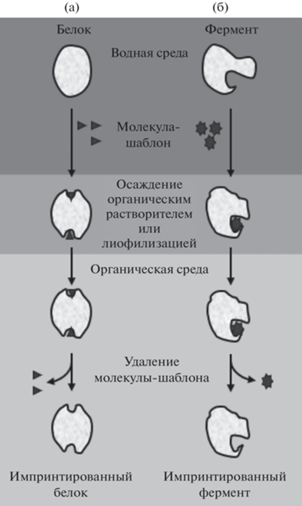
Журнал аналитической химии, 2023, T. 78, № 8, стр. 675-689
Белковые молекулы: шаблоны и матрицы в молекулярном импринтинге
П. С. Пиденко a, К. Ю. Пресняков a, Н. А. Бурмистрова a, *
a Саратовский государственный университет им. Н.Г. Чернышевского, Институт химии
410012 Саратов, ул. Астраханская, 83, Россия
* E-mail: naburmistrova@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 07.12.2022
После доработки 04.02.2023
Принята к публикации 09.02.2023
- EDN: VSBGTH
- DOI: 10.31857/S0044450223070125
Аннотация
В обзоре рассмотрены вопросы молекулярного импринтинга с участием белковых молекул. Проведен анализ работ, опубликованных за последние пять лет в области биоимпринтинга и посвященных определению биомолекул, а также усилению ферментативной активности. Основное внимание уделено импринтингу белковых молекул как методу модификации структуры белковой молекулы за счет образования сайтов связывания в присутствии субстратов (белковыми молекулами с молекулярным отпечатками или импринтированными белками). Показана перспективность импринтинга белковых молекул при решении аналитических задач. Обсуждена неоднозначная трактовка термина “биоимпринтинг” при решении различных задач.
Создание эффективных биомиметических систем молекулярного распознавания является важной и актуальной задачей современной химии. В настоящее время значительное число аналитических исследований, в том числе при доклинической [1], клинической [2] и ветеринарной диагностике [3], проводят с использованием различных форматов иммуноанализа, основанного на применении антител в качестве специфических рецепторных элементов. Несмотря на неоспоримые преимущества антител, существующие ограничения их применения и хранения, обусловливают значительный интерес к созданию искусственных рецепторных систем. Молекулярный импринтинг, основанный на получении молекулярных отпечатков (молекулярно импринтированных полимеров, МИП) различных соединений при синтезе полимерной матрицы в присутствии субстратов, является одной из наиболее эффективных технологий получения специфических сайтов связывания [4–7]. Впервые такого рода материалы, обладающие способностью к повышенной адсорбции отдельных алкилбензолов, были получены русским ученым М.В. Поляковым в 30-е годы прошлого века при полимеризации силикагеля в присутствии соответствующих углеводородов [4]. Общая схема синтеза МИП включает сополимеризацию функционального и сшивающего мономеров в присутствии субстратов (молекул шаблонов). Последующее элюирование молекул шаблона из полимерной матрицы позволяет получить структуру, которая характеризуется наличием “молекулярной памяти” по отношению к молекулам шаблона [7]. Достаточная жесткость полимерной структуры, достигаемая за счет перекрестного сшивания, отвечает за сохранение специфического расположения функциональных групп в МИП [8, 9]. Основным преимуществом применения молекулярного импринтинга является универсальность и относительная простота проведения синтеза, высокая стабильность получаемых структур и высокая специфичность сайтов связывания [8].
Традиционно синтез МИП основан на формировании селективных сайтов связывания в присутствии субстратов в органических и неорганических полимерах синтетического и природного происхождения. Альтернативным подходом к синтезу МИП является использование в качестве матрицы молекул белковой природы. Рецепторы, синтезированные таким методом, называют белковыми молекулами с молекулярным отпечатками или импринтированными белками (ИБ). Первоначально термин ИБ использовали для задач, связанных с усилением стабильности [10–12] и активности [10, 12, 13] ферментов. Возможность иммобилизации ИБ на подложках позволила начать применять их для решения аналитических задач. Первым примером применения ИБ в качестве рецепторного элемента распознавания и определения можно считать работу группы Маттиассона [14], опубликованную в 2016 г.
