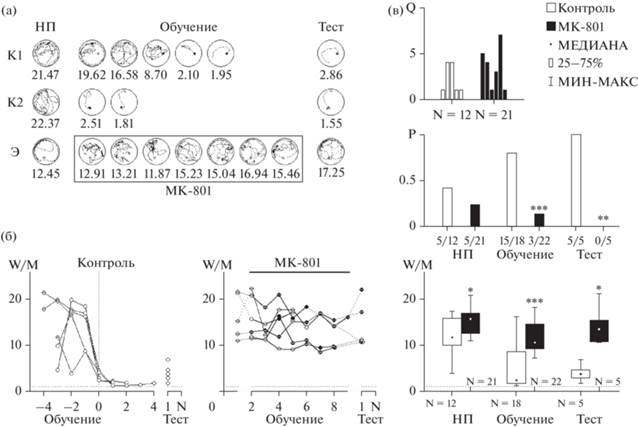
Динамика обучения в контрольной и экспериментальной группах показана на рис. 5 (б). Обученные животные с любой стратегией пространственного поведения имеют индекс выполнения w/c ≤ 1 (Коршунов, 2019). Попытки, в которых крысы достигли этого результата, использованы как точки синхронизации и обозначены “0” на оси X (рис. 5 (б), контроль). После этой попытки индекс дирекциональности w/m у всех контрольных крыс стремится к 1 (рис. 5 (б), контроль). Ни одна крыса из экспериментальной группы не достигла индекса w/c ≤ 1, w/m-индекс после обучения на фоне МК-801 не отличается от результатов наивных попыток (рис. 5 (б), MK-801). Крыса с худшим результатом в контрольной группе (рис. 5 (б), контроль) показала достоверно лучшие показатели, чем любое из экспериментальных животных (рис. 5 (б), MK-801). Экспериментальным животным потребовалось почти вдвое больше попыток, чтобы впервые найти платформу (рис. 5 (в)). Пространственное поведение в экспериментальной группе также было нарушено. Индекс дирекциональности w/m в контроле при обучении был достоверно ниже, чем аналогичный показатель в экспериментальной группе (Mann–Whitney test, z = –3.384702, p < < 0.001, рис. 5 (в)); w/m- и w/c-индексы в экспериментальной группе не отличались от результатов в наивных попытках (Mann–Whitney test, z = 0.456435, p > 0.6, рис. 5 (в)). Во время обучения контрольная группа достоверно лучше находила платформу (15 успешных попыток из 18) по сравнению с экспериментальной группой (3 из 22) (точный тест Фишера, p < 0.001, рис. 5 (в)). Различия между контрольной и экспериментальной группой после обучения были также достоверны (точный тест Фишера, p < 0.01, рис. 5 (в)). Все контрольные крысы нашли подводную платформу при тестировании. Ни одна экспериментальная крыса невидимую платформу при тестировании не нашла, несмотря на большее число попыток при обучении (43 попытки всего, 22 после первого нахождения платформы) по сравнению с контролем (30 попыток всего, 18 после нахождения платформы).
