Теплоэнергетика, 2024, № 4, стр. 82-88
Прогнозирование тепловой нагрузки систем централизованного теплоснабжения на основе SCSO-TCN
M. Gong a, *, C. Han a, J. Sun a, Y. Zhao a, S. Li b, c, W. Xu c, d
a School of Integrated Circuit Science and Engineering, Tianjin University of Technology
300384 Tianjin, Xiqing District, No. 391 Bin Shui Xi Dao Road, China
b Tianjin University
300072 Tianjin, Nankai District, Beiyang Ave, China
c Sea Island Environment Science and Technology Research Institute (Tianjin) Co., Ltd
300072 Tianjin, Nankai District, North Side of Anshan West Road Middle Section, Hetong Building, China
d Institute of Marine Energy and Intelligent Construction, Tianjin University of Technology
300384 Tianjin, Xiqing District, No. 391 Bin Shui Xi Dao Road, China
* E-mail: gmj790@163.com
Поступила в редакцию 30.08.2022
После доработки 25.12.2022
Принята к публикации 25.01.2023
Аннотация
Прогнозирование тепловой нагрузки играет важнейшую роль в регулировании систем централизованного теплоснабжения (СЦТ). Для этого часто используется алгоритм глубокого машинного обучения – временнáя сверточная сеть (the temporal convolutional network – TCN). Однако для настройки TCN требуется довольно много гиперпараметров. Ручная настройка временных сверточных сетей неэффективна. В настоящей работе предлагается гибридная модель, основанная на так называемой оптимизации стаи барханных (песчаных) котов (sand cat swarm optimization – SCSO) и TCN (SCSO-TCN). В этой модели для оптимизации используются следующие гиперпараметры: число фильтров, размеры фильтра, процент отсева и размер партии. Для проверки эффективности модели SCSO-TCN ее сравнивали с двумя другими гибридными моделями: оптимизацией роя частиц (particle swarm optimization – PSO) с TCN (PSO-TCN) и алгоритмом поиска воробья (sparrow search algorithm – SSA) с TCN (SSA-TCN). Для тестовых расчетов использовались данные о тепловой нагрузке трех тепловых пунктов, расположенных в г. Тяньцзин (Китай). Результаты расчетов показывают, что гибридная модель SCSO-TCN имеет более высокую точность прогнозирования и лучшую способность к обобщению, чем модели PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN.
В настоящее время в мире насчитывается около 80 000 централизованных тепловых сетей (СЦТ) [1], которые являются частью городских энергетических структур. В СЦТ передача тепла осуществляется по тепловой сети от центрального источника тепла к потребителям по всему городу или определенному району. Системы централизованного теплоснабжения обладают такими достоинствами, как высокая эффективность использования энергии, незначительное воздействие на окружающую среду, удобство для потребителей [2]. Однако СЦТ имеют один очевидный существенный недостаток – инерционность [3]. Чтобы удовлетворить требования потребителей, тепловую нагрузку системы следует определять заранее. Поэтому точное прогнозирование тепловой нагрузки становится необходимостью [4].
Методика прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки СЦТ существенно зависит от применяемых моделей управления данными. В таких моделях используются в основном метеорологические данные, а также статистические данные по прогнозируемой потребности в количестве тепла. Ранее для построения таких моделей применялись следующие классические статистические модели: множественная линейная регрессия (multiple linear regression – MLR) [5], авторегрессионная модель скользящего среднего (autoregressive moving average model – ARMA) [6] и сезонная авторегрессионная интегрированная модель прогнозирования скользящего среднего (seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average – SARIMA) [7]. Преимуществами статистических моделей являются их простота и легкость для понимания, а их недостатками – низкая точность предсказания и чувствительность к выпадающим значениям.
Модели машинного обучения более эффективны. Машинное обучение позволяет выявить статистические закономерности, что дает возможность компьютерным системам генерировать точные прогнозы на основе предоставленного набора данных. К настоящему времени опубликовано довольно много работ, в которых оценивается производительность машинного обучения при прогнозировании тепловой нагрузки. Экспериментальные данные подтверждают, что прогнозы, полученные с помощью метода опорных векторов (support vector machine – SVM) [8–11], искусственной нейронной сети (artificial neural network – ANN) [12–14] и экстремального повышения градиента (XGBoost) [15, 16], являются более точными и стабильными, чем прогнозы, построенные по классическим моделям.
