Геомагнетизм и аэрономия, 2023, T. 63, № 3, стр. 306-320
Выделение солнечно-суточной анизотропии космических лучей локальным и глобальным методами
А. В. Белов 1, *, Н. С. Шлык 1, **, М. А. Абунина 1, А. А. Абунин 1, В. А. Оленева 1, В. Г. Янке 1, А. А. Мелкумян 1
1 Институт земного магнетизма, ионосферы и распространения радиоволн
им. Н.В. Пушкова РАН (ИЗМИРАН)
Москва, Троицк, Россия
* E-mail: abelov@izmiran.ru
** E-mail: nshlyk@izmiran.ru
Поступила в редакцию 20.10.2022
После доработки 25.11.2022
Принята к публикации 28.11.2022
- EDN: UJBTLX
- DOI: 10.31857/S0016794022600594
Аннотация
По данным нейтронного монитора ст. Москва с помощью гармонического анализа получены характеристики солнечно-суточной анизотропии космических лучей в спокойные дни за длительный период с 1965 по 2020 гг. Установлено, что средний суточный ход вариаций космических лучей нейтронных мониторов ст. Москва практически полностью описывается двумя гармониками солнечно-суточной анизотропии и не содержит признаков других влияний. Сравнение со среднесуточными характеристиками экваториальной составляющей векторной анизотропии космических лучей, полученными по данным мировой сети нейтронных мониторов с помощью метода глобальной съемки, показало хорошее согласие результатов двух методик. Из сравнения локальных и глобальных результатов получены оценки приемных коэффициентов первой гармоники анизотропии космических лучей для нейтронного монитора ст. Москва и предложен новый экспериментальный метод расчета приемных коэффициентов отдельных детекторов. Обсуждены и обоснованы ограничения локальной методики, а также возможности продолжения и расширения данного исследования.
1. ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Галактические космические лучи (КЛ) приходят к Земле со всех сторон и почти изотропно. Однако небольшая неоднородность в угловом распределении интенсивности потока КЛ (или анизотропия КЛ) существует постоянно [Forbush, 1969]. Хорошо выделяется суточная волна, связанная с вращением Земли вокруг своей оси, ее часто называют солнечно-суточной анизотропией. Она была обнаружена сразу после начала регулярных наблюдений КЛ в 30-е годы прошлого века (напр., [Thompson, 1939; Duperier, 1946]). Достаточно посмотреть на практически любой короткий (хватит нескольких дней) ряд данных любого достаточно большого наземного детектора КЛ, чтобы увидеть в нем повторяемость с приблизительным периодом в одни сутки.
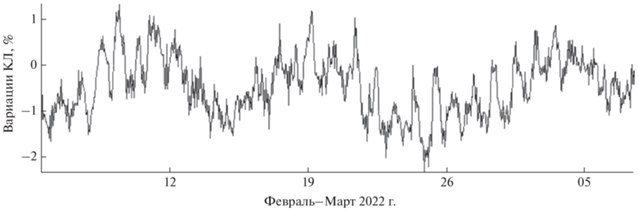
На рисунке 1 приведен произвольно взятый период вариаций КЛ, зарегистрированных на типичном нейтронном мониторе (НМ). Суточная волна видна во все дни периода. Даже не зная ее природу, естественно связать ее с вращением Земли и нетрудно догадаться, что так проявляется анизотропия КЛ.
Более чем за 80 лет исследований анизотропии КЛ было опубликовано огромное число работ (см., напр., [Forbush, 1969; Thompson, 1939; Duperier, 1946; Elliot, 1952; Firor et al., 1954; Sarabhai and Nerurkar, 1956; Kane, 1966; Nagashima et al., 1968; Sekido et al., 1968; Jacklyn and Vrana, 1969; Somogyi, 1969; Swinson, 1969, 1995; Briggs et al., 1970; Pomerantz and Duggal, 1972; Forbush and Beach, 1975; Крымский и др., 1981]). Большое внимание к этой научной области связано с тем, что анизотропия чутко реагирует на все основные проявления солнечной активности, например, основные солнечные циклы (11- и 22-летний) [Forbush, 1969; Duggal et al., 1970; Pomerantz and Duggal, 1971; Forbush, 1973; Forbush and Beach, 1975; Moraal, 1976; Samsonov et al., 1979; Mori et al., 1981; Bieber and Chen, 1991; Крымский и др., 2007; Oh et al., 2010; Tiwari et al., 2012; Абунина и др., 2013б; Munakata et al., 2013, 2014] или короткопериодные флуктуации параметров солнечного ветра и межпланетного магнитного поля, которые являются причиной Форбуш-эффектов (ФЭ) [Forbush, 1937, 1938; Yoshida, 1956; Kaminer et al., 1981; Dvornikov et al., 1983; Mishra and Mishra, 2007; Абунина и др. 2013а].
Большинство исследований проводилось разным способами по данным одного или нескольких наземных детекторов [Mori et al., 1977; Sari et al., 1978; Kumar et al., 1993; Oh et al., 2010], с использованием ионизационных камер [Comptom, 1934; Шафер, 1984; Beer et al., 2012 и ссылки в ней] или по данным шаров-зондов [Bazilevskaya and Svirzhevskaya, 1998; Stozhkov et al., 2009]. Большому числу работ по анизотропии КЛ отчасти способствовала легкость ее выделения. Но следует подчеркнуть, что довольно легко получить среднесуточные характеристики солнечно-суточной анизотропии только в сравнительно спокойные периоды. Во время возмущений среднесуточные характеристики малополезны, а выделение анизотропии в более короткие периоды (например, за каждый час) – это более трудная задача, требующая специальных подходов и методов.
Глобальные методы изучения вариаций первичных КЛ (например, метод глобальной съемки – GSM (Global Survey Method)) объединяют одновременные наземные наблюдения КЛ на отдельных детекторах для получения основных характеристик их вариаций за пределами атмосферы и магнитосферы Земли. В данном методе вся сеть НМ используется как единый многоканальный прибор, где в роли каждого канала выступает станция, которая получает информацию из определенного сектора, а все каналы целиком перекрывают небесную сферу. Многоканальность такого прибора обеспечивает надежность и непрерывность измерений, при этом статистическая точность сети заметно возрастает, а влияние аппаратурных эффектов существенно уменьшается. К примеру, отдельный нейтронный монитор (НМ64) обеспечивает статистическую точность 0.1‒0.2%/ч, в то время как вся сеть станций обеспечивает точность порядка ~0.01%/ч.
Метод глобальной съемки позволяет определить плотность (изотропную часть интенсивности) и анизотропию потока галактических КЛ за каждый час за пределами магнитосферы и атмосферы. Одна из самых первых и успешных реализаций глобального метода была создана в Якутске [Крымский и др., 1966а, 1966б, 1967, 1981; Altuchov et al., 1969]. Практически в это же время свою методику предложили и японские исследователи [Nagashima, 1971].
Немного позже, в начале 70-х гг., модификация этого метода была разработана в ИЗМИРАН [Belov et al., 1973, 1974] и применена для обработки нескольких событий в октябре–ноябре 1968 г., а затем использовалась для обработки часовых данных нейтронных мониторов за весь период наблюдений. Детальное описание версии GSM, разработанной в ИЗМИРАН, приведено в работах [Белов и др., 2018; Belov et al., 2018].
Группа иркутских исследователей разработала свою версию – глобально-спектрографический метод [Dvornikov and Sdobnov, 1998], который стал самым сложным и многоцелевым из существующих в мире методов обработки данных НМ. Он используется для вычисления первой и второй гармоники анизотропии космических лучей и для определения вариаций планетарного распределения жесткостей геомагнитного обрезания [Дворников и др., 1986; Richardson et al., 2000].