Цель обзора – анализ работ, посвященных решению аналитических задач при использовании молекулярного импринтинга с участием биомолекул как в роли шаблона, так и матричного полимера. Показаны преимущества применения импринтированных белковых молекул как синтетического аналога природных антител при определении низко- и высокомолекулярных веществ.
БИОИМПРИНТИНГ И ИМПРИНТИРОВАННЫЕ БЕЛКОВЫЕ МОЛЕКУЛЫ. ОСОБЕННОСТИ ТЕРМИНОЛОГИИ
Развитие методов молекулярного импринтинга с участием белковых молекул привело к неоднозначному использованию термина “биоимпринтинг”, что вызывает определенные трудности при поиске и анализе литературных данных.
Традиционно в аналитической химии термином “биоимпринтинг” обозначают процессы формирования сайтов связывания, специфичных к веществам и структурам биологического происхождения – биомолекулам [15, 16], клеткам [17, 18], вирусам [19], ДНК и РНК [20–22], бактериям [23]. В то же время понятие “биоимпринтинг” применяют и для описания процесса импринтинга белковых молекул в присутствии субстратов, приводящего к образованию сайтов связывания, используемых для распознавания и определения низко- и высокомолекулярных соединений [14, 15, 24, 25]. Такое толкование обусловлено тем, что техника синтеза ИБ для решения аналитических задач [14] основана на подходах, разработанных ранее для решения задач биокатализа [26], где под “биоипринтингом” понимают процесс усиления и сохранения активности ферментов, а также модификацию белков для придания им ферментативных свойств [27–29]. Кроме того, при описании модификации белковой структуры в процессе импринтинга также используют понятия “конформационная модификация” [30], “ферментативная память” [31], “импринтированный белок” [11, 32], “аналог переходного состояния (биомолекулярный импринтинг) (transition state analogue (biomolecular imprinting)” [26, 33], “молекулярный (био)импринтинг на основе межфазной активации (interfacial activation-based molecular (bio)-imprinting)” [10].
Таким образом, при решении аналитических задач на основе модификации структуры белковой молекулы за счет импринтинга, вероятно, более целесообразно использовать термин “импринтированные белки”, а не “биоимпринтинг”. Процессы синтеза ИБ следует характеризовать в зависимости от типа молекулы шаблона.
МОЛЕКУЛЯРНОЕ РАСПОЗНАВАНИЕ В АНАЛИЗЕ БИООБЪЕКТОВ (БИОИМПРИНТИНГ)
Современная классификация МИП по типу синтеза включает объемный, поверхностный и эпитопный импринтинг. Ввиду сложностей, возникающих при удалении молекул шаблона из полимерной матрицы, и диффузным ограничениям при образовании комплексов МИП–молекула шаблона, объемный импринтинг не применяется при создании МИП, специфичных к биообъектам. В то же время метод поверхностного импринтинга в случае биообъектов является более эффективным и представляет собой основной метод синтеза биоимпринтированных полимеров.
Ранее опубликованы обзоры работ, рассматривающих возможности применения молекулярного биоимпринтинга для распознавания клеток [17], при разработке биосенсоров [18], а также при решении задач биомедицины и биотехнологии [34, 35]. В данном обзоре рассмотрены работы, посвященные аналитическому применению биоимпринтированных систем (табл. 1).
Таблица 1.