Глубокое машинное обучение позволяет установить сложную взаимосвязь между тепловыми нагрузками и входными характеристиками. В [17] для прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки предлагается гибридная модель, объединяющая метод отбора похожих дней и глубокую нейронную сеть (deep neural network – DNN). Использование такой гибридной модели значительно повышает точность прогноза. Рекуррентная нейронная сеть (recurrent neural network – RNN) [18] и сеть с долгой кратковременной памятью (long short-term memory network – LSTM) [19, 20] продемонстрировали превосходную производительность при прогнозировании потребления тепла в СЦТ. В [21] для прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки СЦТ применяется временнáя сверточная сеть (TCN). Авторы провели сравнение TCN с RNN и LSTM и выявили преимущества временнóй сверточной сети.
Однако качество прогноза, полученного с помощью TCN, существенно зависит от параметров модели. Для улучшения прогностической способности модели в некоторых опубликованных работах предлагается уточнять параметры модели с помощью алгоритмов оптимизации [22–24]. Авторы [25] для такого уточнения используют алгоритм поиска светлячков и метод опорных векторов SVM, что дает возможность повысить уровень прогнозирования модели. В [26] для изменения параметров SVM применяется алгоритм оптимизации кузнечиков. Комбинирование различных методов — это способ сделать прогностическую модель более точной. Это побудило авторов настоящей работы найти такой алгоритм оптимизации гиперпараметров TCN, котрый позволил бы дополнительно улучшить адаптивность и точность оценки временнóй сверточной сети.
Не так давно в литературе началось обсуждение нового алгоритма оптимизации – оптимизации стаи барханных (песчаных) котов (SCSO) [27], который по сравнению с другими алгоритмами имеет несколько преимуществ:
позволяет сбалансированно контролировать переходы между стадиями поиска добычи (разведки) и нападения на нее;
требует наличия меньшего числа исходных данных и проведения меньшего количества вычислений;
может быть довольно легко реализован.
Эти преимущества побудили авторов данной работы использовать модель SCSO-TCN для прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки СЦТ, при этом SCSO применяется для поиска параметров TCN в пределах заранее определенной области.
Подробное описание СЦТ и принципа ее работы, предпосылок прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки, а также применения временной сверточной сети приведены в [28].
ОПТИМИЗАЦИИ СТАИ БАРХАННЫХ (ПЕСЧАНЫХ) КОТОВ (SCSO)
Оптимизация SCSO имитирует поведение барханных (песчаных) котов, которые пытаются выжить в природе. Эти коты способны улавливать низкие частоты (ниже 2 кГц), а также обладают исключительными навыками охотника. Предлагаемый алгоритм, основанный на этих двух функциях, состоит из двух основных этапов [поиск (разведка) и нападение (эксплуатация)] и сбалансированно контролирует переходы на этапах разведки и эксплуатации.
Начальная популяция. Для решения задачи оптимизации в первую очередь следует указать значения задействованных вариантов – количество барханных котов. При оптимизации p-размерности возможным решением является $1 \times p$ c массивом $\{ {{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}},...,{{x}_{p}}\} $. Каждая переменная ${{x}_{i}}$ должна находиться между верхней ${{x}_{1}}$ и нижней ${{x}_{p}}$ границами. Это гарантирует, что процесс оптимизации остается в пределах определенного пространства параметров.
Далее необходимо инициализировать матрицу размерами ${{{\mathbf{N}}}_{{pop}}} \times {{{\mathbf{M}}}_{p}}$ (${{{\mathbf{N}}}_{{pop}}}$ – размер популяции, ${{{\mathbf{M}}}_{p}}$ – переменное число).
Разведка (поиск добычи). Как уже отмечалось, барханный кот может слышать частоты ниже 2 кГц. Тем самым определяется диапазон чувствительности барханного кота. В математических уравнениях это означает, что чувствительность ${{\vec {r}}_{G}}$ уменьшается линейно от 2 до 0 согласно следующему выражению:
(1)
${{\vec {r}}_{G}} = {{s}_{M}} - \frac{{2{{s}_{M}}{\text{ite}}{{{\text{r}}}_{c}}}}{{{\text{ite}}{{{\text{r}}}_{{\max }}} + {\text{ite}}{{{\text{r}}}_{{\max }}}}},$Поскольку значение ${{s}_{M}}$ получено на основе слуховых возможностей песчаного кота, ему присвоено значение 2. В зависимости от условий решаемой задачи значение ${{s}_{M}}$ можно изменить.
