Журнал высшей нервной деятельности им. И.П. Павлова, 2023, T. 73, № 6, стр. 749-763
Вклад вербальных обозначений в процессы быстрого картирования и явного кодирования
Е. И. Перикова 1, *, М. Г. Филиппова 1, 2, Д. Н. Макарова 1, Д. С. Гнедых 1
1 Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет
Санкт-Петербург, Россия
2 Институт мозга человека им. Н.П. Бехтеревой РАН
Санкт-Петербург, Россия
* E-mail: e.perikova@spbu.ru
Поступила в редакцию 09.03.2023
После доработки 03.07.2023
Принята к публикации 03.07.2023
- EDN: ZQXBWD
- DOI: 10.31857/S0044467723060060
Аннотация
С целью изучения роли вербального обозначения в усвоении информации о новых объектах в зависимости от стратегии речевого научения проведено исследование эффективности распознавания новых объектов, изученных с помощью стратегий быстрого картирования и явного кодирования, с учетом глазодвигательной активности. Тридцати двум испытуемым визуально предъявлялись изображения восьми новых плодов растений по восемь раз каждое, которые в 50% случаев аудиально сопровождались уникальным, а в других 50% случаев – общим вербальным обозначением. В качестве проверочного задания использовался зрительный поиск целевого изображения среди дистракторов. Согласно полученным данным, стратегия быстрого картирования позволяла быстрее усваивать новые слова в сравнении с явным кодированием. Обнаружено положительное влияние уникального вербального обозначения новых плодов на выполнение задачи зрительного поиска, причем бóльшая значимость такого обозначения оказалась характерна для быстрого картирования в сравнении с явным кодированием.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Свойственная человеку тенденция сопоставлять только что услышанное новое слово с объектом, у которого нет известного ему названия, лежит в основе языкового научения как у детей, так и у взрослых. Есть два способа осуществить такое сопоставление. Первый из них предполагает формирование нового понятия путем отвержения известных объектов, которые находятся рядом с неизвестным, т.е. по принципу дизъюнктивного силлогизма (A или B). В таком случае отказ от референтов, названия которых уже известны индивиду, является необходимым условием при поиске референта для новой словоформы. Согласно второму способу индивид изначально стремится к сопоставлению новой словоформы с новым объектом (“сопоставление новизны с новизной”), при этом отвержение известного объекта как имеющего возможность быть обозначенным новой словоформой не является обязательным для сопоставления с ней нового объекта (Halberda, 2006). Использование и того, и другого способа находит подтверждение в ряде исследований, однако данные по возрастным периодам их использования противоречивы. В частности, показано, что сопоставление новизны с новизной не является доступным с самого начала овладения языком, а формируется у детей после 20-го месяца жизни, когда они приобретают достаточный словарный запас и языковой опыт (Mervis, Bertrand, 1994). Суждения же на основе дизъюнктивного силлогизма могут быть сделаны детьми уже с 12 мес. (Cesana-Arlotti, 2018) (хотя в более позднем исследовании этот результат был опровергнут (Feiman et al., 2022)), а при оперировании абстрактными понятиями – с 2.5 лет (Grigoroglou et al., 2019). L.A. Mason и R.S. Bass (2020) показали, что при выполнении теста на словарный запас в ситуации выбора на рисунке незнакомого предмета с неизвестным названием дети 5–6 лет используют сопоставление новизны с новизной (однако в данном исследовании участвовали только дети из семей с низким доходом). K.R. Repnik (2021) в ряде исследований показала, что многоязычные взрослые при сопоставлении новых слов с новыми объектами, представленными в альтернативе с уже известными, опираются на дизъюнктивный силлогизм. Кроме того, было выявлено, что на точность и скорость обработки информации испытуемыми в задании на установление взаимосвязи между словом и объектом влияет как их языковой опыт, так и количество языков, которыми они владеют, – чем больше они знали языков, тем быстрее справлялись с заданием. Между тем стоит отметить, что опора на тот или иной способ для познания окружающей действительности не всегда требует знания языка: показано, что еще до овладения речью дети способны справляться с заданиями, в основе которых лежит тот или иной способ, но при этом сами задания не содержат лингвистических стимулов (Mody, Carey, 2016; Hill et al., 2012; Feiman et al., 2022). Таким образом, роль вербального обозначения (названия) в процессе усвоения новых объектов остается не до конца проясненной: не установлено, насколько наличие уникального названия у нового объекта способствует усвоению и сохранению информации о нем.
Современные исследования на взрослых выборках, в том числе в рамках теории лингвистической относительности, говорят в пользу важной роли названий для усвоения новых и различения схожих объектов. В частности, обнаружено положительное влияние наличия названий у объектов на их заметность: после того, как участники исследования слышали слово, обозначающее цвет, улучшалась их способность различать цвета в задании выбора между одновременно представленными цветными стимулами (Forder, Lupyan, 2019). Было также установлено, что вербальное обозначение объектов способствует более точному сохранению информации о них в памяти – в исследовании A.S. Souza с коллегами запоминание новых объектов по определенному признаку (по форме) происходило лучше при обозначении их каким-либо названием по сравнению с объектами без названий (при сравнении количества правильных ответов в проверочном задании для того и другого условия) (Souza et al., 2021). Кроме того, усвоение правил категоризации происходит успешнее, если индивид оперирует при этом общепринятыми названиями, по сравнению с редко употребляемыми (Котов, Жердева, 2020). Однако в других исследованиях при необходимости запоминания названий объектов, напротив, наблюдается снижение точности информации об их индивидуальных свойствах или затруднение их категоризации. В частности, в исследовании А.А. Котова и Т.Н. Котовой (2013) такому снижению способствовало произнесение испытуемыми названия объекта вслух (анализировалось количество правильных и неправильных ответов в задании на распознавание тестовых объектов, в том числе показатели скорости выполнения). В свою очередь, при изучении влияния принадлежности объекта к определенной категории на способность к его различению среди других объектов M.I. Morozov (2017) обнаружил, что испытуемые искали целевые объекты, имеющие название, медленнее, чем таковые без названий.