Примеры биоимпринтированных полимеров
| Мономер/носитель | Шаблон | cmin/ДОС | ИФ | Метод исследования | Литература |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Полиуретан/– | Escherichia coli Rhodococcus rhodochrous Sarcina aurantiaca |
–/– | ∼2 | Абсорбционная спектроскопия | [36] |
| Полиуретан (полиэтиленимин)/– | Микрогранулы полиметилметакрилата | –/– | 20 | Проточная цитометрия | [37] |
| 3-(Аминопропил)триметоксисилан, тетраэтоксисилан/нано-частицы серебра | Двухцепочечная ДНК точечного мутантного гена экзона 21 EGFR | 12.5 нМ/ 1.5–93 мкМ | 4.1 | ЦВА, ДИВА | [20] |
| 1,2-Диаминобензол/графитовый электрод | Судан II (1-(2,4-диметилфенилазо)-2-нафтол) | 0.3 нМ/ 1.0–500.0 нМ | – | ЦВА, КВВА | [21] |
| N,N'-метиленбисакриламид N-изопропилакриламид/эластомер-ная копия дифракционной решeтки | Вирус ямчатости древесины яблони | 10 нг/мл/– | – | Лазерный дифракционный анализ | [19] |
| Толуидиновый синий/золотой электрод | Простат-специфический антиген | –/0.001– 40 мМ | – | ЦВА, ДИВА | [38] |
| Толуидиновый синий/стеклоуглеродный электрод | Конъюгат простат-специфического антигена c пероксидазой хрена | 2.23 нг/мл/ 0.01–100 мкг/мл | – | ДИВА, КВВА, Хроноамперометрия | [16] |
| 1,2-Диаминобензол/модифицированный графитовый электрод | Дофамин | 6 нМ/ 20–7000 нМ | – | ЦВА, ДИВА | [22] |
| Тетраметоксисилан, метилтриметоксисилан, 2-(метокси(полиэтиленокси) пропил)триметоксисилан (олиго(окись этилена)силан)/– | Цитохром С, зеленый флуоресцентный белок, бычий сывороточный альбумин, пероксидаза хрена, глюкозооксидаза, лизоцим | –/– | 8 | Абсорбционная спектроскопия Флуоресцентная спектроскопия | [39] |
Биоипринтинг клеточных структур открывает возможность получения микро- и нанотопографических отпечатков, сохраняющих форму и размер поверхности слоя клеток [40, 41]. При этом процесс биоимпринтинга включает стадии выращивания клеток, внутриклеточной фиксации и заливки полимерным материалом для получения отпечатка. Основными полимерными материалами, использующимися для клеточного биоимпринтинга, являются полидиметилсилоксан, полистирол и полиметакрилат [42]. В плане повышения степени биоразложения и экологичности материала альтернативой могут служить пластмассы на основе казеина, апробированные при получении отпечатков мышечных клеток мыши (миобласты C2C12) [42].
Известны примеры успешного применения биоимпринтинга клеток для решения аналитических задач. Описан [36] метод концентрирования и идентификации микроорганизмов в водных образцах. Предложена оригинальная схема иммуноферментного анализа (ИФА), в которой первичные антитела заменены на отпечатки соответсвующих бактерий в полидиметилсилоксане и полиуретане, а вторичные антитела – бифункциональными наночастицами SiO2, коньюгироваными с пероксидазой хрена (ПХ). Полученые отпечатки обладали высокой специфичностью и позволили увеличить эффективность сорбции соответствующих им бактериальных культур ∼ в два раза.
В работе [37] предложена методика направленного выделения раковых клеток из крови, основанная на применении шаблона-имитатора (микрогранул полиметилметакрилата) в качестве размерного аналога клеток лейкемии человека (HL60). Синтезированый материал характеризовался высокими характеристиками удерживания клеток и специфичностью. Дополнительное введение модификаторов (1% полиэтиленимина, 3% Полоксамера-407) позволило увеличить эффективность удерживания клетки HL60 в 20 раз. При оптимальной композиции материала удержание клеток HL60 в пять раз превышало этот показатель по сравнению с мононуклеарными клетками периферической крови человека.