Местоположение песчаного кота обновляется с помощью вектора $\vec {R}$:
При $\left| {\vec {R}} \right| > 1$ поисковые агенты (песчаные коты) вынуждены искать цели (проводить разведку). При $\left| {\vec {R}} \right| < 1$ поисковые агенты должны атаковать цели (эксплуатация – нападение на добычу). Благодаря такой стратегии, SCSO имеет хорошо сбалансированный переход от разведки к эксплуатации.
Каждый песчаный кот обладает собственной чувствительностью к побегу из локальной оптимальной ловушки, что описывается следующим выражением:
Каждый песчаный кот оставляет свою позицию для лучшего кандидата на эту позицию. Это действие можно записать как
(4)
$\vec {P}(t + 1) = \vec {r} \times \left[ {{{{\vec {P}}}_{{bc}}}(t) - {\text{rand}}(0,1){{{\vec {P}}}_{c}}(t)} \right],$Эксплуатация (нападение на добычу). В период эксплуатации расстояние ${{\vec {P}}_{{rnd}}}$ между лучшим решением ${{\vec {P}}_{{bc}}}$ и текущим положением песчаного кота ${{\vec {P}}_{c}}$ рассчитывается следующим образом:
(5)
${{\vec {P}}_{{rnd}}} = \left| {{\text{rand}}(0,1) \cdot {{{\vec {P}}}_{{bc}}}(t) - {{{\vec {P}}}_{c}}(t)} \right|.$Предполагается, что чувствительность каждого поискового агента (песчаного кота) представляет собой окружность, а направление его движения определяется случайным углом $\theta $ на этой окружности. Для выбора угла в методе SCSO применяется колесо рулетки. Песчаный кот изменяет значения своих переменных в соответствии с уравнением
ТЕСТОВЫЙ ЭКСПЕРИМЕНТ
Основными факторами, влияющими на тепловую нагрузку, являются временные и погодные условия, параметры работы СЦТ и запросы потребителей. Временные факторы относятся к месяцу, дню и часу и отражают структуру загрузки потребителей. Другими словами, действия потребителей можно рассматривать как функцию временных факторов. В работе [29] отмечается, что влияние временных факторов на прогнозы незначительно. Поэтому в данной работе временные факторы как входные характеристики не рассматриваются.
Такие погодные условия, как температура наружного воздуха, относительная влажность, сила и направление ветра, индекс качества воздуха (air quality index – AQI) и др., оказывают существенное влияние на тепловую нагрузку. Внутренними характеристиками СЦТ являются температура, давление и скорость теплоносителя, а также тепловая инерция системы, которая обеспечивает корреляцию между статистическими и последующими отопительными нагрузками.
На базе СЦТ в г. Тяньцзин (Китай) авторы установили систему для сбора информации, в которую поступают данные о погоде и оперативные данные от трех тепловых пунктов (ТП): № 1, 2 и 3. Важными входными характеристиками считаются тепловая нагрузка на сутки вперед и на час вперед, температура наружного воздуха, относительная влажность, сила и направление ветра, а также AQI.
Настройка и оценка точности модели
В поверочном эксперименте необработанный набор данных случайным образом разделяется на обучающий и тестовый наборы. Для ТП № 1 на тестовый набор выделяется 168 выборок, а остальные выборки приходятся на обучающий набор. Базы данных ТП № 2 и 3 являются менее наполненными. Обучающий набор должен охватывать определенный объем выборочных данных, чтобы обеспечить точность прогноза, полученного с помощью используемой модели. Так, для ТП № 2 и 3 имелось только 72 выборки, которые разбивались на тестовый и обучающий наборы.
Как уже отмечалось, для оптимизации TCN может использоваться SCSO, или оптимизация роя частиц (PSO), или алгоритм поиска воробьев (SSA). Ограничения сверху и снизу по количеству фильтров, размеру фильтра, проценту отсева и размеру партии выбраны следующим образом: [5, 20], [2, 10], [0.05, 0.3], [5, 30 ] . В табл. 1 перечислены гиперпараметры для рассматриваемых алгоритмов оптимизации.