Отдельно стоит упомянуть, что существует еще один глобальный способ исследования солнечно-суточных вариаций КЛ – это метод кольца станций, который позволяет получать свойства углового распределения КЛ без разложения на гармоники. Он позволяет получить мгновенное (точнее, ежечасное) долготное распределение интенсивности КЛ, не прибегая к его моделированию. Данный метод основан на том, что основной вклад в скорость счета НМ вносят первичные КЛ, приходящие с достаточно узкой полосы долгот. В связи с этим для метода кольца станций используются данные не всех НМ, исключаются высокоширотные (приполярные), низкоширотные и высокогорные станции. Подробное описание метода кольца станций, его особенности, ограничения и применимость приведены в работах [Абунина и др., 2020а, 2020б; Abunina et al., 2020].
Есть и другой метод, похожий на описанный выше метод кольца станций, но реализованный для меньшего числа высокоширотных станций, входящих в проект Spaceship Earth (https://neutronm.bartol.udel.edu/). Этот метод рассчитывает ежечасное питч-угловое распределение интенсивности КЛ и также позволяет наблюдать предвестники приближающихся межпланетных возмущений. Оба упомянутых метода сейчас реализованы в реальном времени, ознакомиться с результатом их работы можно по ссылкам (https:// crst.izmiran.ru/aid/ros) и (https://neutronm.bartol. udel.edu/spaceweather/lossconegraph. html).
Существуют также локальные методы исследования вариаций КЛ, в основе которых лежит обработка данных одного или нескольких НМ различными способами. Так, разными авторами на протяжении уже нескольких десятилетий используется метод гармонического анализа временны́х рядов скорости счета НМ [Patel et al., 1968; Forbush, 1973; Singh and Badruddin, 2006; Oh et al., 2010; Tivari et al., 2012] или Фурье-анализ [Mathews et al., 1969; Dubey, 2001; Mishra and Mishra, 2006; Sabbah, 2013; Okike, 2021]. В этих исследованиях описаны различные особенности поведения анизотропии КЛ в разные периоды времени (в т.ч. в спокойные и во время ФЭ), энергетический спектр анизотропии, долговременные изменения и т.д. Подобные исследования проводились также по данным мюонных телескопов (напр., [Mori et al., 1977; Fenton et al., 1983; Munakata et al., 2013, 2014]).
Наглядность – это одно из преимуществ локального метода выделения анизотропии. Есть и другие. Локальный подход почти незаменим там, где нет возможности организовать одновременные наблюдения КЛ для всей небесной сферы. Это трудно сделать для более высоких энергий, чем эффективные энергии НМ и пока невозможно осуществить на других планетах (на Марсе, к примеру). Невозможно было обойтись без локальных методов в начале 19-го солнечного цикла, когда уже были непрерывные наблюдения, но еще не было мировой сети НМ. Локальные методы дали нам основные сведения о второй и третьей гармониках анизотропии КЛ [Крымский и др., 1973; Kota, 1975; Кравцов, 1980; Munakata and Nagashima, 1985; Kaushik et al., 2001; Munakata et al., 2022]. И, по-видимому, они же будут пополнять эти сведения в ближайшие время, поскольку включение высоких гармоник в модель вариации, используемой в глобальных методах, делает результаты менее надежными из-за большого числа определяемых параметров. Вторая гармоника неплохо выделяется во время больших ФЭ, когда она велика, что показано в (напр., [Kamoldinov et al., 1975; Krivoshapkin et al., 1981; Richardson et al., 2000]), но не в спокойные периоды. Локальный подход может быть основным (и, как минимум, важен) для изучения долгопериодных вариаций (связанных с солнечными циклами или сезонных) и для определения энергетической (жесткостной) зависимости характеристик анизотропии КЛ.
Перечисляя достоинства локальных методов (а они многочисленны), нельзя забывать и о его ограничениях и недостатках. Главный из которых в том, что он мало пригоден для изучения короткопериодных вариаций. Гармонический анализ данных отдельного детектора КЛ не подходит для надежного выделения анизотропии во время ФЭ. Назовем только две главные причины, препятствующие этому. Во-первых, характеристики анизотропии могут значительно и быстро изменяться в это время, а в больших ФЭ это неизбежно. Во-вторых, изменения изотропной части интенсивности КЛ во время ФЭ вносят существенный (часто определяющий) вклад в результаты гармонического анализа, и эти результаты теряют связь с реальной анизотропией. В целом можно сделать вывод (несколько упрощенный): в спокойные времена локальный подход хорош, а иногда и неизбежен, тогда как в возмущенные периоды нужны глобальные методы.
Целью данной работы является создание и описание методики выделения солнечно-суточной анизотропии потока КЛ в спокойные дни на примере данных нейтронного монитора ст. Москва за длительный период с 1965 по 2020 гг., а также сравнение полученных характеристик солнечно-суточной анизотропии с результатами обработки данных методом глобальной съемки.
Рис. 1.
Вариации скорости счета НМ ст. Москва в феврале–марте 2022 г. Адаптировано с (http://cr0.izmiran.ru/mosc/).
2. ДАННЫЕ
Выбор данных нейтронного монитора ст. Москва представляется естественным, поскольку авторы работают именно в ИЗМИРАН, им легче понять особенности данных этого детектора и полученных на их основе результатов. Но это не единственная причина выбора. НМ ст. Москва один из самых больших (5 секций) и наиболее долго работающих нейтронных мониторов. Первые данные НМ ст. Москва относятся к 1958 г., а с мая 1966 г. нейтронный монитор старого типа (МГГ) был заменен на современный монитор типа НМ64. Понятно, что длинный однородный ряд данных нужен для изучения долгопериодных вариаций. А размер детектора для данного исследования имеет особое значение, поскольку анизотропия КЛ в спокойные периоды мала и сравнима со статистической погрешностью среднечасовых данных нейтронных мониторов.
3. МЕТОДЫ
Основной метод, используемый в работе, – это гармонический анализ после скользящего сглаживания. Вначале сглаживается скорость счета за каждые 24 ч со сдвигом на час. Если NR(k) – сглаженная скорость счета для часа k, a N(k) – скорость счета в k-тый час, то вариацию для этого часа можно записать как:
(1)
$\delta _{k}^{{obs}} = \frac{{N\left( k \right) - {{N}_{R}}\left( k \right)}}{{{{N}_{R}}\left( k \right)}} \times 100\% .$И в ней должны содержаться все суточные гармоники. Если таких гармоник только две, то их можно представить в виде:
(2)
$\begin{gathered} {{\delta }_{k}} = {{c}_{0}} + {{c}_{1}}{\text{cos}}\left( {{{\varphi }_{k}}} \right) + {{c}_{2}}{\text{sin}}\left( {{{\varphi }_{k}}} \right) + \\ + \,\,{{c}_{3}}{\text{cos}}\left( {2{{\varphi }_{k}}} \right) + {{c}_{4}}{\text{sin}}\left( {2{{\varphi }_{k}}} \right), \\ \end{gathered} $Дисперсия между ожидаемой и наблюдаемой вариацией может быть рассчитана следующим образом:
(3)
$D = \sigma _{2}^{2} = \frac{1}{{19}}\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {{{{\left( {\delta _{k}^{{obs}} - {{\delta }_{k}}} \right)}}^{2}}} ,$4. РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ИХ ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
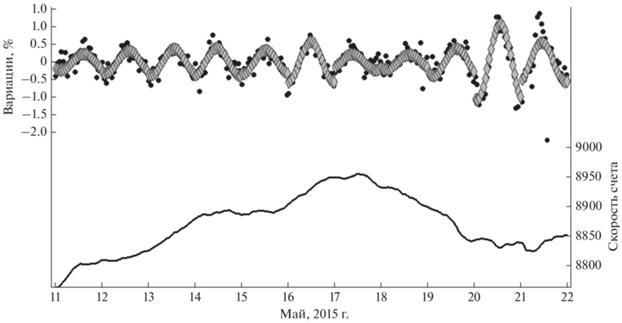
На рисунке 2 представлен пример типичного периода (11–22 мая 2015 г.) обрабатываемого ряда данных НМ ст. Москва. В нижней части рисунка показана сглаженная за скользящие 24 ч скорость счета НМ (правая ось). За каждый час в соответствующих сутках были посчитаны среднечасовые отклонения от сглаженной скорости счета $(\delta _{k}^{{obs}})$ согласно формуле (1), на рисунке эти значения отмечены черными точками в верхней части. Затем был проведен гармонический анализ, позволивший отобразить суточную вариацию в виде синусоиды (ромбы), и были рассчитаны соответствующие значения дисперсии $(\sigma _{2}^{2})$ по формуле (3).