Значительный интерес представляет применение метода биоимпринтинга в сочетании с различными связывающими агентами (антителами, аптамерами и пептидами) для решения задач распознавания и захвата циркулирующих опухолевых клеток. Безметочный подход к определению циркулирующих опухолевых клеток поджелудочной железы, выделяемых из здоровых клеток периферической крови, и определение селективности опухолевых клеток-мишеней по отношению к здоровым клеткам крови человека предложены в работе [40]. Многостадийный процесс синтеза молекулярных отпечатков на пленке полиэтилентерефталата позволил получить импринтированный материал, способный захватывать и концентрировать опухолевые клетки поджелудочной железы из смешанной клеточной популяции, который использовали для изоляции клеток опухоли поджелудочной железы от здоровых лейкоцитов.
Примерами применения молекулярного импринтинга при разработке биосенсоров являются работы [20, 21]. Электрохимический нанобиосенсор для определения противоракового препарата гемцитабина на основе взаимодействия с мутантным экзоном 21 гена человека EGFR предложен в работе [20], импринтинг фактор (ИФ) материала составил 4.1. Авторами работы [21] разработана сенсорная система для определения красителя Судан II на основе ДНК-импринтированного поли-о-фенилендиамина. Показано, что разработанный ДНК-биосенсор в 1.8 раза эффективнее сорбирует молекулы Судана II и в 2.1 раза меньше сорбирует молекулы Судана I по сравнению с известным аналогом. Это свидетельствует о перспективности предложенного подхода как для повышения сорбционной емкости, так и для улучшения селективности определения.
Достоинством биоимпринтинга является возможность получения “молекулярных отпечатков” и значительно более крупных структур. В работе [19] использовали гидрогель, синтезированный реакцией окислительной кополимеризации N,N'-метиленбисакриламида, N-изопропилакриламида и N,N,N',N'-тетраметилэтилендиамина в присутствии аптамера вируса ямчатости древесины (стебля) яблони для изготовления сенсора. Аналитические характеристики разработанного сенсора (табл. 1) сопоставимы с классическим ИФА и флуоресцентными методами определения.
Биоимпринтинг белков. Анализ работ, посвященных молекулярному импринтингу белковых молекул и их использованию при разработке биосенсоров, дан в обзоре [43]. Сложность молекулярной структуры белковых молекул вызывает определенные трудности при разработке такого типа сенсорных элементов. В то же время известны примеры успешного применения биоимпринтинга при разработке электрохимических сенсоров для определения белковых молекул [16, 38, 44].
Сардаремелли и сотр. [16] разработали биосенсор для определения H2O2 в модельных соединениях и в составе плазмы крови человека методами дифференциальной импульсной вольтамперометрии, квадратно-волновой вольтамперометрии и хроноамперометрии. Модификацию стеклоуглеродного электрода биоимпринтированным материалом проводили методом электрополимеризации толуидинового синего в присутствии конъюгата простат-специфического антигена c ПХ. Биосенсор позволил определять H2O2 в модельных смесях и искусственно загрязненных образцах плазмы крови человека на уровнях 0.001–40 мМ и 0.005–25 мМ соответственно. Другой пример электрохимического биосенсора для определения H2O2 в образце плазмы крови человека, а также ПХ представлен в работе [38]. В качестве подложки для синтеза биоимпринтированного полимера на основе ß-циклодекстрина использовали стеклоуглеродный электрод, определение H2O2 проводили методом хроноамперометрии при pH 6.98. Последовательную модификацию золотого электрода глутаральдегид–цистеаминовой матрицей и МИП на основе толуидинового синего использовали для определения простат-специфического антигена в образце человеческой плазмы [44].
Авторами работ [16, 38, 44] показано, что аналитические характеристики определения аналитов сопоставимы с известными сенсорными системами. Это свидетельствует о перспективности применения биоимпринтированных полимеров в биомедицинских исследованиях. В то же время отсутствие информации о сорбционных характеристиках материалов не позволяет в полной мере оценить их практическую значимость.