Таблица 1.
Значения гиперпараметров для рассматриваемых алгоритмов оптимизации для трех тепловых пунктов
| Номер ТП | PSO-TCN | SSA-TCN | SCSO-TCN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [12, 6, 0.231, 19] | [5, 2, 0.05, 5] | [16, 8, 0.218, 21] |
| 2 | [8, 2, 0.142, 8] | [5, 2, 0.219, 5] | [6, 2, 0.063, 6] |
| 3 | [10, 9, 0.158, 6] | [5, 2, 0.05, 5] | [5, 2, 0.05, 5] |
Для оценки производительности модели применяется тестовый набор. Среднеквадратическая ошибка (mean squared error – MSE), средняя абсолютная ошибка (mean absolute error – MAE) и коэффициент вариации среднеквадратической ошибки (coefficient of variation of root mean square error – CVRRMSE) выбираются для оценки точности прогноза. Эти ошибки рассчитываются следующим образом:
(8)
${\text{MAE}} = \frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\left| {{{Q}_{n}} - {{{\hat {Q}}}_{n}}} \right|} ;$(9)
${\text{CVRMSE}} = \frac{{\sqrt {\frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {{{{({{Q}_{n}} - {{{\hat {Q}}}_{n}})}}^{2}}} } }}{{\frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {{{Q}_{n}}} }},$Экспериментальные данные
Чтобы проверить точность прогноза и его способность адаптироваться к новым данным, было проведено сравнение результатов, полученных с помощью моделей SCSO-TCN, PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN. Результаты прогноза по этим моделям представлены на рис. 1. В табл. 2 приведены статистические показатели моделей.
Рис. 1.
Результаты прогнозирования тепловой нагрузки Q для трех тепловых пунктов № 1 (а), № 2 (б) и № 3 (в), полученные с использованием трех моделей прогнозирования. 1 – фактическая нагрузка; нагрузка, определенная с помощью модели: 2 – PSO-TCN; 3 – SSA-TSN; 4 – SCSO-TCN
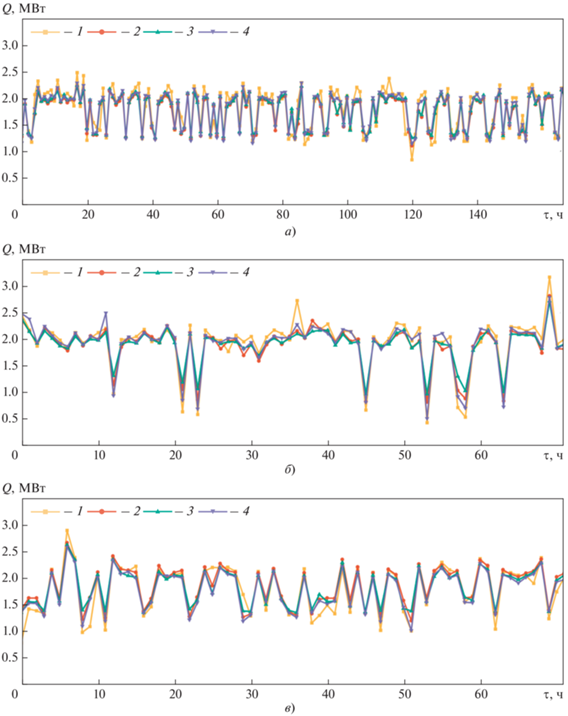
Таблица 2.