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Несмотря на многолетнюю историю изучения ДПП-подобной пластичности, ее роль в обучении остается дискуссионной (Morris, 1994; Jeffery, 1997; Holscher, 1999). Обнаруженные при обучении изменения ВП при надлежащих контролях оказались связанными с изменениями температуры мозга при двигательной активности (Moser et al., 1993). Различия в потенцируемости связей у обученных и необученных животных обусловлены стрессом (Shors et al., 1989, Jeffery, 1997). Если механизмы обучения ДПП-подобны, то модификация синапсов до “насыщения” должна блокировать обучение (Castro et al., 1989), но оказалось, что “насыщенная” потенциация гиппокампальных связей на обучение не влияет (Korol et al., 1993; McNamara et al., 1993). Прямые измерения синаптической эффективности в обучении зависят от нейросетевых процессов, не контролируемых экспериментатором (Коршунов, 2001). Результаты генетических манипуляций противоречивы (Jeffery, 1997) и не допускают однозначных трактовок. Селективная блокада НМДАр не приводит к нарушениям синаптической передачи, но блокирует ДПП, поэтому фармакологические методы рассматривались как наиболее перспективные. В работе (Priestley et al., 1998) на анестезированных крысах показано, что МК-801 в дозе 0.12 мг/кг с последующим довведением 1.8 мкг/час успешно блокирует ДПП в ДЗФ при стимуляции ПП. При системном введении доз антагониста (0.2–0.33 мг/кг), блокирующих ДПП в гиппокампе, были выявлены нарушения поведения и обучения в различных поведенческих задачах (Butelman, 1989; Tan et al., 1989; Tricklebank et al., 1989; Ward et al., 1990). Обнаруженная корреляция рассматривается как подтверждение связи ДПП-подобной пластичности с обучением. Однако в работе (Olney et al., 1993) было показано, что, начиная с дозы 0.18 мг/кг, МК-801 токсичен для пирамидных и мультиполярных нейронов 3–4 слоев цингулярой коры и вызывает гибель клеток. При удалении ретросплениальной области цингулярной коры (Whishaw et al., 2001) крысы не способны решать гиппокамп-зависимые пространственные задачи, более того, даже временное отключение этой области ведет к пространственным дефицитам, связанным с изменениями гиппокампальных плейс-полей (Cooper, Mizumori, 2001). Поскольку дозы, блокирующие ДПП, были токсичны для цингулярной коры, вряд ли найденные корреляции свидетельствуют об общности механизмов ДПП и обучения. Даже при использовании нетоксичных доз антагониста, блокирующих ДПП, методологическая ошибка заключается в том, что если механизмы обучения менее резистентны к блокаде НМДАр, то возможна ложная корреляция между ДПП и обучением (Коршунов, 2012). После любого системного введения блокатора его концентрация в мозге растет градуально, таким образом, поведенческие дефициты начинаются раньше нарушений индукции ДПП. Новизна нашего подхода в том, что, используя низкие, нетоксичные дозы неконкурентного антагониста НМДАр МК-801, не блокирующие ДПП, нам удалось отделить обучение и поведенческие нарушения от ДПП – подобной пластичности. ДПП при низких дозах МК-801 не отличается от ДПП на фоне инъекций изотонического р-ра NaCl (см. рис. 1 (б)), в то же время дефициты поведения наблюдаются и в домашней клетке, и в бассейне Морриса как у наивных, так и у хорошо обученных животных. Дозы, не блокирующие ДПП в гиппокампе, нарушают поведение крыс не только в гиппокамп-зависимых аллоцентрических задачах, но и в эгоцентрических, где участие гиппокампа необлигатно. Этот факт ставит под сомнение корреляции между ДПП-подобной пластичностью и гипокамп-зависимыми формами обучения, найденные в ранее опубликованных работах.
Можно предположить, что дефициты обучения могут быть обусловлены гиперактивностью животного и сенсомоторными нарушениями под действием блокатора. Однако, если механизмы обучения интактны и блокатор нарушает только воспроизведение, то после отмены препарата животное должно демонстрировать лучшие результаты, чем при наивной попытке. Тем не менее феномен латентного или “молчащего” обучения (Rossato et al., 2018) в нашей работе не обнаружен. В экспериментальной группе после обучения на фоне блокатора тестирование не выявило разницы с наивными попытками. Таким образом, механизмы обучения были нарушены при сохранной ДПП-подобной пластичности.
МК-801 нарушает воспроизведение ранее заученной реакции, но не ее хранение. Под действием низких доз антагониста НМДАр поведение хорошо обученных крыс неотличимо от наивных, но после выведения препарата обученные животные легко решали аллоцентрическую задачу без какой-либо дополнительной тренировки, что означает, что животные помнили позицию платформы. Сходные результаты описаны для других форм обучения (object recognition memory task) (Chan et al., 2019).
Побочный результат нашего исследования включал регистрацию нейронной активности в ДЗФ и поле СА1 гиппокампа при плавании крыс в бассейне Морриса. Предварительные данные показали, что низкие дозы МК-801, не блокирующие ДПП, драматически нарушают паттерн нейронной активности, и эти изменения коррелируют с нарушениями пространственного поведения крыс в бассейне Морриса. Мы предполагаем, что дефициты обучения на фоне антагонистов НМДА-рецепторов связаны с нарушениями динамических процессов в ЦНС, а не с блокадой ДПП-подобной пластичности. Эксперименты в этом направлении продолжаются.