Рис. 2.
Пример типичного периода. Сглаженная за скользящие 24 ч скорость счета НМ ст. Москва (нижняя кривая), результат гармонического анализа (ромбы) и среднечасовые отклонения от нее (вариации скорости счета – черные точки).
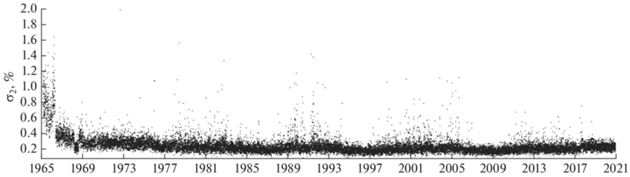
Рассмотрим остаточную дисперсию для спокойных периодов более подробно. Мы ограничились днями, для которых часовая вариация КЛ не отклонялась от сглаженного среднего больше чем на 3%. Распределение величины σ2 за все дни 1965–2020 гг. приведено на рис. 3.
Рис. 3.
Распределение величины σ2 за все дни 1965–2020 гг., в которые часовая вариация КЛ не отклонялась от сглаженного среднего больше чем на 3%.
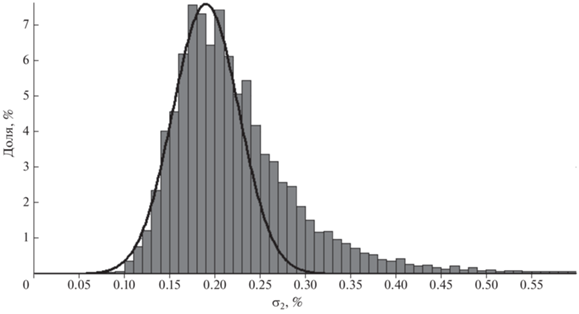
Можно видеть, что σ2 чаще всего была в диапазоне 0.16–0.22%. Это близко к ожидаемой стандартной статистической погрешности НМ ст. Москва, которая в зависимости от числа работающих счетчиков и интенсивности первичных КЛ, менялась для среднечасовых данных от 0.15 до 0.21%. Из-за этой неизбежной статистической погрешности практически невозможно идеальное совпадение наблюдений и используемой аппроксимации, и, действительно, мы не видели σ2 < 0.08%, а σ2 < 0.15% встречалась редко. Левая часть распределения не противоречит нормальному распределению. Его можно аппроксимировать функцией вида:
(4)
${{b}_{{{\text{max}}}}}{\text{exp}}\left( { - \frac{1}{2}{{{\left( {\frac{{{{\sigma }_{2}} - {{\sigma }_{{2m}}}}}{{{{\sigma }_{n}}}}} \right)}}^{2}}} \right),$Полученные результаты позволяют рассмотреть долгосрочные изменения качества данных. На рис. 4 показаны изменения величины σ2 за весь рассматриваемый период с 1965 по 2020 гг.
Наблюдаемые изменения остаточной дисперсии, в основном, объясняются двумя факторами: изменениями площади детектора и циклом солнечной активности. В периоды пониженной солнечной активности дисперсия низкая и практически нет ее выбросов вверх. В максимумах солнечной активности дисперсия, в среднем, выше, чем в минимумах, и часто наблюдаются аномально большие значения (по-видимому, во время больших ФЭ).
Самые большие долгопериодные изменения были в начальный период (1965–1966 гг.), когда НМ типа МГГ был заменен на 12НМ64. Это снизило остаточную дисперсию приблизительно на порядок. Как и предполагалось при выборе исследуемого периода, возможности НМ типа МГГ (за исключением высокогорных) для выделения анизотропии КЛ существенно ограничены. Надежные результаты для отдельных дней не получишь, нужно усреднять данные за много дней. В период работы НМ64 дисперсия продолжала снижаться при увеличении количества счетчиков (до 18, с января 1995 г). Наилучшее качество данных держалось в 2006–2017 гг., когда счетчиков было 24, с 2017 г. количество нормально работающих счетчиков было 21–23, и дисперсия несколько возросла. Аномально низкая дисперсия в 1968 г., согласно воспоминаниям старожилов института, обусловлена экспериментами с мертвым временем регистратора.
В целом, можно утверждать, что НМ ст. Москва вполне пригоден для выделения среднесуточных характеристик анизотропии, а модель с двумя первыми гармониками достаточна и адекватна.
5. НЕОБХОДИМЫЕ ОГРАНИЧЕНИЯ
Поскольку нас интересуют не просто вариации КЛ в течение дня, а вариации, обусловленные анизотропией КЛ, необходимо помнить про ограничения локальной методики. Среднесуточные характеристики анизотропии КЛ невозможно точно определить с помощью гармонического анализа, если они существенно изменяются в течение суток. При этом остаточная дисперсия увеличивается. Она возрастет так же и при проблемах с данными аппаратурного и методического происхождения. Таким образом, величина σ2 – это один из основных критериев надежности полученных результатов. В данном исследовании для получения численных результатов мы использовали только дни с σ2 < 0.25%, а это 69.1% всех дней. Кроме этого не использовались дни с пропусками данных, но таких дней было мало.
Еще одним важным критерием для отбора подходящих дней был критерий нелинейности в поведении изотропной части вариации. Любая такая нелинейность искажает результаты гармонического анализа, создавая ложные гармоники анизотропии. Для того чтобы оценить размер этой опасности, мы аппроксимировали сглаженные средние данные отдельно за каждые сутки простой линейной функцией:
где tk – час от начала суток. Относительные отклонения от этой функции, рассчитанные как: дают еще одну остаточную дисперсию:(7)
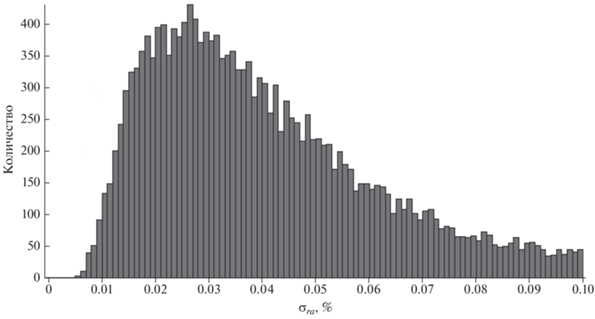
$\sigma _{{ra}}^{2} = \frac{1}{{22}}\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {\delta _{r}^{2}\left( {{{t}_{k}}} \right)} .$Величину σra можно считать индексом нелинейности. Она определяется из анализа сглаженных данных и поэтому σra < σ2, что видно из распределения, приведенного на рис. 5.