Помочь разрешить отмеченные противоречия можно, на наш взгляд, приняв во внимание вклад вербального обозначения в процессы научения новым понятиям с учетом стратегий речевого научения (Гнедых и др., 2022), таких как быстрое картирование (fast mapping, далее FM) и явное кодирование (explicit encoding, далее EE). Первая стратегия позволяет усваивать информацию из контекста путем исключения лишнего, вторая подразумевает прямое соотнесение изучаемого объекта с его названием. Для FM-стратегии отказ от известных отвлекающих объектов занимает центральное место при сопоставлении вербального обозначения с новым объектом (принцип дизъюнктивного силлогизма), на основании чего формируется предположение о связи названия и его референта (Medina et al., 2011; Trueswell et al., 2013). EE-стратегия использует способ сопоставления новизны с новизной без опосредующих предположений (Щербакова и др., 2022). Более ранние исследования, посвященные изучению эффективности языкового научения у взрослых, находят на поведенческом уровне преимущества то одной, то другой стратегии. С одной стороны, показано превосходство стратегии EE над FM, выражающееся в более высокой точности ответов при сопоставлении образа объекта (изображения) со словоформой (Greve et al., 2014). С другой стороны, выявлено, что слова, выученные с помощью FM-стратегии, интегрируются в лексикон немедленно (Coutanche, Thompson-Schill, 2014), тогда как для EE-стратегии важна консолидация выученной информации во время ночного сна (Merhav et al., 2015). Однако более поздние работы указывают на схожий уровень эффективности данных стратегий (Shtyrov et al., 2021; Perikova et al., 2022). Такая противоречивость данных может быть связана с недостаточной сбалансированностью заданий в обучающих сессиях ранних исследований (подробный анализ см. (Shtyrov et al., 2019; Щербакова и др., 2022)), что делает возможным объяснения найденных различий в эффективности изучаемых стратегий влиянием дополнительных переменных. В исследованиях, проведенных за последние годы, этому аспекту стали уделять больше внимания, что привело к более согласованным поведенческим данным.
Результаты нейрофизиологических исследований показывают наличие различных механизмов, лежащих в основе данных стратегий научения. T. Atir-Sharon с коллегами выявили разное участие областей головного мозга в запоминании новых слов посредством той или иной стратегии: при использовании FM в большей степени активируется передняя височная доля, тогда как при EE – гиппокамп (Atir-Sharon et al., 2015). Также было выявлено, что FM-стратегия поддерживается левополушарным височным полюсом (зонами Брока и Вернике), в то время как ЕЕ-стратегия наряду с данными зонами также задействует неречевые области левого полушария (теменные и лобные) и кору правого полушария (Shtyrov et al., 2021, 2022). Временны́е параметры активности нейронной динамики (данные ЭЭГ) при усвоении новых слов с помощью этих двух стратегий также отличаются: для FM-стратегии характерна взаимосвязь успешности выполнения проверочных заданий с более ранними пиками (176–216 мс), для EE – с более поздними (260–300 мс) (Shtyrov et al., 2022).
В соответствии с обсуждаемыми данными, предполагая отсутствие поведенческих различий между двумя стратегиями научения при наличии нейрофизиологических различий, нами было принято решение использования в новом исследовании психофизиологических методов, в частности регистрации движений глаз с помощью видеоокулографа. Данный метод успешно используется в психолингвистических исследованиях (Походай и др., 2022), в том числе посвященных проверке гипотезы о необходимости использования принципа дизъюнктивного силлогизма для усвоения новых понятий. Например, в одном из таких экспериментов было выявлено, что взрослые испытуемые систематически отклоняют известные объекты перед соотнесением новых названий с новыми объектами (Halberda, 2006). В результате изучения движений глаз во время чтения была обнаружена высокая чувствительность к наличию новых слов в тексте: для их прочтения требовалось больше времени, чем для слов, уже известных испытуемым. При этом на новых словах, встречающихся в отдельных предложениях, взгляд задерживался дольше, чем на этих же словах в абзацах (Wochna, Juhasz, 2013).
Чаще всего видеоокулограф используется в исследованиях научения новым словам на детской выборке, и только в FM-условии (Axelsson et al., 2021; Ellis et al., 2015 и др.) или близких к нему, например, в условии быстрого случайного обучения (quick incidental learning, QUIL) (Chung, Yim, 2020). Однако такой дизайн не позволяет говорить о специфике научения с помощью FM-стратегии, выявленной на основе анализа движения глаз, так как отсутствует сравнение с ЕЕ-стратегией научения. На настоящий момент нам известно только одно исследование на взрослой выборке, в котором анализ движений глаз применялся при изучении процессов научения с включением обеих стратегий (Warren et al., 2016). По результатам эксперимента D.E. Warren с коллегами (Warren et al., 2016) не было обнаружено значимых различий во времени фиксации взгляда при выполнении задания на установление семантического соответствия слова и изображения между двумя стратегиями научения. Дизайн нашего исследования восполняет недостаток экспериментальных результатов в данной области.
В классических парадигмах исследований научения языку с помощью FM- и ЕЕ-стратегий используется вербальное обозначение, соответствующее новому объекту (т.е. присвоенное ему уникальное название). Как было сказано выше, наличие у объекта вербального обозначения может как облегчать, так и затруднять усвоение информации о нем. При этом в естественной среде знакомство с новым объектом посредством той или иной стратегии может происходить и в отсутствие возможности узнать его уникальное название. В связи с этим возникает вопрос, является ли стратегия научения (ЕЕ или FM) фактором, определяющим влияние вербального обозначения на усвоение информации об объекте (будет ли оно препятствовать или способствовать научению).
Научение с помощью EE-стратегии подразумевает акцент на названии нового объекта, т.к. в данном случае прямое указание на объект сопровождается вербальным обозначением (например, “Это глорп” (Щербакова и др., 2022)). Можно предположить, что за счет привлечения внимания к вербальному обозначению в памяти формируется обобщенный образ объекта без его подробной детализации, в отличие от FM-условия, где внимание, напротив, привлекается к какому-либо конкретному признаку объекта (например, “Там на столе стоят ваза, чашка и глорп. Какого цвета глорп?” (там же)) вместо его названия. Эта особенность FM-условия, согласно нашим предположениям, должна способствовать лучшему различению индивидуальных характеристик изучаемого объекта, что и проверялось в настоящем исследовании. С этой целью сопоставлялась эффективность зрительного поиска объектов, изученных при помощи обеих стратегий. Также мы ожидали обнаружить бо́льшую значимость вербального обозначения для стратегии EE в сравнении с FM, что проверялось путем сопоставления эффективности зрительного поиска объектов при наличии и отсутствии у них уникальных названий при использовании обеих стратегий. Запись глазодвигательной активности при выполнении заданий призвана конкретизировать особенности зрительного поиска для объектов, изученных при использовании той или иной стратегии с наличием или отсутствием уникальных вербальных обозначений.