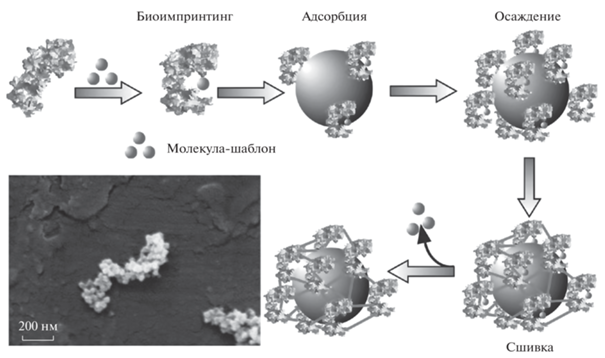
Интересный вариант нестандартной матрицы для биоимпринтинга белков предложен в работе [39]. Палочковидные бактерии Bacillus subtilis использовали как носитель при создании микронных отпечатков белков (цитохром C или зеленый флуоресцентный белок) в кремнеземной пленке (рис. 1). Полученный материал характеризовался высоким значением ИФ (8) и специфичностью по отношению к другим белкам, а именно к бычьему сывороточному альбумину (БСА), ПХ, глюкозооксидазе (ГО), лизоциму. Авторами обсуждены причины высокой специфичности синтезированных МИП к цитохрому C.
Рис. 1.
Схема биоимпринтинга белков с применением бактерий. а – иммобилизация бактерий на поверхности стекла; б – белки, иммобилизованные на поверхности бактерий; в – нанесение кремнеземного золя; г – отпечатки, селективные к белку, образовавшиеся в пленке кремнезема после удаления белковых бактерий. Адаптировано из [39].
ИМПРИНТИРОВАННЫЕ БЕЛКОВЫЕ МОЛЕКУЛЫ
Импринтинг белковых молекул – широко распространенная техника в современной энзимологии, биотехнологии и производстве биотоплив. В данном разделе рассмотрена основа этого направления импринтинга, его краткая история и современное состояние. Импринтингом белковых молекул следует считать метод модификации структуры белковой молекулы за счет образования сайтов связывания [45]. Замена органического полимера на белковую молекулу позволяет сохранить общую концепцию молекулярного импринтинга, включающую основные этапы получения селективного сайта связывания и подходы распознавания целевых молекул [14].
Привлекательность использования белковых молекул в молекулярном импринтинге и распознавании обусловлена набором их уникальных свойств [46]. Упорядоченная укладка аминокислотной последовательности формирует трёхмерную структуру белка, характеризующуюся хиральной активностью, включающую в себя щели, полости и набор функциональных групп, способных взаимодействовать как с небольшими лигандами, некоторыми видами поверхностей и с другими биополимерами посредством нековалентных гидрофобных связей. Кроме того, при взаимодействии двух и более структур проявляются кооперативные эффекты, в результате которых система получает новые свойства, отсутствующие у отдельных компонентов [47]. Взаимодействие белка с лигандом приводит к образованию наиболее комплементарного сайта связывания среди энергетически доступных конформационных микросостояний посредством незначительного изменения локальной структуры белка. Это позволяет лигандам вступать во взаимодействие с малоразличимыми конформациями белка. Таким образом, структурная память в таких системах достигается посредством конформационных изменений при образовании комплекса белок–молекула шаблона. Стабилизация и фиксация модифицированной структуры происходит при переводе комплекса в безводные среды [48], а в водных средах за счет использования сшивающих агентов [14].