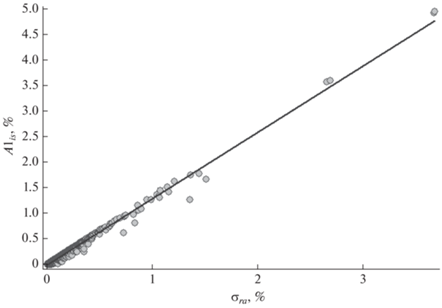
Здесь, как и в распределении σ2, левая часть могла бы принадлежать узкому нормальному распределению, которое создается в спокойное время флуктуациями КЛ без реальной нелинейности, но правая часть свидетельствует, что значительная нелинейность в поведении изотропной части КЛ – скорее правило, чем исключение. Величина σra тесно связана с амплитудой ложных гармоник (рис. 6). Можно видеть, что в отдельные возмущенные дни ложная солнечно-суточная вариация не только сопоставима с реальной анизотропией, но и может ее существенно превышать. Иногда (во время больших ФЭ) A1is > 1%.
Похожая связь существует между σra и амплитудой ложной второй гармоники анизотропии – A2is. Вторая ложная гармоника также может в возмущенные периоды в разы превышать обычные амплитуды второй гармоники, создаваемой анизотропией КЛ.
Для получения результатов, требующих уверенности, что мы имеем дело с эффектами анизотропии КЛ, были использованы дни с σra < 0.06% (71.9% от всех дней). Совместное использование всех критериев (полнота данных, σ2 < 0.25% и σra < 0.06%) оставило нам 57.8% из начального ряда данных.
В предыдущем примере (рис. 2) были отбракованы 3 дня из 11 (11, 20 и 21 мая). 11 мая из-за критерия σra < 0.06%, а 20–21 мая из-за критерия σ2 < < 0.25%. В эти дни наблюдались небольшие межпланетные возмущения и Форбуш-эффекты малой величины. Больших ФЭ в этот период не было, но небольшие ФЭ зарегистрированы не только в отбракованные дни, но и 12, 16–19 мая. Однако в эти дни плотность КЛ менялась достаточно регулярно и линейно по времени, а анизотропия КЛ была достаточно стабильна в течение суток, и эти дни вписались в утвержденные критерии.
Полученные результаты (обсуждаемые также далее) говорят в пользу того, что наша выборка дней и использованные критерии достаточно хороши для выделения анизотропии КЛ локальным методом. Однако нужно заметить, что хотя в этой выборке нет дней с большими значениями A1is и A2is, но приблизительно в половине дней A1is была в диапазоне 0.03–0.08%. В этой статье мы обсуждаем численные результаты, полученные при усреднении за длительный период, и ложные суточные волны на них практически не влияют. Но в будущем при более детальном анализе, вероятно, придется применять более жесткие критерии, особенно для индекса нелинейности σra.
6. СРАВНЕНИЕ АМПЛИТУД СОЛНЕЧНО-СУТОЧНОЙ АНИЗОТРОПИИ, ПОЛУЧЕННЫХ ЛОКАЛЬНЫМ И ГЛОБАЛЬНЫМ МЕТОДОМ
На рисунке 7 приведены среднесуточные амплитуды солнечно-суточной анизотропии (точки), полученные в шести последних солнечных циклах двумя способами: глобальным (Axyg, верхняя панель) и локальным (Axy, нижняя панель) методом. Кривыми соответственно показаны 27-дневные скользящие средние значения амплитуд анизотропии. Значения Axy и Axyg получались из составляющих вектора анизотропии Ax и Ay, определенных локальным методом, и $A_{x}^{k}$ и $A_{y}^{k},$ определяемых из GSM за каждый час k:
(9)
$Axyg = \sqrt {{{{\left( {\frac{1}{{24}}\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {A_{x}^{k}} } \right)}}^{2}} + {{{\left( {\frac{1}{{24}}\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {A_{y}^{k}} } \right)}}^{2}}} .$Рис. 7.
Среднесуточные амплитуды первой гармоники анизотропии КЛ (точки), полученные по данным НМ ст. Москва (нижняя панель) и с помощью GSM (верхняя панель) за 1965–2020 гг. Кривыми показаны соответствующие 27-дневные скользящие средние значения амплитуд анизотропии.
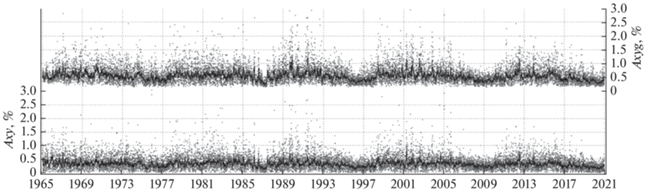
Хорошо видно, что поведение амплитуд анизотропии связано с солнечной активностью: в периоды повышенной активности они увеличиваются, а в отдельные дни это повышение значительно, иногда на порядок. Проверка таких дней показывает, что они связаны с большими ФЭ. В годы минимума солнечной активности средние амплитуды заметно снижаются, а выбросы вверх практически исчезают. Все эти особенности хорошо видны и в ряду Axyg, и в ряду Axy, а значит можно говорить о согласии в главных чертах долговременного поведения солнечно-суточной анизотропии, полученного разными способами.
Амплитуды Axyg и Axy достаточно хорошо коррелируют между собой (рис. 8): регрессионный коэффициент, определяющий наклон прямой равен 0.652 ± 0.004, а коэффициент корреляции сс = = 0.78. В среднем Axy приблизительно в 1.5 раза меньше Axyg.
Рис. 8.
Связь амплитуд солнечно-суточной анизотропии КЛ, полученных глобальным и локальным методами.
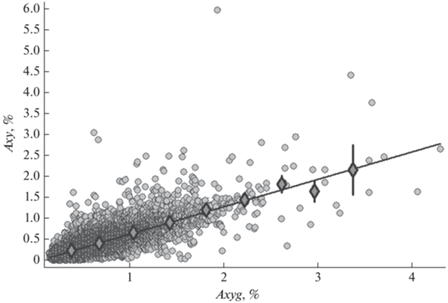
Дело в том, что GSM дает информацию об истинной амплитуде векторной анизотропии КЛ с жесткостью 10 ГВ, а солнечно-суточная анизотропия, определяемая по данным наземного детектора, собирающего частицы КЛ из широкого приемного сектора, имеет меньшую амплитуду. Можно считать, что
где С11 – это приемный коэффициент наземного детектора для солнечно-суточной анизотропии.В обычно используемом нашей группой варианте метода глобальной съемки [Белов и др., 2018] для НМ ст. Москва используется величина С11 = = 0.661, рассчитанная для плоского спектра анизотропии в диапазоне 0–100 ГВ [Yasue et al., 1982]. В целом, получается хорошее согласие отношения величин амплитуд Axy и Axyg с С11.
7. СРАВНЕНИЕ ФАЗ ВЕКТОРНОЙ СОЛНЕЧНО-СУТОЧНОЙ АНИЗОТРОПИИ, ПОЛУЧЕННЫХ ЛОКАЛЬНЫМ И ГЛОБАЛЬНЫМ МЕТОДОМ
Среднесуточные фазы солнечно-суточной анизотропии, полученной локальным (Pxy) и глобальным (Pxyg) методом, рассчитывались следующим образом:
(12)
$Pxyg = {\text{arctg}}\frac{{\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {A_{y}^{k}} }}{{\sum\limits_{k{\kern 1pt} = {\kern 1pt} 1}^{24} {A_{x}^{k}} }}.$В дальнейшем изложении фазы будут отсчитываться от направления на антисолнце, против часовой стрелки. Таким образом, типичным направлением фазы анизотропии является 90°.