МЕТОДИКА
Выборка: N = 32, возраст 18–35 лет (средний возраст 22.5 ± 3.6; 22 женщины), праворукие носители русского языка как единственного родного, с нормальным или скорректированным до нормы зрением. Исследование одобрено этическим комитетом Санкт-Петербургского психологического общества (протокол № 15 от 19.05.2022).
Стимульный материал. Разработаны зрительные (изображения плодов; филлеры) и слуховые (псевдослова; контекстные предложения) стимулы. Отобраны восемь пятибуквенных существительных русского языка – названия экзотических и огородных плодов с одинаковым чередованием согласных и гласных звуков (фонетическая структура: согласный–гласный–согласный–гласный–согласный; напр., “томат” или “банан”) и схожими показателями частотности (средняя частотность словоформы = 5.28 ± 1.29, первой = = 6.68 ± 0.99 и последней = 8.72 ± 0.98 биграмм, согласно (Ляшевская, Шаров, 2009)). На основе отобранных существительных составлены 8 пятибуквенных псевдослов (далее – новые слова), имеющих аналогичную фонетическую структуру (напр., первый слог от слова “лимон”, а последний – от слова “горох” в результате образовали слово “лирох”). Новые слова значимо отличались по оценкам узнаваемости от реально существующих (t = = 82.16, р < 0.001) (по результатам опроса экспертов, в группу которых вошли носители русского языка как родного; N = 29, 8 мужчин, средний возраст 29.6 ± 6.31).
В качестве семантических референтов слов использовались фотографии известных и малоизвестных (редких) плодов, т.е. незнакомых большинству представителей русскоязычного культурного сообщества (например, нони). Для каждого плода использовались восемь фотографий, изображающих его как в целом, так и в разрезанном виде. Для EE-условия также были созданы филлеры – изображения, не имеющие смысловой нагрузки; для создания каждого было использовано четыре повернутых (45, 90, 180, 360 градусов) полупрозрачных изображения предметов с размытием. Графические характеристики всех стимулов были стандартизованы с помощью методов зрительной унификации (устранение графического шума, отцентровка объектов, приведение изображения к размеру 400 × × 400 pxl, усреднение стимулов по шкале свечения).
Графические стимулы были оценены по узнаваемости экспертной группой респондентов (N = 200, 75 мужчин, средний возраст 28.75 ± 4.65 лет) – носителей русского языка. Сбор данных осуществлялся с помощью интернет-ресурса “Яндекс.Толока”. Узнаваемость известных плодов была значимо выше узнаваемости редких (t = 16.18; р < 0.001), филлеры получили более низкие оценки узнаваемости в сравнении как с известными (Z = –4.637; p < < 0.001), так и с малоизвестными плодами (Z = –4.383; p < 0.001).
Для создания EE- и FM-условий научения были составлены наборы из восьми вопросительных предложений для каждой стратегии, отличающиеся по своей структуре. Содержание вопросов в двух условиях касалось наличия или отсутствия визуальных характеристик плодов. При предъявлении стимулов в EE-условии применялась конструкция из двух предложений. В первом предложении в зависимости от условия вербализации названия использовалась указывающая на новый плод лексема и уникальное или общее вербальное обозначение в именительном падеже (например, “Перед Вами ЛИРОХ” или “Перед Вами НОВЫЙ ПЛОД” соответственно). Второе предложение содержало вопрос, касающийся одной из визуальных характеристик плода (например, “Фиолетовый ли он?”). В FM-условии вопрос состоял из одного предложения, последним членом которого также являлось уникальное или общее вербальное обозначение в именительном падеже (например, “Фиолетовый ли ЛИРОХ?” или “Фиолетовый ли НОВЫЙ ПЛОД?”). Все вопросы предполагали выбор одного из двух вариантов ответа: “Да” или “Нет” (в 50% случаев – “Да”, и в 50% – “Нет”).
Примеры предложений для одного плода (фингерлайм) представлены в табл. 1.
Таблица 1.
Примеры зрительных и слуховых стимулов для одного объекта Table 1. Examples of visual and auditory stimuli for the object sample
| Примеры нового плода в разрезанном и целом виде | Первая часть вопроса EE-условия | Вторая часть вопроса EE-условия | Вопросы в FM-условии |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
На экране ХХХХХ | Он вытянутый? | Вытянутый ли ХХХХХ? |
| Посмотрите, вот ХХХХХ | Он надломан? | Надломлен ли ХХХХХ? | |
| Вот ХХХХХ | Он волнистый? | Волнистый ли ХХХХХ? | |
| Это ХХХХХ | Он бурый? | Бурый ли ХХХХХ? | |
 |
На картинке ХХХХХ | Он выжатый? | Выжатый ли ХХХХХ? |
| На мониторе ХХХХХ | Объемный ли он? | Объемный ли ХХХХХ? | |
| Перед Вами ХХХХХ | Пустой ли он? | Пустой ли ХХХХХ? | |
| Вы видите ХХХХХ | Белый ли он? | Белый ли ХХХХХ? |
Примечание: Зрительные стимулы предлагались участникам исследования в цвете в ходе обучающей сессии. Название стимула менялось от испытуемого к испытуемому. Note: Visual stimuli were presented to subjects in color during the training session. The name of the stimulus changed from subject to subject.
Стимульные слова и предложения были записаны в виде звуковых дорожек с помощью инструмента Yandex SpeechKit. По результатам предварительного опроса (N = 16, 8 мужчин, средний возраст 21.2 ± 6.12 лет) был отобран синтезированный голос, получивший более высокие оценки вероятности принадлежности человеку, дружелюбия, привлекательности и степени доверия в сравнении с голосами четырех реальных дикторов (H-test = = 10.83; p = 0.028). Дополнительно все аудиодорожки были скорректированы двумя экспертами, носителями русского языка, по параметрам “тембр голоса” и “ударение”.
Полученные аудиодорожки позволили производить замену словоформы в каждом из стимульных предложений, что обеспечило возможность контрбалансировки соответствия словоформ и их визуальных референтов. Кроме того, соответствие уникальных и общих вербальных обозначений изображениям объектов и предложений для семантизации (EE- и FM-условий) было индивидуальным для каждого из участников. Таким образом, использовались 32 последовательности элементов стимульных наборов.