ВЫВОДЫ
1. Большие дозы препаратов, блокирующие ДПП, приводят к ложной корреляции между ДПП и обучением, поскольку поведение и механизмы обучения менее устойчивы к блокаде НМДАр, чем ДПП-подобная пластичность.
2. Низкие дозы антагонистов НМДАр нарушают обучение без блокады ДПП-подобной пластичности, таким образом, наши данные не подтверждают гипотезу о роли ДПП-подобной пластичности в обучении.
3. Блокада НМДАр нарушает воспроизведение ранее заученных реакций у хорошо обученных животных, не затрагивая механизмы хранения памяти.
Список литературы
Александров Ю.И. Научение и память: традиционный и системный подходы. Журн. высш. нервн. деят. им. И.П. Павлова. 2005. 55(6): 842–860.
Зайченко M.И., Григорьян Г.А., Маркевич В.А. Влияние МК-801 на реконсолидацию пространственной памяти в 8-канальном радиальном лабиринте зависит от условий ее реактивации. Журн. высш. нервн. деят. им. И.П. Павлова. 2018. 68(2): 216–226. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0044467718020077
Коршунов В.А. Проблемы адекватности методов, применяемых для тестирования синаптической пластичности при обучении. Журн. высш. нервн. деят. им. И.П. Павлова. 2001. 51(2): 267–278. PMID: 11548613
Коршунов В.А. Дефицит гиппокамп-зависимых форм обучения при блокаде НМДА-рецепторов не связан с нарушениями долговременной посттетанической потенциации (ДПП). II-Всероссийская конференция с международным участием “Гиппокамп и память: норма и патология”. 10–14 сентября 2012 г., Пущино, Россия. с. 13–14.
Коршунов В.А. Метод исправления перспективных искажений при видеотрекинге животных в бассейне Морриса. Журн. высш. нервн. деят. им. И.П. Павлова. 2014. 64(2): 240–245. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0044467714020117
Коршунов В.А. Простые индексы для оценки выполнения задач в бассейне Морриса. 15-й Международный Междисциплинарный Конгресс “Нейронаука для Медицины и Психологии”. Судак, Крым, Россия, 30 мая–10 июня 2019 г. с. 237. https://doi.org/10.29003/m442.sudak.ns2019-15/237
Abraham W.C., Kairiss E.W. Effects of NMDA-antagonist 2AP5 on complex spike discharge by hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1988. 89(1): 36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(88)90477-6
Adams W.K., Halberstadt A.L., Van den Buuse M. Hippocampal serotonin depletion unmasks differences in the hyperlocomotor effects of phencyclidine and MK-801: quantitative versus qualitative analyses. Front. Pharmacol. 2013. 4: 109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00109
Ahlander M., Misane I., Schott P.A., Ogren S.O. A behavioral analysis of the spatial learning deficit induced by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 (dizocilpine) in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. 21(3): 414–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00116-X
Bannerman D.M., Butcher S.P., Good M.A., Morris R.G. Intracerebroventricular infusion of the NMDA receptor-associated glycine site antagonist 7-chlorokynurenate impairs water maze performance but fails to block hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 1997. 68(3): 252–270. https://doi.org/10.1006/nlme.1997.3797
Bliss T.V.P., Collingridge G.L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993. 361 (6407): 31–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/361031a0
Butcher S.P., Davis S., Morris R.G. A dose-related impairment of spatial learning by the NMDA receptor antagonist, 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (AP5). Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1990. 1(1): 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-977x(90)90005-u
Butelman E.R. A novel NMDA antagonist, MK-801, impairs performance in a hippocampal-dependent spatial learning task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989. 34(1): 13–16. PMID: 2696982https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(89)90345-6
Castro C.A., Silbert L.H., McNaughton B.L., Barnes C.A. Recovery of spatial learning deficits after decay of electrically induced synaptic enhancement in the hippocampus. Nature (London). 1989. 342(6249): 545–548.