Долговременные изменения фаз первой гармоники анизотропии КЛ (точки), полученные по данным НМ ст. Москва (нижняя панель) и с помощью GSM (верхняя панель), приведены на рис. 9. Соответствующими кривыми показаны 27-дневные скользящие средние значения фаз анизотропии. Как известно [Forbush and Beach, 1975; Mori et al., 1981; Крымский и др., 2007], изменения фаз солнечно-суточной анизотропии связаны с полярностью общего магнитного поля Солнца и подчиняются солнечному магнитному циклу. Это свойство хорошо видно на рисунке. Влияние полярности наиболее заметно в минимумах солнечной активности, наибольшие долговременные отличия фаз от средних величин наблюдаются в последнем минимуме (2019–2020 гг.) и в минимумах при той же полярности 70-х и 90-х гг. Именно в эти периоды видно наиболее аномальное поведение усредненных фаз анизотропии в кривых на рис. 9.
Рис. 9.
Фазы первой гармоники анизотропии КЛ (точки), полученные по данным НМ ст. Москва (нижняя панель) и с помощью GSM (верхняя панель) за каждый день в 1965–2020 гг. Кривыми показаны соответствующие 27-дневные скользящие средние значения фаз анизотропии.
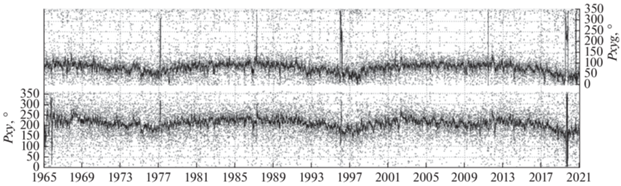
Большие изменения и нетипичные значения фаз в отдельные дни объясняются не только изменчивостью анизотропии КЛ в возмущенные периоды, но и большой погрешностью в определении фаз при малых амплитудах анизотропии. По этой причине большой разброс фаз мы видим не только в периоды высокой активности, но и в спокойные годы, когда амплитуды, в основном, малы.
При явном согласии в долговременном поведении фаз, полученных двумя различными способами, между этими фазами присутствует почти постоянная разница около 130°–140°. Так и должно быть, поскольку GSM дает оценку истинного направления анизотропии (а не направления на источник, которое отличается от направления анизотропии на 180°), и кроме того магнитосфера меняет направление прихода первичных частиц КЛ сложным образом в зависимости от точки наблюдения, энергии и направления частиц. По этой причине существует некоторый сдвиг:
где P11 – эффективный магнитосферный снос направления для солнечно-суточной анизотропии для данного наземного детектора. Для НМ ст. Москва в используемой версии GSM P11 = = 51.59° [Yasue et al., 1982]. Если сдвинуть фазы солнечно-суточной анизотропии, полученные по данным НМ ст. Москва, на эту величину, то распределения фаз Pxy и Pxyg становятся похожими (рис. 10). Распределение фаз, полученное с помощью GSM несколько уже, чем по данным НМ ст. Москва, что говорит о лучшей точности глобальной методики.Рис. 10.
Распределение среднесуточных фаз солнечно-суточной анизотропии, полученные по данным НМ ст. Москва (черные столбцы) и с помощью GSM (серые столбцы).
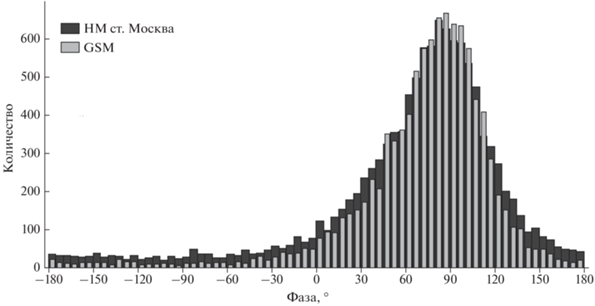
Отметим, что сравнение солнечно-суточной анизотропии, определяемой глобальным и локальным методами, позволяет оценивать приемные коэффициенты (C11 и P11) для первой гармоники из экспериментальных данных. Подробнее эту возможность обсудим в следующих разделах.
8. СРЕДНИЙ СУТОЧНЫЙ ХОД ВАРИАЦИЙ КЛ
Для того чтобы получить средний суточный ход вариаций КЛ на НМ ст. Москва были использованы вариации δk, рассчитанные по формуле (2). Они усреднялись отдельно для каждого часа суток для 11 784 дней с σ2 ≤ 0.25% и σra ≤ 0.06%. При этом ранние годы (1965–1967 гг.) были исключены, поскольку после использования критериев отбора в них оставалось мало подходящих дней. Результаты усреднения показаны на рис. 11.
Рис. 11.
Суточный ход вариаций скорости счета НМ ст. Москва, усредненный в спокойные дни (σ2 ≤ 0.25% и σra ≤ 0.06%) за период 1968–2020 гг. По нижней оси приведено локальное время.
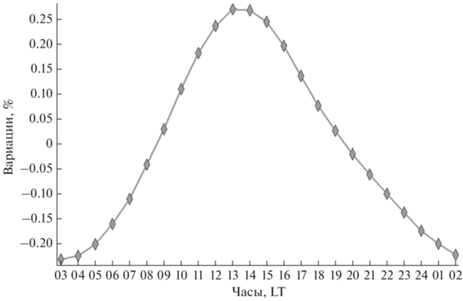
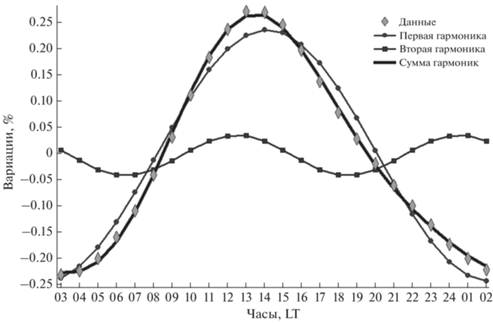
Сразу видно, что средний суточный ход соответствует гладкой регулярной функции, и эта функция близка к синусоиде. Действительно, полученный суточный ход почти идеально описывается моделью, приведенной на рис. 12, с коэффициентом корреляции сс = 0.9995 и остаточной дисперсией величиной 0.006%.
Рис. 12.
Средняя суточная вариация потока КЛ на НМ ст. Москва (ромбы) и соответствующие ей первая (кружки) и вторая (квадраты) гармоники, а также их сумма (толстая кривая). По нижней оси приведено локальное время.
Это означает, что в среднем многолетнем суточном ходе вариаций КЛ на НМ ст. Москва отсутствует влияние каких-то других факторов кроме ожидаемых двух первых гармоник анизотропии. Конечно, не надо думать, что на суточную вариацию другие факторы вообще не влияют. В отдельные дни такое влияние может быть (и действительно было) значительным, но при многолетнем усреднении и рассмотрении спокойных периодов оно практически исчезает.