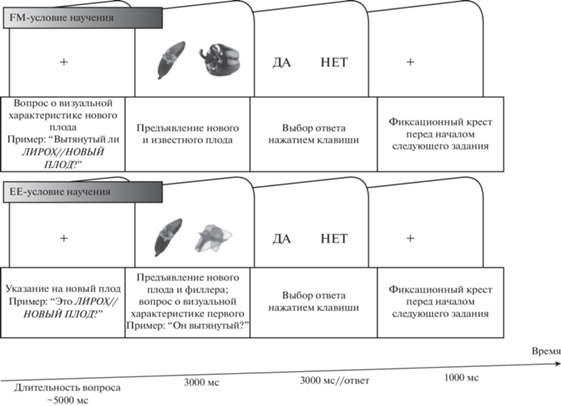
Обучающая сессия. В центре монитора (Dell S2716DG, Китай, диагональ 27 дюймов) предъявлялся фиксационный крест и звучало указание на плод, которое в 50% случаев подразумевало присвоение ему уникального вербального обозначения (например, “Перед Вами ЛИРОХ” в EE-условии или вопрос “Вытянутый ли ЛИРОХ?” в FM-условии). В других 50% случаев вместо названия плода использовалось общее вербальное обозначение (например, EE: “Вы видите НОВЫЙ ПЛОД”; FM: “Вытянутый ли НОВЫЙ ПЛОД?”). Затем демонстрировались два изображения (целевое и нецелевое): целевым изображением был новый плод, нецелевым – известный плод для FM-условия и филлер – для EE-условия. В EE-условии дополнительно звучал вопрос (например, “Он вытянутый?”, рис. 1). Использование в обоих условиях двух изображений и вопросов о визуальных характеристиках новых плодов позволило уравновесить условия между собой. Левое/правое расположение целевого изображения было уравновешено между испытаниями. Участники выбирали ответ “да” или “нет”, нажимая кнопку указательным пальцем левой руки с помощью специальной клавиатуры (RB-740, Cedrus Corp., США). Каждый плод с семантической привязкой предъявлялся восемь раз, порядок предъявления определялся условием псевдорандомизации. Цвет фона для всех этапов предъявления был белый (255, 255, 255), а плоды – цветные (для формирования целостного представления о каждом из них). До основной обучающей сессии все испытуемые проходили тренировку, включающую 8 заданий. Обучающая сессия была реализована в Presentation v. 23.1 (Neurobehavioral Systems Inc., США).
Рис. 1.
Пример последовательности предъявления стимулов. Примечание: в обучающей сессии изображения были цветными. Fig. 1. An example of the stimulus sequences. Note that the images were colourful in the training session.
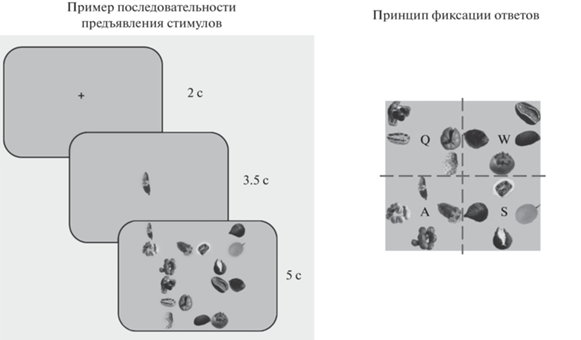
Проверочная сессия. Испытуемый выполнял задачу зрительного поиска целевого изображения среди 15 дистракторов (по два изображения каждого нового плода в черно-белом варианте). Карты для поиска целевого изображения включали в себя четыре неявно представленных квадранта, в которых располагались плоды (по четыре картинки в квадранте, две из которых иллюстрировали один плод в целом и разрезанном виде). Каждый квадрант обозначал одно из четырех условий научения: FM с уникальным и общим вербальным обозначением, EE с уникальным и общим вербальным обозначением. Каждый плод, который встречался в обучающей сессии, поочередно помещался во все квадранты. Таким образом, целевой плод единожды располагался среди плодов (далее дистракторов), изученных в том же условии, и трижды – среди дистракторов, изученных в альтернативных условиях, при этом объекты из разных условий не перемешивались по квадрантам. Всего было создано 1024 карты, по 32 для каждого испытуемого. Размер изображения каждого плода – 295 × 295 pxl, цвет фона – серый (205, 205, 205), общий размер карты – 1770 × 1770 pxl.
Пример стимуляционной последовательности задачи зрительного поиска представлен на рис. 2. В ходе каждого задания испытуемому предъявлялся фиксационный крест, после чего – целевое изображение, и затем – карта поиска. Задача испытуемого состояла в том, чтобы найти целевое изображение и обозначить, в каком квадранте оно находится, с помощью нажатия следующих клавиш на клавиатуре компьютера: Q – если целевое изображение находится в левом верхнем квадранте, W – в правом верхнем квадранте, A – в левом нижнем квадранте, S – в правом нижнем квадранте (рис. 2). Время поиска было ограничено – 5 с, но испытуемый мог дать ответ раньше. Во время поиска происходила запись глазодвигательной активности.
Рис. 2.
Стимуляционная последовательность в проверочном задании. Fig. 2. The stimulus sequence in the assessment task.
Запись движений глаз производилась с помощью оборудования EyeLink 1000 Plus (SR Research Ltd., Канада) с камерой, расположенной под монитором с частотой дискретизации 1000 Гц, с точностью измерений от 0.15 до 0.5. Для показа стимулов использовался монитор Dell S2716DG (Китай, диагональ 27 дюйма). Испытуемым предлагалось сесть перед экраном компьютера и положить подбородок на специальную подставку, фиксирующую положение головы. Предъявляемое на экране изображение находилось на расстоянии 65 см от глаз испытуемого. Камера, регистрирующая движения глаз, располагалась под монитором компьютера и никак не препятствовала полноте обзора.
После индивидуальной настройки оборудования испытуемому предлагалось пройти тренировочную и основную части задания зрительного поиска, каждая из которых сопровождалась процедурой калибровки и валидизации. В ходе калибровки испытуемому было необходимо следить за “мишенью”, движущейся по экрану, для фиксации взгляда в 9 контрольных точках. Процедура валидизации повторяла задачу фиксации взгляда в тех же контрольных точках для подтверждения успешности калибровки. После завершения настройки аппаратуры и успешно пройденной тренировки испытуемый приступал к основному заданию. Задание было реализовано в программе SR Research Experiment Builder (Version 2.3.1).