Cercato M.C., Colettis N., Snitcofsky M., Aguirre A.I., Kornisiuk E.E., Baez M.V., Jerusalinsky D.A. Hippocampal NMDA Receptors and the Previous Experience Effect on Memory. J. Physiol. Paris, 2014. 108(4–6): 263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphysparis.2014.08.001
Cercato M.C., Vázquez C.A., Kornisiuk E., Aguirre A.I., Colettis N., Snitcofsky V., Jerusalinsky D.A., Baez M.V. GluN1 and GluN2A NMDA Receptor Subunits Increase in the Hippocampus During Memory Consolidation in the Rat. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017. 10: 242. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00242
Chan M., Austen J.M., Eacott M.J., Easton A., Sanderson D.J. The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 fails to impair long-term recognition memory in mice when the state-dependency of memory is controlled. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2019. 161: 57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2019.03.006
Christian E.P., Deadwyler S.A. Behavioral Functions and Hippocampal Cell Types: Evidence for Two Nonoverlapping Populations in the Rat. J. Neurophysiol. 1986. 55(2): 331–348. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1986.55.2.331
Cooper B.G., Mizumori S.J.Y. Temporary Inactivation of the Retrosplenial Cortex Causes a Transient Reorganization of Spatial Coding in the Hippocampus.J. Neurosci. 2001. 21(11): 3986–4001.
Ezrokhi V.L., Zosimovskii V.A., Korshunov V.A., Markevich V.A. Restoration of Decaying Long-term Potentiation in the Hippocampal Formation by Stimulation of Neuromodulatory Nuclei in Freely Moving Rats. Neurosci. 1999. 88(3): 741–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00232-2
Holscher C. Synaptic Plasticity and Learning and Memory: LTP and Beyond. J. Neurosci. Research. 1999. 58: 62–75. PMID: 10491572
Jeffery K.J. LTP and Spatial Learning—Where to Next? Hippocampus. 1997. 7: 95–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1997)7:1 <95::AID-HIPO10>3.0.CO;2-D
Keith J.R., Rudy J.W. Why NMDA-receptor-depenent long-term potentiation may not be a mechanism of learning and memory: reappraisal of the NMDA-receptor blockade strategy. Physiology. 1990. 18: 251–257. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03327238
Kikusui T., Aoyagi A., Kaneko T. Spatial Working Memory Is Independent of Hippocampal CA1 Long-Term Potentiation in Rats. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2000. 114 (4): 700–706. PMID: 10959528
Korol D.L., Abel T.W., Church L.T., Barnes C.A., McNaughton B.L. Hippocampal synaptic enhancement and spatial learning in the Morris swim task. Hippocampus, 1993. 3: 127–132.
Korshunov V.A, Averkin R.G. A Method of Extracellular Recording of Neuronal Activity in Swimming Mice. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2007. 165: 244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.06.014
Korshunov V.A. Miniature multichannel preamplifier for extracellular recordings of single unit activity in freely moving and swimming small animals. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2012. 206: 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.02.007
Lamberty Y., Gower A.J. Simplifying environmental cues in a Morris-type water maze improves place learning in old NMRI mice. Behav. Neural. Biol. 1991. 56 (1): 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-1047(91)90315-h
Leung L.W.S., Desborough K.A. APV, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, blocks the hippocampal theta rhytm in behaving rats. Brain Res. 1988. 463: 148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(88)90538-0
McNamara R.K., Kirkby R.D., dePape G.E., Skelton R.W., Corcoran M.E. Differential effects of kindling and kindled seizures on place learning in the Morris water maze. Hippocampus. 1993. 3: 149–152.
McNaughton N., Ruan M., Woodnorth M.A. Restoring theta-like rhythmicity in rats restores initial learning in the Morris water maze. Hippocampus. 2006. 16(12): 1102–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20235
Monaghan D.T., Cotman C.W. Distribution of N-metyl-D-aspartate-sensitive L-[3H] glutamate-binding sites in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1985. 5: 2909–2919. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02909.1985
Morris R.G.M. NMDA receptors and memory encoding. Neuropharmacology. 2013. 74: 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.014
Morris R.G.M., Steele R.J., Bell J.E., Martin S.J. N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors, Learning and memory: Chronic intraventricular infusion of the NMDA receptor antagonist d-AP5 interacts directly with the neural mechanisms of spatial learning. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2013. 37(5): 700–717. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12086
Morris R.G.M. The neural basis of learning with Particular Reference to the Role of Synaptic Plasticity. Where Are We a Century after Cajal’s Speculations? -in “Animal learning and Cognition”, Ed. N.J. Mackintosh, Academic press, 1994.