Амплитуда первой гармоники, соответствующей многолетней суточной вариации и показанной на рис. 12, Axy = 0.239 ± 0.002%, а ее направление (фаза) составляет 31.9° ± 0.4°. Приведем аналогичные величины и для второй гармоники: Axy2 = 0.0386 ± 0.0017%, а ее ось (максимумы) направлены на 15.3° ± 2.5° и 195.3° ± 2.5°. В данной работе мы больше не будем говорить о второй гармонике, поскольку здесь мы сравниваем глобальный и локальный подходы, а в тот вариант глобального метода, который нами используется, вторая гармоника не включена. Однако в дальнейшем будет интересно изучить свойства полученной второй гармоники и ее изменения во времени.
Для первой гармоники у нас имеются полные данные для сравнения. Мы рассчитали средний вектор анизотропии (Axyg), используя те же самые дни, участвовавшие в определение средней суточной вариации на НМ ст. Москва. Оказалось, что в спокойные дни средняя амплитуда Axyg = = 0.362 ± 0.003%, а фаза Pxyg = 80.1° ± 0.3°.
Отношение средних амплитуд Axy/Axyg дает С11 = 0.661 ± 0.009%, что в точности совпадает с приемным коэффициентом, используемом в нашем варианте GSM. Сравнение средних фаз дает оценку P11 = Pxyg – Pxy = 48.1° ± 0.3°, что всего на 3.5° отличается от рассчитанной величины P11 [Yasue et al., 1982]. Таким образом, сравнение результатов, полученных двумя методами в спокойные дни позволяет получить значительно более точные оценки приемных коэффициентов, чем оценки, полученные для всех дней, включая возмущенные. Это еще одно напоминание о том, что в возмущенные дни в суточную вариацию вмешиваются факторы, не связанные с анизотропией КЛ.
На основе полученных результатов можно утверждать, что сопоставление характеристик анизотропии КЛ, определенных независимо глобальным и локальным методом, дает возможность оценивать приемные коэффициенты наземных детекторов по экспериментальным данным.
9. НАПРАВЛЕНИЯ ДАЛЬНЕЙШИХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ
Одним из перспективных направлений однозначно является исследование долгопериодных (многолетних) вариаций амплитуды и фазы солнечно-суточной анизотропии, которые зависят от цикла солнечной активности и магнитного солнечного цикла. Как было показано выше, эти изменения одинаково хорошо описываются и глобальным, и локальным методами, а доступные ряды данных отдельных детекторов включают периоды, когда мировая сети НМ, используемая в GSM, еще не существовала.
Локальный метод, использующий для анализа данные только спокойных дней, позволяет сравнить спокойные периоды при разных уровнях солнечной активности (например, в максимуме и минимуме циклов, когда полярность магнитного поля Солнца еще изменяется или уже устойчива) и при разных полярностях солнечного магнитного поля, когда отличаются радиальные градиенты потока КЛ. Обнаружение изменения фазы анизотропии КЛ позволит уточнить данные о начале и окончании влияния переполюсовки магнитного поля Солнца на КЛ.
Исследование сезонных вариаций анизотропии также возможно с использованием локального метода, в т.ч. можно провести оценку влияния температурного эффекта, который значительно отличается в летний и зимний периоды.
Кроме того, существуют довольно длительные (>нескольких солнечных оборотов) аномалии в величине и направлении анизотропии, которые не были ранее основательно исследованы: например, хорошо выражены периоды пониженной анизотропии в минимумах солнечной активности; существует аномалия 1974 г., когда внезапно поменялась фаза анизотропии из-за обратной смены полярности солнечного магнитного поля и др.
Нами также было показано, что локальный метод применим и для оценки качества работы детектора на основании анализа распределения дисперсии между ожидаемой и наблюдаемой вариацией КЛ.
Очень интересной и полезной также представляется возможность экспериментального определения приемных коэффициентов при сопоставлении данных конкретного детектора с результатами GSM, поскольку теоретические расчеты приемных коэффициентов довольно сложны, не вполне однозначны и произведены не для всех наземных детекторов КЛ.
Оценка надежности разделения изотропных и анизотропных вариаций также является важной задачей, поскольку часто изотропные вариации влияют на анизотропию (например, во время ФЭ), и, в частности из-за этого, использование локального метода и гармонического анализа подходит только для спокойных периодов.
Определение жесткостного спектра анизотропии на основании данных одного НМ невозможно, но привлечение к сравнению обработанных аналогичным образом данных других станций (значительно отличающихся жесткостью геомагнитного обрезания) или данных мюонных детекторов позволит оценить жесткостной спектр.
Что касается короткопериодных вариаций, данный метод также вполне применим для исследования 27-дневных циклов изменения амплитуды и фазы анизотропии, поскольку в спокойные периоды в минимуме солнечной активности хорошо прослеживается, например, воздействие высокоскоростных потоков из долгоживущих корональных дыр. Кроме того, существуют периоды аномально высоких или низких значений анизотропии, наблюдающиеся на протяжении нескольких дней, причины и свойства которых также могут быть исследованы и объяснены на основании наших данных.
Отдельной темой могут стать вариации второй гармоники анизотропии КЛ, поскольку локальный метод определяет ее в спокойные периоды вполне надежно. Интересно также изучить взаимосвязь вариаций плотности КЛ с изменениями 1-ой и 2-ой гармоник анизотропии.
10. ОСНОВНЫЕ ВЫВОДЫ
1. Получены характеристики солнечно-суточной вариации, наблюдавшейся на нейтронном мониторе ст. Москва в спокойные дни за период 1965–2020 гг.
2. Сравнение этих результатов со среднесуточными характеристиками экваториальной составляющей векторной анизотропии, полученными с помощью GSM, показало хорошее согласие.
3. Средний суточный ход вариаций КЛ на НМ ст. Москва практически полностью описывается двумя гармониками солнечно-суточной анизотропии и не содержит признаков других влияний.
4. Показано, что при правильном применении глобальная и локальная методики выделения векторной анизотропии надежны и дополняют друг друга.
5. Из сравнения локальных и глобальных результатов получены оценки приемных коэффициентов первой гармоники анизотропии для НМ ст. Москва. Предложен новый экспериментальный метод расчета приемных коэффициентов отдельных детекторов.
6. Обсуждены и обоснованы ограничения локальной методики. Во время Форбуш-эффектов она не дает надежных результатов.
7. Подробно обсуждены возможности продолжения и расширения данного исследования.
Список литературы
− Абунина М.А., Абунин А.А., Белов А.В., Ерошенко Е.А., Асипенка А.С., Оленева В.А., Янке В.Г. Связь параметров Форбуш-эффектов с гелиодолготой солнечных источников // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 53. № 1. С. 13–22. 2013а.
− Абунина М.А., Абунин А.А., Белов А.В., Ерошенко Е.А., Оленева В.А., Янке В.Г. Долгопериодные изменения амплитудно-фазовой взаимозависимости первой гармоники анизотропии космических лучей // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 53. № 5. С. 601–610. 2013б.
− Абунина М.А., Белов А.В., Ерошенко Е.А., Абунин А.А., Оленева В.А., Янке В.Г., Мелкумян А.А. Метод кольца станций в исследовании вариаций космических лучей: 1. Общее описание // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 60. № 1 С. 41–48. 2020а. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0016794020010022
− Абунина М.А., Белов А.В., Ерошенко Е.А., Абунин А.А., Оленева В.А., Янке В.Г., Мелкумян А.А. Метод кольца станций в исследовании вариаций космических лучей: 2. Примеры использования // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 60. № 2 С. 187–194. 2020б. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0016794020020029
− Белов А.В., Ерошенко Е.А., Янке В.Г., Оленева В.А., Абунина М.А., Абунин А.А. Метод глобальной съемки для мировой сети нейтронных мониторов // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 58. № 3. С. 374–389. 2018. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0016794018030082
− Дворников В.М., Сдобнов В.Е., Сергеев А.В. Метод спектрографической глобальной съемки для изучения вариаций интенсивности космических лучей межпланетного и магнитосферного происхождения / Сб. “Вариации космических лучей и исследования космоса”, ИЗМИРАН. С. 232–237. 1986.