Статистический анализ выполнялся с использованием программного обеспечения IBM SPSS Statistics, v. 26.0. Время реакции испытуемых в ходе обучающей сессии выступало показателем усвоения новых слов. Проводился дисперсионный анализ с повторными измерениями (rmANOVA) с внутригрупповыми факторами ПОРЯДОК ПРЕДЪЯВЛЕНИЯ ПЛОДОВ (восемь предъявлений каждого плода), СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ (FM/EE) и ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ (уникальное/общее название). В качестве показателей эффективности поиска целевого объекта в проверочной сессии использовались параметры времени реакции и времени сканирования карты поиска, а также показатели глазодвигательной активности: количество саккад и время латентной моторной реакции. Из анализа результатов времени реакции исключались данные, превышающие два стандартных отклонения. RmANOVA применялся для выявления значимых эффектов и взаимодействий. Апостериорные сравнения производились с использованием t-критерия Стьюдента для зависимых выборок. В качестве внутригрупповых факторов использовались СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ и ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ целевых объектов и дистракторов.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ
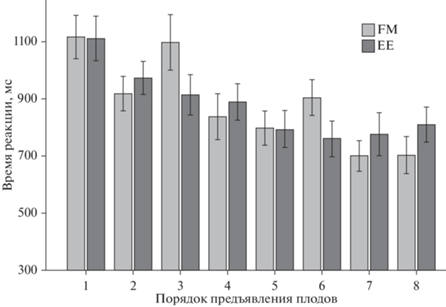
Усвоение новых слов. Значимым оказалось влияние фактора ПОРЯДОК ПРЕДЪЯВЛЕНИЯ ПЛОДОВ (F(1, 31) = 13.15; p < 0.001, η2 = = 0.295) на время реакции в процессе обучения, причем скорость ответов значимо уменьшалась после четвертого (860.5 ± 414) предъявления плода в сравнении с первым (1109.7 ± 486; PБонферрони = 0.0007). Было выявлено взаимодействие факторов ПОРЯДОК ПРЕДЪЯВЛЕНИЯ ПЛОДОВ × СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ (F(1, 31) = 2.51; p = 0.017, η2 = = 0.075). Для плодов, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM, ускорение ответов происходило быстрее (четвертое vs первое предъявление PБонферрони = 0.006), чем для плодов, с которыми они познакомились в условии EE (пятое vs первое предъявление PБонферрони = 0.017) (рис. 3).
Рис. 3.
Динамика времени ответа на вопрос о визуальной характеристике нового плода в условиях FM и EE. На графике отражено среднее время реакции и ошибка среднего, * – уровень статистической значимости различий < 0.05. Fig. 3. The reaction time during the training session for the fruit presentation in FM and EE conditions. The graphs show the reaction time and the error of the mean. * – p < 0.05.
Наличие уникальных названий у дистракторов. Наличие уникальных названий у дистракторов, среди которых осуществлялся зрительный поиск, показало преимущества сразу по трем показателям: по времени реакции и времени сканирования карты поиска, а также по количеству саккад. Для каждого из этих параметров оказался значим фактор ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора.
В отношении времени реакции (F(1, 31) = = 6.13; p = 0.019, η2 = 0.165) при поиске целевых объектов среди дистракторов с уникальными названиями испытуемым требовалось меньше времени (1462 ± 307) по сравнению с поиском среди дистракторов с общими названиями (1578 ± 298). Фактор СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ значимости не показал (F(1, 31) = = 3.38; p = 0.076), также не было обнаружено взаимодействия факторов СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора (F(1, 31) = 1.43; p = 0.240).
В отношении времени сканирования карты поиска фактор ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора также оказался значимым (F(1, 31) = 10.71; p = 0.003, η2 = 0.257): опять же время сокращалось при поиске среди дистракторов с уникальными названиями (1471 ± 425) в сравнении с поиском среди дистракторов с общими названиями (1646 ± 505). Как и в случае со временем реакции, фактор СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ значимости не показал (F(1, 31) = 1.71; p = 0.201), также не было обнаружено взаимодействия факторов СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора (F(1, 31) = 0.239; p = 0.629).
Анализ количества саккад показал, что фактор ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора является значимым (F(1, 31) = = 6.78; p = 0.014, η2 = 0.179): при поиске целевых объектов среди дистракторов с уникальными названиями испытуемые совершали меньше саккад (5.42 ± 1.46), чем при поиске среди дистракторов с общими названиями (6.0 ± 1.7). Как и в двух предыдущих случаях, не было обнаружено значимости как фактора СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ (F(1, 31) = 2.21; p = 0.147), так и взаимодействия факторов СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ дистрактора (F(1, 31) = 0.126; p = 0.725).
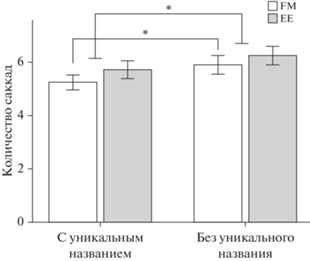
Наличие названий у целевых объектов. Для зависимой переменной “количество саккад” двухфакторный дисперсионный анализ (СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ) показал значимость фактора ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ (F(1, 31) = 4.32; p = 0.046, η2 = 0.122): для нахождения плодов, которым были присвоены уникальные названия, испытуемым требовалось меньше саккад (5.5 ± 1.55), чем для нахождения плодов с общими названиями (5.9 ± 1.53). На рис. 4 можно видеть, что эта тенденция в большей мере характерна для плодов, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM (только в этом случае есть значимые различия между плодами с уникальными и общими названиями (t(31) = –2.54; p = = 0.16)). Однако значимости ни фактор СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ (F(1, 31) = 2.26; p = 0.143), ни взаимодействие факторов СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ не достигли (F(1, 31) = 0.99; p = 0.328).
Рис. 4.
Количество саккад при поиске плодов, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM и EE, с уникальными названиями и без таковых. На графике отражено среднее количество саккад и ошибка среднего, * – уровень статистической значимости различий < 0.05. Fig. 4. The number of saccades in the search task for fruits learned with and without labels in the FM and EE condition, p < 0.05. The graphs show the number of saccades and the error of the mean. * – p < 0.05.