Morris R.G. Synaptic plasticity and learning: selective impairment of learning rats and blockade of long-term potentiation in vivo by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist AP5. Journal of Neuroscience. 1989. 9(9): 3040–3057. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03040.1989
Moser E.I., Mathiesen I., Andersen P. Assosiation between brain temperature and dentate field potentials in exploring and swimming rats. Science. 1993. 259: 1324–1326.
Nakazawa K., Quirk M.C., Chitwood R.A., Watanabe M., Yeckel M.F., Sun L.D., Kato A., Carr C.A., Johnston D., Wilson M.A., Tonegawa S. Requirement for Hippocampal CA3 NMDA Receptors in Associative Memory Recall. Science. 2002. 279: 211–218. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071795
Olney J.W., Sesma M.A., Wozniak D.F. Glutamatergic, Cholinergic and GABAergic Systems in Posterior Cingulate Cortex: Interactions and Possible Mechanisms of Limbic System Disease, in: Vogt, BA, Gabriel, M (Eds.), Neurobiology of Cingulate Cortex and Limbic Thalamus. A Comprehensive Handbook. Birkhauser, Boston, Basel, Berlin, 1993. 557–580 pp.
Paxinos G., Watson C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Fourth edition, Acad. Press, 1998.
Peet M.J., Curry K., Magnuson D.S.K., McLennan H. The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and burst firing of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience. 1987. 22: 563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(87)90353-8
Priestley T., Marshall G.R., Hill R.G., Kemp J.A. L‑687,414, a low efficacy NMDA receptor glycine site partial agonist in vitro, does not prevent hippocampal LTP in vivo at plasma levels known to be neuroprotective. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998. 124(8): 1767–1773.
Prusky G.T., Harker K.T., Douglas R.M., Whishaw I.Q. Variation in visual acuity within pigmented, and between pigmented and albino rat strains. Behav Brain Res. 2002. 136(2): 339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-4328(02)00126-2
Rossato J.I., Moreno A., Genzel L., Yamasaki M., Takeuchi T., Canals S., Morris R.G.M. Silent Learning. Curr Biol. 2018. 28(21): 3508–3515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.09.012
Sengar A.S., Li H., Zhang W., Leung C., Ramani A.K., Saw N.M., Wang Y., Tu Y., Ross P.J., Scherer S.W., Ellis J., Brudno M., Jia Z., Salter M.W. Control of Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation and Learning by Alternative Splicing of the NMDA Receptor Subunit GluN1. Cell Rep. 2019. 29(13): 4285–4294.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.087
Saucier D., Cain D.P. Spatial learning without NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. Nature. 1995. 378(6553): 186–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/378186a0
Shors T.J., Seib T.B., Levine S., Thompson R.F. Inescapable Versus Escapable Shock Modulates Long-Term Potentiation in the Rat Hippocampus. Science. 1989. 244(4901): 224–226.
Tan S., Kirk R.C., Abraham W.C., McNaughton N. Effects of the NMDA antagonists CPP and MK-801 on delayed conditional discrimination. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1989. 98(4): 556–60. PMID: 2505299 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF004419592505299
Tricklebank M.D., Singh L., Oles R.J., Preston C., Iversen S.D. The behavioral effects of MK-801: a comparision with antagonists acting competitevely at the NMDA-receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989. 167: 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(89)90754-1
Ward L., Mason S.E., Abraham W.C. Effects of the NMDA antagonists CPP and MK-801 on radial arm maze performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990. 35(4): 785–790. PMID: 2189143https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(90)90359-p
Whishaw I.Q., Maaswinkel H., Gonzalez C.L.R., Kolb B. Deficits in allothetic and idiothetic spatial behavior in rats with posterior cingulate cortex lesions. Behavioural Brain Research. 2001. 118: 67–76.
Whishaw I.Q. Posterior neocortical (visual cortex) lesions in the rat impair matching-to-place navigation in a swimming pool: a reevaluation of cortical contributions to spatial behavior using a new assessment of spatial versus non-spatial behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2004. 155(2): 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2004.04.013
Whitlock J., Heynen A., Shuler M., Bear M. Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Science. 2006. 313(5790): 1093–1097. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128134
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Журнал высшей нервной деятельности им. И.П. Павлова