− Кравцов Н.Г. Третья гармоника интенсивности космических лучей. Вариации космических лучей и солнечный ветер. Под. ред. Н.П. Чиркова. Якутск: ЯФ СО АН СССР. С. 55–61. 1980.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Алтухов A.M., Кузьмин А.И., Скрипин Г.В. Новый метод исследования анизотропии космических лучей. Исследование по геомагнетизму и аэрономии. М.: Наука. 1966a. 105 с.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Кузьмин A.И., Чирков H.П. Распределение космических лучей и приемные векторы детекторов. I. // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 6. № 8. С. 991–996. 1966б.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Кузьмин А.И., Чирков Н.П. и др. Распределение космических лучей и приемные векторы детекторов. II. // Геомагнетизм и аэрономия. Т. 7. № 1. С. 11–15. 1967.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Скрипин Г.В., Григорьев В.Г. О третьей гармонике в суточной вариации космических лучей / В кн.: Распределение галактических космических лучей и динамика структурных образований в солнечном ветре. Якутск: ЯФ СО АН СССР. С. 118–125. 1973.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Кривошапкин П.А., Мамрукова В.П., Григорьев В.Г., Герасимова С.К. 11- и 22-летние вариации анизотропии галактических космических лучей // Изв. РАН. Сер. Физ. Т. 71. № 7. С. 1003–1005. 2007.
− Крымский Г.Ф., Кузьмин А.И., Кривошапкин П.А., Самсонов И.С., Скрипин Г.В., Транский И.А., Чирков Н.П. Космические лучи и солнечный ветер. Новосибирск: Наука. 1981. 224 с.
− Шафер Г.В. Прецизионные наблюдения космических лучей в Якутске. Наука, СО, Новосибирск. 1984. 732 с.
− Abunina M.A., Belov A.V., Eroshenko E.A., Abunin A.A., Yanke V.G., Melkumyan A.A., Shlyk N.S., Pryamushkina I.I. Ring of Stations Method in Cosmic Rays Variations Research // Solar Phys. V. 295. N. 1. Article number 69. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01639-7
− Altuchov A.M., Krimsky G.F., Kuzmin A.I. The method of “Global survey” for investigation cosmic ray modulation / Proc. 11th ICRC, Budapest. V. 4. P. 457–460. 1969.
− Bazilevskaya G.A., Svirzhevskaya A.K. On the stratospheric measurements of cosmic rays // Space Sci. Rev. V. 85. P. 431–521. 1998.
− Beer J., McCracken K., von Steiger R. Cosmogenic Radionuclides. Theory and Applications in the Terrestrial and Space Envirinments. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 2012. 425 p. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14651-0
− Belov A.V., Blokh Ya.A., Dorman L.I., Eroshenko E.A., Inozemtseva O.I., Kaminer N.S. Studies of isotropic and anisotropic cosmic ray variations in the Earth’s vicinities during disturbed periods / Proc. 13th ICRC, Denver. V. 2. P. 1247–1255. 1973.
− Belov A.V., Blokh Ya.L., Dorman L.I., Eroshenko E.A., Inozemtseva O.I., Kaminer N.S. Anisotropy and time-dependent changes in the spectrum of cosmic-ray intensity variations during August, 1972 // AN USSR, Izv., Ser. Fiz. V. 38. P. 1867–1875. 1974.
− Belov A., Eroshenko E., Yanke V., Oleneva V., Abunin A., Abunina M., Papaioannou A., Mavromichalaki H. The Global Survey Method applied to ground-level cosmic ray measurements // Solar Phys. V. 293. № 4. article id. 68. 23 pp. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1277-6
− Bieber J.W., Chen J. Cosmic-ray diurnal anisotropy, 1936–1988: Implications for drift and modulation theories // Astrophys. J. V. 372. P. 301–313. 1991.
− Briggs R.M., Hicks R.B., Standi S. Sidereal-time variations in the cosmic ray intensity // Nuovo Cimento. V. 66. № 1. P. 97–104. 1970.
− Dubey S.K., Kumar S., Agrawal R. Results of diurnal anisotropy in CR intensity on different geomagnetic conditions / Proc. 27th ICRC, Hamburg, Germany. P. 3963–3965. 2001.
− Duggal S., Forbush S., Pomerantz M. Variations of the diurnal anisotropy with periods of one and two solar cycles / Proc. 11th ICRC, Budapest. V. 29. P. 55–59. 1970.
− Duperier A. Solar and sidereal diurnal variations of cosmic rays // Nature. V. 158. P. 196. 1946.
− Dvornikov V.M., Sdobnov V.E. Analyzing the solar proton event of 22 October 1989, using the method of Spectrographic Global Survey // Sol. Phys. V. 178. P. 405–422. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005069806374
− Dvornikov V.M., Sdobnov V.E., Sergeev A.V. Analysis of cosmic ray pitch-angle anisotropy during the Forbush-effect in June 1972 by the method of spectrographic global survey / Proc. 19th ICRC, La Jolla. V. 3. P. 249–252. 1983.
− Elliot H. The variations of cosmic ray intensity // Progress in Cosmic Ray Phys. V. 1. P. 453–514. 1952.
− Fenton A.G., Humble J.E., Thambyahpillai T. Long-term changes in the solar diurnal variation / Proc. 18th ICRC, Bangalore, India. V. 10. P. 186–189. 1983.
− Firor J.W., Fonger W.H., Simpson J.A. Cosmic radiation intensity-time variations and their origin. V. The daily variation of intensity // Phys. Rev. V. 94. I. 4. P. 1031–1036. 1954.
− Forbush S.E. On the effects in the cosmic-ray intensity observed during the recent magnetic storm // Phys. Rev. V. 51. P. 1108–1109. 1937.
− Forbush S.E. On cosmic ray effects associated with magnetic storm // Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity. V. 43. № 3. P. 203–218. 1938.
− Forbush S.E. Variation with a period of two solar cycles in the cosmic-ray diurnal anisotropy and the superposed variations correlated with magnetic activity // J. Geophys. Res. V. 74. I. 14. P. 3451–3468. 1969.
− Forbush S.E. Cosmic ray diurnal anisotropy 1937–1972 // J. Geophys. Res. V. 78. № 34. P. 7933–7941. 1973.
− Forbush S., Beach L. Cosmic-ray diurnal anisotropy and the Sun’s polar magnetic field / Proc. 14th ICRC, Munich. V. 4. P. 1204–1208. 1975.
− Jacklyn R., Vrana A. Recent evidence concerning the sidereal anisotropy in the charged primary cosmic radiation / Proc. Astron. Soc. Australia. V. 1. P. 278. 1969.
− Kaminer N.S., Kuzmicheva A.E., Mymrina N.V. The Cosmic-ray anisotropy associated with high-velocity solar wind flux / Proc. 17th ICRC, Paris, France. V. 4. P. 146–149. 1981.
− Kamoldinov S.M., Mamrukova V.P., Altukhov A.M., Krivoshapkin P.A., Krymsky G.F. The Influence of Magnetic “Corks” upon the Galactic Cosmic Ray Distribution / Proc. 14th ICRC, München, Germany. V. 3. P. 1102. 1975.