Также не было обнаружено взаимодействия этих факторов после проведения схожего анализа с зависимой переменной “время реакции” (F(1, 31) = 1.98; p = 0.169). В этом случае вновь значимым оказался фактор ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ (F(1, 31) = 4.32; p = 0.037, η2 = 0.132): нахождение плодов с уникальными названиями осуществлялось быстрее (1483 ± 289), чем плодов с общими названиями (1560 ± 293). Причем поиск плодов с уникальными названиями, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM (1406 ± 281), осуществлялся быстрее (t(31) = = –2.67; p = 0.011), чем поиск этих же плодов с общими названиями (1541 ± 348.4), тогда как для EE-стратегии по данному параметру различий не было обнаружено (t(31) = –0.45; p = 0.656) (рис. 5). При этом фактор СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ оказался значим лишь на уровне статистической тенденции (F(1, 31) = = 4.32; p = 0.058).
Рис. 5.
Время поиска плодов, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM и EE, с уникальными названиями и без таковых. На графике отражено среднее время реакции и ошибка среднего, * – уровень статистической значимости различий < 0.05. Fig. 5. The search reaction time for the fruit learned with and without labels in the FM and EE condition. The graphs show the reaction time and the error of the mean. * – p < 0.05.
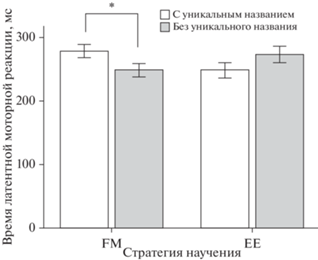
И, наконец, было выявлено значимое взаимодействие факторов СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ × ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ для зависимой переменной “латентная моторная реакция” (т.е. время от начала последней фиксации взгляда в области расположения целевого объекта до правильного ответа) (F(1, 31) = 7.45; p = 0.010, η2 = 0.194). Полученный результат представлен на рис. 6. В случае с объектами, изученными в условиях FM с уникальными названиями, время латентной моторной реакции было больше, чем в этом же условии с общими названиями (277 ± 56 > 247 ± 59; t(31) = –2.65; p = 0.012), а в случае с объектами, изученными в условиях EE, наблюдалась противоположная тенденция, которая, однако, не достигла значимости (t(31) = –1.60; p = 0.119). Факторы СТРАТЕГИЯ НАУЧЕНИЯ (F(1, 31) = 0.126; p = = 0.725) и ВЕРБАЛЬНОЕ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ (F(1, 31) = 0.071; p = 0.791) сами по себе оказались не значимыми.
Рис. 6.
Время латентной моторной реакции при поиске плодов, с которыми испытуемые знакомились в условии FM и EE, с уникальными названиями и без таковых. На графике отражено среднее время реакции и ошибка среднего, * – уровень статистической значимости различий < 0.05. Fig. 6. The motor reaction latency in the search task for fruits learned with and without labels in the FM and EE condition. The graphs show the reaction time and the error of the mean. * – p < 0.05.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Согласно полученным данным, усвоение новых понятий происходило при использовании обеих стратегий (для FM – после четвертого предъявления нового объекта, для EE – после пятого). Интересно, что бо́льшая скорость научения наблюдалась в условии FM по сравнению с EE независимо от наличия или отсутствия уникального вербального обозначения. В предыдущих исследованиях чаще всего данные стратегии сравнивались на основании правильных ответов и времени реакции в проверочных заданиях (Coutanche, Thompson-Schill, 2014; Cooper et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2022 и др.). В нашем эксперименте мы проанализировали скорость ответов испытуемых на вопросы, звучащие в процессе обучения, что является несколько иным подходом к изучению эффективности усвоения информации, получаемой с помощью FM- и EE-стратегий. Данный подход чаще используется в ситуации, когда предметом изучения становятся дополнительные факторы в условиях научения. Так, например, в исследовании C. Li с коллегами (2020) с помощью анализа времени реакции изучалось влияние предыдущих знаний респондентов на обучение в условиях FM и EE. Участников просили запомнить ассоциации между новыми картинками и названиями. Половина из них была из знакомых ранее респондентам категорий, а другая половина – из незнакомых. Было выявлено, что в условии FM участники выполнили задание на запоминание ассоциаций лучше для знакомых категорий, чем для незнакомых, и в этом же случае быстрее реагировали. Возможно, полученные нами данные обусловлены спецификой нейронной динамики изучаемых стратегий, которая была выявлена нами ранее во взаимосвязи с успешностью усвоения новых слов: для FM она была характерна на раннем этапе обработки информации, для EE – на более позднем (Shtyrov et al., 2022). О высокой скорости усвоения слов посредством FM-стратегии свидетельствуют и другие исследования. Например, в работе M.J. Vasilyeva c коллегами(2019) была показана интеграция новых ассоциаций в неокортикальные лексико-семантические сети у взрослых уже после однократного предъявления ассоциации слова и объекта.
Альтернативное объяснение различий успешности усвоения информации с помощью двух стратегий научения может быть связано со спецификой разработанной нами экспериментальной парадигмы. В частности, для создания FM-условия контекстное обучение предполагало структуру одного вопросительного предложения, в то время как для EE-условия испытуемым предлагались по два контекстных предложения, предполагающие указание на объект и вопрос о нем. Такая структура представления информации может требовать от испытуемых бо́льших усилий при ее обработке в EE-условии (и, соответственно, замедлять ее усвоение) в сравнении с FM-условием. Другой инновационной особенностью обучающей сессии в данном исследовании стало наличие вопросов, требующих явного вывода о внешних характеристиках объекта в двух условиях научения. Насколько нам известно, это первое исследование с такой структурой научения, которое целенаправленно уравновешивает два условия по своей сложности для испытуемых. Однако использование явного вывода в EE-условии может смещать внимание испытуемых к анализу деталей нового объекта, делая его более близким по структуре обработки информации с FM-условием. Тем не менее для подтверждения выдвинутых предположений и проверки выявленной в нашем исследовании тенденции нужны дальнейшие исследования, в том числе с анализом параметров активности нейронной динамики в процессе научения.