Считается [8, 46], что первой попыткой создания сайта связывания в белковой молекуле явилась работа Полинга [49], в которой описывался возможный способ in vitro получения антител с необходимой специфичностью из γ-глобулинов быка. Глобулин или другой белок предлагалось [50, 51] поместить в раствор, содержащий антиген, а затем обработать денатурирующим агентом или подвергнуть воздействиям, вызывающим раскручивание концов цепи. Устранение влияния денатурирующих условий приводило к ренатурации цепей и, как следствие, к образованию устойчивой в данных условиях конфигурации, комплиментарной антигену и получившей свойства специфического гомологического антитела. В качестве матричного белка использовали бычий γ-глобулин, в качестве антигенов – трифенилэтиленовый краситель метиловый синий и полисахарид пневмококка III типа. Осаждение поликлональных γ-глобулинов полисахаридом пневмококка III типа показало определенную степень селективного распознавания. Считается, что полученные экспериментальные результаты обладают некоторой степенью “сомнительности”; возможно, в связи с этим идея создания искусственных антител трансформировалась в работы Дики [52] по молекулярному импринтингу на основе кремнезема для разделения смеси метилового оранжевого и этилового оранжевого. Несмотря на дальновидность Полинга, первой работой, посвященной применению описанного им подхода, можно считать работу Лиу 2004 г. [26]. В то же время работы по модификации структуры белков техникой “биоимпринтинга” за счет перевода белков в органические среды и, как следствие, усиления ферментативной активности протеазы субтилизина в органических растворителях известны с конца 1980-х годов [31]. В дальнейшем биоимпринтинг успешно применяли для сохранения конформации и химических свойств белковых молекул при глубоком замораживании или осаждении [53], улучшения свойств ферментов в системах без растворителя [12], а также в виде метода импринтирования белковых молекул при создании систем селективного распознавания [54, 55]. К области применения последних относится изготовление клинических лекарств и платформ целевой доставки лекарственных веществ в организме, поскольку получаемые белковые материалы обладают свойствами, аналогичными природным ферментам [56].
Ферментативные системы. Использование биокатализа в органическом синтезе является более эффективной и экологически чистой альтер-нативой традиционным химическим методам [57, 58]. Биоимпринтинг можно рассматривать как один из существующих в настоящее время экономически выгодных методов получения стабильных ферментов, характеризующихся селективными или энантиоселективными свойствами.
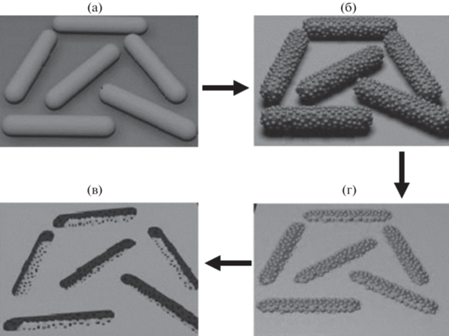
Основные этапы биоимпринтинга ферментов и белков представлены на рис. 2 [58]. Образование комплекса между белковой молекулой и молекулой-шаблоном осуществляется в водном растворе, перевод комплекса в органический растворитель вызывает осаждение импринтированного белка и фиксацию “переходного” состояния. На следующем этапе происходит удаление молекулы шаблона, что приводит к образованию сайта связывания, устойчивого только в безводных растворителях. Водные растворы создают условия для перехода белковой молекулы к первоначальной термодинамически благоприятной конформации и, как следствие, для разрушения сайта связывания. Закс и Клибанов [57–59] используют термин “pH-память”, обозначающий сохранение и проявление ферментами каталитической активности, соответствующей кислотности водного раствора, в котором они находились при импринтинге. Объяснение этого эффекта связано с сохранением ионогенными группами белка состояния ионизации при его дегидратации и помещении в органический растворитель.
Наибольшее распространение среди ферментов, применяемых в биотехнологии, получили липазы [60] благодаря их способности катализировать ряд реакций в различных по составу средах. Тем не менее низкая стабильность и снижение активности в органических средах существенно ограничивает число коммерчески доступных липаз. Например, липаза, продуцируемая дрожжами рода Candida antarctica, проявляет ферментативные свойства в органической среде, однако стоимость препарата достаточно высока (2600 $/кг в 2021 г.) [61]. Биоимпринтинг, наряду с иммобилизацией ферментов [62] и созданием липидного покрытия [63], является одним из методов модификации липаз. В случае использования липаз в качестве матричных молекул требуется межфазная активация, что связано с наличием “крышки”, закрывающей сайт связывания в водной среде и контролирующей доступ субстрата к активному центру [13, 64]. Активация межфазной поверхности двухвалентными катионами, неполярными органическими растворителями и поверхностно-активными веществами способствует повышению каталитических свойств липаз. Кроме того, успешным является применение жирных кислот, являющихся субстратами липаз, в качестве лигандов и соединений, способствующих межфазной активации [13, 48, 65, 66].