Оценка точности алгоритмов оптимизации для трех тепловых пунктов
| Номер ТП | PSO-TCN | SSA-TCN | SCSO-TCN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | MAE | CVRMSE | MSE | MAE | CVRMSE | MSE | MAE | CVRMSE | |
| 1 | 0.0287 | 0.1271 | 0.0938 | 0.0274 | 0.1218 | 0.0916 | 0.0217 | 0.1066 | 0.0816 |
| 2 | 0.0282 | 0.1289 | 0.0864 | 0.0409 | 0.1400 | 0.1040 | 0.0173 | 0.0995 | 0.0676 |
| 3 | 0.0301 | 0.1195 | 0.0966 | 0.0342 | 0.1298 | 0.1030 | 0.0280 | 0.1165 | 0.0932 |
Анализ рисунка позволяет сделать следующие выводы:
рассмотренные модели дают довольно точные прогнозы, поскольку показатель CVRMSE не превышает 30%, что, по мнению авторов [15], вполне приемлемо для практического применения той или иной модели;
прогноз, составленный по предлагаемой в настоящей работе модели SCSO-TCN, по сравнению с PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN имеет наименьшую ошибку;
исходные данные и количество обучающих выборок для трех тепловых пунктов различаются, однако прогнозы, полученные с помощью SCSO-TCN, являются более точными по сравнению с прогнозами, построенными по моделям PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN.
Таким образом, модель SCSO-TCN обладает наилучшей адаптивностью и эффективностью.
Наибольшая неопределенность прогноза получена для ТП № 3, поскольку для этого пункта было недостаточно исходных данных, что затруднило их разделение на обучающий и тестовый наборы.
ВЫВОДЫ
1. По точности прогноза тепловой нагрузки системы централизованного теплоснабжения гибридная модель SCSO-TCN превосходит такие модели, как PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN.
2. Модель SCSO-TCN обладает лучшей адаптивностью и эффективностью по сравнению с моделями PSO-TCN и SSA-TCN.
3. Для получения более точного прогноза с помощью модели SCSO-TCN необходимы дополнительные данные о тепловой нагрузке на рассматриваемом тепловом пункте.
Список литературы
Load forecasting of district heating system based on Informer / M.J. Gong, Y. Zhao, J.W. Sun, C.T. Han, G.N. Sun, B. Yan // Energy. 2022. V. 253. P. 124179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124179
Lake A., Rezaie B., Beyerlein S. Review of district heating and cooling systems for a sustainable future // Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2017. V. 67. P. 417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.061
A survey of district heating systems in the heating regions of Northern China / X. Xu, S.J. You, X.J. Zheng, H. Li // Energy. 2014. V. 77. P. 909–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.09.078
The status of 4th generation district heating: Research and results / H. Lund, P.A. Ostergaard, M. Chang, S. Werner, S. Svendsen, P. Sorknaes, J.E. Thorsen, F. Hvelplund, B.O.G. Mortensen, B.V. Mathiesen, C. Bojesen, N. Duic, X.L. Zhang, B. Moller // Energy. 2018. V. 164. P. 147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.08.206
Analysis and evaluation of the operation data for achieving an on-demand heating consumption prediction model of district heating substation / J.J. Yuan, Z.H. Zhou, K. Huang, Z. Han, C.D. Wang, S.L. Lu // Energy. 2021. V. 214. P. 118877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118872
Dahl M., Brun A., Andresen G.B. Using ensemble weather predictions in district heating operation and load forecasting // Appl. Energy. 2017. V. 193. P. 455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.02.066
Fang T.T., Lahdelma R. Evaluation of a multiple linear regression model and SARIMA model in forecasting heat demand for district heating system // Appl. Energy. 2016. V. 179. P. 544–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.133
Forecasting of consumers heat load in district heating systems using the support vector machine with a discrete wavelet transform algorithm / M. Protic, S. Shamshirband, D. Petkovic, A. Abbasi, M.L.M. Kiah, J.A. Unar, L. Zivkovic, M. Raos // Energy. 2015. V. 87. P. 343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.04.109
Appraisal of the support vector machine to forecast residential heating demand for the district heating system based on the monthly overall natural gas consumption / N. Izadyar, H. Ghadamian, H.C. Ong, Z. Moghadam, C.W. Tong, S. Shamshirband // Energy. 2015. V. 93. P. 1558–1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.10.015
Prediction of heating load fluctuation based on fuzzy information granulation and support vector machine / T. Wang, T.Y. Ma, D.S. Yan, J. Song, J.S. Hu, G.Y. Zhang, Y.H. Zhuang // Therm. Sci. 2021. V. 25. Is. 5. P. 3219–3228. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI200529307W
Applied machine learning: Forecasting heat load in district heating system / S. Idowu, S. Saguna, C. Ahlund, O. Schelen // Energy Build. 2016. V. 133. P. 478–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.09.068