В результате проведенного эксперимента найдено подтверждение теории лингвистической относительности о значимости уникальных вербальных обозначений объектов для их распознавания. Наши результаты показывают не только доказанную ранее значимость используемых в языке названий (Winawer et al., 2007; Ting Siok et al., 2009), но и важную роль впервые воспринятых индивидом псевдослов в качестве обозначений новых объектов. В реализованном эксперименте эффективность зрительного поиска новых объектов возрастала при наличии уникальных названий как у самих целевых объектов, так и у дистракторов, среди которых осуществлялся поиск. Это в некотором смысле согласуется с результатами, полученными C. Vales и L.B. Smith (2015): в задании на зрительный поиск целевые объекты, которым были даны уникальные названия, находились быстрее. В данном эксперименте названия сопровождали образ объекта (изображение), который нужно было впоследствии отыскать среди других объектов (похожее задание было использовано в работах Forder, Lupyan, 2019 и Souza et al., 2021), в нашем же исследовании вербальное обозначение присутствовало только в процессе обучения (но не в задании на зрительный поиск). Это может говорить о том, что наличие названия играет важную роль на этапе кодирования информации об объекте, а не только в момент его восприятия для решения задачи распознавания.
Вопреки нашему предположению о бóльшей значимости вербального обозначения для EE в сравнении с FM, полученные результаты говорят об обратном – более важно наличие названий у объектов, изучаемых с помощью FM-стратегии: зрительный поиск именно этих объектов ускорялся при наличии у них уникальных названий. Однако для этих же плодов (FM с уникальными названиями) возрастало и латентное время моторной реакции после фиксации взгляда на целевом объекте. Это может быть объяснено в рамках предположения T. Medina c коллегами (2011) и J. Trueswell с коллегами (2013), согласно которому FM-стратегия, в основе которой лежит принцип дизъюнктивного силлогизма (Repnik, 2021), подразумевает выдвижение гипотезы о значении слова при первом столкновении с ним. При следующих встречах с этим объектом данная гипотеза проверяется в новом контексте, что делает ассоциацию вербального обозначения с его визуальным референтом менее устойчивой в сравнении с EE-стратегией и побуждает испытуемых больше опираться на название. В результате при использовании FM-стратегии идентификация объектов с уникальными названиями вызывает больше трудностей, побуждая испытуемых совершать дополнительную процедуру контроля. Такой контроль выражается в более длительном времени обработки информации с момента фиксации взгляда на этих объектах до моторной реакции. При актуализации стратегии “сопоставления новизны с новизной”, задействованной в EE-условии, уникальное название оказывается, вероятно, более устойчиво связано с визуальным референтом и не требует дополнительной верификации при распознавании. Высказанная идея будет проверяться в будущих исследованиях.
Кроме того, предположение, согласно которому в условии EE внимание индивида в большей мере сконцентрировано на вербальном обозначении объекта, чем на его признаках, а при FM – наоборот, также требует дальнейшей проверки с помощью иных тестовых заданий. Задание на зрительный поиск не дало возможности удостовериться, что выбор целевых объектов совершается на основе лучшего запоминания их индивидуальных характеристик или же подсказки в виде названия. В связи с этим для проверки выдвинутого предположения нужны более чувствительные тесты, например, свободное воспроизведение индивидуальных признаков объектов, изученных с помощью той или иной стратегии с использованием названий и без них.
Результат о большей значимости вербального обозначения у объекта для FM-стратегии также интересно рассмотреть в сравнении с исследованием D.E. Warren и коллег (2016). В данном эксперименте окулограф использовался на этапе научения с помощью FM-стратегии, что позволило выявить значимые различия во времени фиксации взгляда на целевом стимуле до и после звучания его вербального обозначения. Это подчеркивает важность наличия уникального названия у объекта в FM-условии. Испытуемым также было предложено задание на распознавание (с принудительным выбором из трех альтернатив), которое заключалось в следующем: одновременно предъявлялись три изученных новых объекта и звучала инструкция “Нажмите на …”, за которой следовало название одного из объектов. В процессе выполнения данного задания не было обнаружено различий во времени фиксации взгляда на объектах, изученных с помощью FM- и ЕЕ-стратегий. И вновь отличие данного задания на распознавание от используемого в нашем исследовании заключается в предъявлении уникального названия целевого объекта в момент поиска. Можно предположить, что наличие названия могло облегчить задачу соотнесения, направляя зрительное внимание с помощью такой подсказки на целевой объект, что позволило находить объекты одинаково эффективно, независимо от того, в каком условии они изучались (т.е. подсказка нивелировала эффект условия). В проведенном нами исследовании такая подсказка в момент зрительного поиска не давалась, и испытуемым нужно было опираться только на визуальный образ объекта и память о том, имеет ли он уникальное название или нет. На наш взгляд, это позволило избежать влияния дополнительных переменных на результат выполнения задания, что проявилось в появлении различий в значимости вербального обозначения между условиями научения.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Результаты экспериментального исследования показывают положительное влияние вербального обозначения на усвоение информации о новых объектах. При этом наличие уникальных названий у объектов оказалось более значимым для их поиска среди дистракторов, если сами объекты были изучены с помощью стратегии FM в сравнении с EE.
Список литературы
Гнедых Д.С., Филиппова М.Г., Макарова Д.Н., Перикова Е.И. Проблемы и перспективы исследований научения новым словам: быстрое картирование vs явное кодирование. Вестник СПбГУ. Психология. 2022. 12 (4): 527–543.
Котов А.А., Котова Т.Н. Произношение имен объектов и категориальный эффект восприятия. Психология. Журнал ВШЭ. 2013. 10 (3): 75–85.
Котов А.А., Жерждева М.Р. Влияние легкости наименования пространственных признаков на научение новым правилам категоризации. Психология. Журн. ВШЭ. 2020. 17 (1): 145–155.
Походай М.Ю., Бермудес-Маргаретто Б., Штыров Ю.Ю., Мячиков А.В. Методика айтрекинга в психолингвистике и параллельная регистрация с ЭЭГ. Журн. высш. нерв. деят. им. И.П.Павлова. 2022. 72 (5): 609–622.
Щербакова О.В., Кирсанов А.С., Филиппова М.Г., Перикова Е. И., Благовещенский Е.Д., Штыров Ю.Ю. Эксплицитное и имплицитное усвоение новых слов: поведенческие корреляты и нейрофизиологические механизмы. Щербакова О.В. От слова – к репрезентации. Нейрокогнитивные основы вербального научения. СПб.: Скифия-принт, 2022. С. 22–96.