− Kane R.P. Sidereal component of the diurnal variation of cosmic ray intensity // Nuovo Cimento. V. 41. № 1. P. 90–114. 1966.
− Kaushik S.C., Shrivastava P.K., Rastogi V.K. Comparative study of first three harmonics of cosmic ray intensity during recent solar cycle / Proc. 27th ICRC, Hamburg, Germany. P. 3809. 2001.
− Kota J. On the second spherical harmonics of the cosmic ray angular distribution // J. Phys. A: Mathematical and General. V. 8. I. 8. P. 1349–1360. 1975. https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/8/8/019
− Krivoshapkin P.A., Krymskii G.F., Mamrukova V.P., Skripin G.V., Shafer G.V. The second harmonic of cosmic-ray anisotropy and energy spectrum of the Forbush-decreases / Proc. 17th ICRC, Paris, France. V. 4. P. 164. 1981.
− Kumar S., Gulati U., Khare D.K., Richharia M.K. Comparative study of diurnal anisotropy in CR intensity on quiet days and all days // Bull. Astr. Soc. India. V. 21. P. 395–397. 1993.
− Mathews T., Venkatesan D., Wiison B. G. Pronounced diurnal variation in cosmic-ray intensity // J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. V. 74. № 5. P.1218–1229. 1969.
− Mishra R.A., Mishra R.K. Influence of solar heliospheric parameters on cosmic rays anisotropy // Astrophysics. V. 49. № 4. P. 555–566. 2006.
− Mishra R.K., Mishra R.A. Interplanetary transients and cosmic-ray anisotropy // Solar Phys. V. 240. P. 359–372. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-006-0242-y
− Moraal H. Observations of the eleven-year cosmic-ray modulation cycle // Space Sci. Rev. V. 19. I. 6. P. 845–920. 1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173707
− Mori S., Yasue S., Ichinose M., Munakata Y. Cosmic ray daily variation at solar activity minimum / Proc 15th ICRC, Budapesht. V. 4. P. 65–69. 1977.
− Mori S., Swinson D.B., Fujimoto K., Nagashima Y. 22-year variation in the solar diurnal anisotropy of cosmic rays / Proc 17th ICRC, Paris, France. V. 10. P. 218–221. 1981.
− Munakata K., Kozai M., Kato C., Kota J. Long-term variation of the solar diurnal anisotropy of galactic cosmic rays observed with the Nagoya multi-directional muon detector // Astrophys. J. V. 791. id 22. 16 p. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/791/1/22
− Munakata K., Kozai M., Kato C. et al. Large amplitude bidirectional anisotropy of cosmic-ray intensity observed with world-wide networks of ground-based neutron monitors and muon detectors in November, 2021 // Astrophys. J. V. 938. id 30. 11 p. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/ac91c5
− Munakata K., Kozai M., Ishizaki A., Nakajima T., Kato C., Yasue S., Kota J. Long term variation of the solar diurnal anisotropy of galactic cosmic rays over four solar activity cycles / Proc. 33rd ICRC, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. P. 1370. 2013.
− Munakata K., Nagashima K. The First three harmonics of solar daily variation caused by the diffusive propagation of galactic cosmic rays through the heliosphere / Proc. 19th ICRC, La Jolla, USA. V. 5. P. 98. 1985.
− Nagashima K., Ueno H., Mori S., Sagisaka S. A two-way sidereal anisotropy // Can. J. Phys. V. 46. P. S611–S613. 1968.
− Nagashima K. Three-dimensional cosmic ray anisotropy in interplanetary space // Rep. Ionosphere Space Res. V. 25. P. 189–211. 1971.
− Oh S.Y., Yi Y.,·Bieber J.W. Modulation cycles of galactic cosmic ray diurnal anisotropy variation // Solar Phys. V. 262. P. 199–212. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-009-9504-9
− Okike O. Amplitude of the usual cosmic ray diurnal and enhanced anisotropies: Implications for the observed magnitude, timing, and ranking of Forbush Decreases // Astrophys. J. V. 915. I. 1. id.60. 23 p. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/abfe60
− Patel D., Sarabhai V., Subramanian G. Anisotropies of galactic cosmic rays in the solar system // Planet. Space Sci. V. 16. P. 1131–1146. 1968.
− Pomerantz M.A., Duggal S.P. The cosmic ray solar diurnal anisotropy // Space Sci. Rev. V. 12. I. 1. P. 75–130. 1971.
− Pomerantz M.A., Duggal S.P. North-south anisotropies in the cosmic radiation // J. Geophys. Res. V. 77. P. 263–265. 1972.
− Richardson I.G., Dvornikov V.M., Sdobnov V.E., Cane H.V. Bidirectional particle flows at cosmic ray and lower (~1 MeV) energies and their association with interplanetary coronal mass ejections/ejecta // J. Geophys. Res. V. 105. P. 12 579–12 592. 2000.
− Sabbah I. Solar magnetic polarity dependency of the cosmic ray diurnal variation // J. Geophys. Res.: Space Physics. V. 118. P. 4739–4747. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgra.50431
− Samsonov I., Grigoryev V., Samsonova Z., Chirkov N. Anomalous behavior of the solar wind speed and galactic cosmic ray anisotropy with solar activity cycle / Proc. 16th ICRC, Kyoto. V. 3. P. 508–513. 1979.
− Sarabhai V., Nerurkar N. Time variations of primary cosmic rays // Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Sciences. V. 6. P. 1–42. 1956.
− Sari J.W., Venkatesan D., Lanzerotti L.J., Maclennan C.G. Diurnal variation of cosmic ray intensity 1. Two approaches to the study // J. Geophys. Res. V. 83. № A11. P. 5139–5150. 1978.
− Sekido Y., Nagashima K., Kondo I., Murayama T., Okuda H., Sakakibara S. Sidereal time variation of high-energy cosmic rays observed by an air Cerenkov telescope // Can. J. Phys. V. 46. P. S607–S610. 1968.
− Singh M., Badruddin. Study of the cosmic ray diurnal anisotropy during different solar and magnetic conditions // Solar Phys. V. 233. P. 291–317. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-006-2050-9
− Somogyi A.J. Some problems of detecting galactic anisotropies // Ann. IQSY. V. 4. P. 269–273. 1969.
− Stozhkov Yu.I., Svirzhevsky N.S., Bazilevskaya G.A., Kvashnin A.N., Makhmutov V.S., Svirzhevskaya A.K. Long-term (50 years) measurements of cosmic ray fluxes in the atmosphere // Adv. Space Res. V. 44. P. 1124–1137. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2008.10.038
− Swinson D.B. Sidereal cosmic-ray diurnal variations // J. Geophys. Res. V. 74. № 24. P. 5591–5598. 1969.
− Swinson D.B. Diurnal variations underground since 1959 / Proc. 24th ICRC, Rome. V. 3. P. 627–630. 1995.
− Thompson J.L. A critical analysis for sidereal time variations of cosmic rays on the pacific // Phys. Rev. V. 55. P. 11–15. 1939.
− Tiwari A.K., Singh A., Agrawal S.P. Study of the diurnal variation of cosmic rays during different phases of solar activity // Solar Phys. V. 279. P. 253–267. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-9962-3
− Yasue S., Mori S., Sakakibara S., Nagashima K. Coupling coefficients of cosmic ray daily variations for neutron monitor stations. Nagoya: Cosmic ray research laboratory. 1982. CRRL Rep. no. 7.
− Yoshida S. Anisotropy of cosmic rays during the cosmic-ray storms // Il Nuovo Cimento. V. 4. № 6. P. 1410–1432. 1956.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Геомагнетизм и аэрономия