Heat demand forecasting algorithm for a Warsaw district heating network / T. Kurek, A. Bielecki, K. Swirski, K. Wojdan, M. Guzek, J. Bialek, R. Brzozowski, R. Serafin // Energy. 2021. V. 217. P. 119347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119347
Yabanova I., Kecebas A. Development of ANN model for geothermal district heating system and a novel PID-based control strategy // Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013. V. 51. Is. 1–2. P. 908–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.10.044
Heat load prediction of small district heating system using artificial neural networks / M.B. Simonovic, V.D. Nikolic, E.P. Petrovic, I.T. Ciric // Therm. Sci. 2016. V. 20. S1355–S1365. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI16S5355S
Multi-step ahead forecasting of heat load in district heating systems using machine learning algorithms / P.N. Xue, Y. Jiang, Z.G. Zhou, X. Chen, X.M. Fang, J. Liu // Energy. 2019. V. 188. P. 116085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116085
Prediction of residential district heating load based on machine learning: A case study / Z.Q. Wei, T.W. Zhang, B. Yue, Y.X. Ding, R. Xiao, R.Z. Wang, X.Q. Zhai // Energy. 2021. V. 231. P. 120950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120950
District heating systems load forecasting: a deep neural networks model based on similar day approach / M. Gong, H. Zhou, Q. Wang, S. Wang, P. Yang // Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2020. V. 14. Is. 3. P. 372–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512549.2019.1607777
Koschwitz D., Frisch J., van Treeck C. Data-driven heating and cooling load predictions for non-residential buildings based on support vector machine regression and NARX recurrent neural network: A comparative study on district scale // Energy. 2018. V. 165. P. 134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.09.068
A comprehensive thermal load forecasting analysis based on machine learning algorithms / S. Leiprecht, F. Behrens, T. Faber, M. Finkenrath // Energy Rep. 2021. V. 7. P. 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.08.140
Heating load forecasting for combined heat and power plants via strand-based LSTM / J.Y. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Zhao, B. Dong, K. Lu, R.R. Wang // IEEE Access. 2020. V. 8. P. 33360–33369. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2972303
Hourly heat load prediction model based on temporal convolutional neural network / J.C. Song, G.X. Xue, X.H. Pan, Y.P. Ma, H. Li // IEEE Access. 2020. V. 8. P. 16726–16741. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2968536
Eseye A.T., Lehtonen M. Short-term forecasting of heat demand of buildings for efficient and optimal energy management based on integrated machine learning models // IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020. V. 16. Is. 12. P. 7743–7755. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2020.2970165
Medium-term heat load prediction for an existing residential building based on a wireless on-off control system / J.H. Gu, J. Wang, C.Y. Qi, C.H. Min, B. Sunden // Energy. 2018. V. 152. P. 709–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.179
Wang M., Tian Q. Dynamic heat supply prediction using support vector regression optimized by particle swarm optimization algorithm // Math. Probl. Eng. 2016. V. 2016. Article ID 3968324. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3968324
Prediction of heat load in district heating systems by support vector machine with firefly searching algorithm / E.T. Al-Shammari, A. Keivani, S. Shamshirband, A. Mostafaeipour, P.L. Yee, D. Petkovic, S. Ch // Energy. 2016. V. 95. P. 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.11.079
Barman M., Choudhury N.B.D., Sutradhar S. A regional hybrid GOA-SVM model based on similar day approach for short-term load forecasting in Assam, India // Energy. 2018. V. 145. P. 710–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.156
Seyyedabbasi A., Kiani F. Sand Cat swarm optimization: a nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems // Eng. Comput. 2023. V. 39. P. 2627–2651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01604-x
Прогнозирование тепловой нагрузки для систем централизованного теплоснабжения с помощью моделей TCN и CatBoost / C. Han, M. Gong, J. Sun, Y. Zhao, L. Jing, C. Dong, Z. Zhao // Теплоэнергетика. 2023. № 9. С. 97–105. https://doi.org/10.56304/S0040363623090047
Statistical analysis of energy consumption patterns on the heat demand of buildings in district heating systems / Z.Y. Ma, H.L. Li, Q. Sun, C. Wang, A.B. Yan, F. Starfelt // Energy Build. 2014. V. 85. P. 464–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.09.048
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Теплоэнергетика