Atir-Sharon T., Gilboa A., Hazan H., Koilis E., Manevitz L.M. Decoding the formation of new semantics: MVPA investigation of rapid neocortical plasticity during associative encoding through fast mapping. Neural Plast. 2015. 804385.
Axelsson E.L., Swinton J., Jiang I.Y., Parker E.V., Horst J.S. Prior Exposure and Toddlers’ Sleep-Related Memory for Novel Words. Brain Sci. 2021. 11 (10): 1366.
Cesana-Arlotti N. Precursors of logical reasoning in preverbal human infants Science. 2018. 359 (6381): 1263–1266.
Chen S., Wang Y., Yan W. More Stable Memory Retention of Novel Words Learned from Fast Mapping than from Explicit Encoding. J Psycholinguist Res. 2022.
Chung H., Yim D. Quick Incidental Learning of Words by Children with and without Specific Language Impairment: An Eye-tracking Study. Commun Sci Disord. 2020. 25 (3): 499–516.
Cooper E., Greve A., Henson R.N. Investigating fast mapping task components: No evidence for the role of semantic referent nor semantic inference in healthy adults. Front. Psychol. 2019. 10: 394.
Coutanche M.N., Thompson-Schill S.L. Fast mapping rapidly integrates information into existing memory networks. J. Exp. Psychol. 2014. 143 (6): 2296–2303.
Ellis E.M., Borovsky A., Elman J.L., Evans J.L. Novel word learning: An eye-tracking study. Are 18-month-old late talkers really different from their typical peers? J. Commun. Disord. 2015. 58: 143–157.
Feiman R., Mody Sh., Carey S. The development of reasoning by exclusion in infancy. Cogn. Psychol. 2022. 135: 101473.
Forder L., Lupyan G. Hearing words changes color perception: Facilitation of color discrimination by verbal and visual cues. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2019. 148 (7): 1105.
Greve A., Cooper E., Henson R.N. No evidence that “fast-mapping” benefits novel learning in healthy older adults. Neuropsychologia. 2014. 60: 52–59.
Grigoroglou M., Chan S., Ganea P.A. Toddlers’ understanding and use of verbal negation in inferential reasoning search tasks. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2019. 183: 222–241.
Halberda J. Is this a dax which I see before me? Use of the logical argument disjunctive syllogism supports word-learning in children and adults. Cogn Psychol. 2006. 53 (4): 310–344.
Hill A., Collier-Baker E., Suddendorf T. Inferential reasoning by exclusion in children (Homo sapiens). J. Comp. Psychol. 2012. 126 (3): 243–254.
Li C., Hu Z., Yang J. Rapid acquisition through fast mapping: stable memory over time and role of prior knowledge. Learning & Memory. 2020. 27 (5): 177–189.
Mason R.S., Bass L.A. Just Ask Me Again: An Analysis of Receptive Vocabulary Performance of Children from Low-Income Environments. EE & D. 2020. 31 (6): 910–926.
Medina T.N., Snedeker J., Trueswell J.C., Gleitman L.R. How words can and cannot be learned by observation. PNAS. 2011. 108 (22): 9014–9019.
Merhav M., Karni A., Gilboa A. Not all declarative memories are created equal: Fast mapping as a direct route to cortical declarative representations. NeuroImage. 2015. 117: P. 80–92.
Mervis C.B., Bertrand J. Acquisition of the Novel Name-Nameless Category (N3C) Principle. Child Development. 1994. 65 (6): 1646.
Mody S., Carey S. The emergence of reasoning by the disjunctive syllogism in early childhood. Cognition. 2016. 154: 40–48.
Morozov M.I. How the strength of the link between an object and its category label influences visual search performance. The Russian J Cogn Sci. 2017. 4 (4): 22–28.
Perikova E., Blagovechtchenski E., Filippova M., Shcherbakova O., Kirsanov A., Shtyrov Y. Anodal tDCS over Broca’s area improves fast mapping and explicit encoding of novel vocabulary. Neuropsychologia. 2022. 168: 108156.
Repnik K.R. Not this, but that.' Exploring disambiguation in the context of multilingual word learning, 2021. PhD thesis. 240 p. https://era.ed.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/1842/37808/Repnik2021.pdf?seque-nce=1&isAllowed=y
Shtyrov Y., Filippova M., Blagovechtchenski E., Kirsanov A., Nikiforova E., Shcherbakova O. Electrophysiological evidence of dissociation between explicit encoding and fast mapping of novel spoken words. Front. Psychol. 2021. 12: 571673.
Shtyrov Y., Filippova M., Perikova E., Kirsanov A., Shcherbakova O., Blagovechtchenski E. Explicit encoding vs. fast mapping of novel spoken words: Electrophysiological and behavioural evidence of diverging mechanisms. Neuropsychologia. 2022. 172: 108268.
Souza A.S., Overkott C., Matyja M. Categorical distinctiveness constrains the labeling benefit in visual working memory. J Mem Lang. 2021. 119: 104242.
Ting Siok W., Kay P., Wang W.S.Y., Chan A.H.D., Chen L., Luke K.-K., Hai Tan L. Language regions of brain are operative in color perception. PNAS. 2009. 106 (20): 8140–8145.
Trueswell J.C., Medina T.N., Hafri A., Gleitman L.R. Propose but verify: Fast mapping meets cross-situational word learning. Cogn Psychol. 2013. 66 (1): 126–156.
Vales C., Smith L.B. Words, shape, visual search and visual working memory in 3-year-old children. Developmental Science. 2015. 18 (1): 65–79.
Vasilyeva M.J., Knyazeva V.M., Aleksandrov A.A., Shtyrov Y. Neurophysiological correlates of fast mapping of novel words in the adult brain. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2019. 13 (304).
Warren D.E., Duff M.C. Not so fast: Hippocampal amnesia slows word learning despite successful fast mapping. Hippocampus. 2014. 24 (8): 920–953.
Warren D.E., Tranel D., Duff M.C. Impaired acquisition of new words after left temporal lobectomy despite normal fast-mapping behavior. Neuropsychologia. 2016. 80: 165–175.
Winawer J., Witthoft N., Frank M.C., Wu L., Wade A.R., Boroditsky L. Russian blues reveal effects of language on color discrimination. PNAS, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007. 104 (19): 7780–7785.
Wochna K.L., Juhasz B.J. Context length and reading novel words: an eye-movement investigation. Br. J. Psychol. 2013. 104 (3): 347–363.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Журнал высшей нервной деятельности им. И.П. Павлова