Примеры импринтированных липаз представлены в табл. 2. Метод синтеза биоимпринтированных ферментов подробно описан на примере липаз, продуцируемых Burkholderia cepacian [66] и Candida rugosa [67, 68], ряд карбоновых кислот использовали в качестве молекул шаблонов. Ферментативные свойства верифицировали по реакции переэтерефикации винилацетата и бензилового спирта. Модификация липазы методом “биоимпринтинга” позволила увеличить начальную скорость реакции в пять раз по сравнению с неимпринтированной липазой, полученной по аналогичной методике без добавления молекул шаблонов. Наибольшее увеличение скорости реакции показала липаза, модифицированная масляной кислотой, что авторы объясняют сопоставимыми размерами молекулы шаблона и субстрата и, как следствие, достижением наилучшей конформации фермента в процессе биоимпринтинга. При использовании перфторкарбоновых кислот самая высокая скорость наблюдалась для липазы, подвергнутой биоимпринтингу в присутствии пентафторпропионовой кислоты.
Таблица 2.
Импринтированные ферменты
| Фермент | Молекула-шаблон | Носитель/ сшивающий агент | ИФ | Метод исследования | Литература | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Липаза | Burkholderia cepacia | Додекановая, тетрадекановая, гексадекановая, октадекановая кислоты | –/– | 4–70 | Титрование | [48] |
| Sus scrofa domesticus | ||||||
| Липаза | Candida rugosa | Метановая, этановая, пропановая кислоты | –/– | 3 | ВЭЖХ-УФ | [65] |
| Липаза | Burkholderia cepacia | Пропановая, трифторэтановая, октановая, этановая пентафторпропионовая, гептафтормасляная, бутановая перфтороктановая, кислоты | –/– | 5 | ВЭЖХ-УФ | [66] |
| Липаза | Candida rugosa | Гексановая, октановая, декановая, додекановая кислоты | –/– | 3–5 | ВЭЖХ-УФ | [67] |
| Липаза | Burkholderia cepacia | н-Дециловая, н-гексиловая, додекановая кислоты | –/п-бензохинон | – | ГХ-ПИД, титрование | [27] |
| Липаза | Candida rugosa | цис-9-Октадеценовая кислота | –/глутаровый альдегид | 10.4 | ГХ-ПИД, ВЭЖХ-МС | [68] |
| Липаза | Burkholderia cepacia | 1-Фенилэтанол, винилацетат, гептан | МНЧ/– | 54 | ВЭЖХ-УФ, титрование | [69] |
| Липаза | Thermomyces lanuginosus | ПАВ | – | – | ГХ-ПИД | [28] |
| Липаза | LipC12 | цис-9-Октадеценовая кислота | Хитозан, полипропиленовые гранулы и порошок | – | Титрование | [59] |
| Липаза | Burkholderia cepacia | Лауриновая, олеиновая, линолевая кислоты, триолеин, оливковое масло | МНЧ, МНЧ@SiO2, УНТ/– | – | ГХ-ПИ/ПФД, титрование | [29] |
| Candida rugosa | ||||||
| Rhizomucor miehei | ||||||
| Липаза B | Candida antarctica | Олванил | –/глутаровый альдегид | 13 | ВЭТСХ | [70] |
| Фосфолипаза D | Streptomyces sp. PMF | Глицерин | SiO2 НЧ/глутаровый альдегид | 14 | ВЭЖХ-ИКФС | [71] |
Используемые сокращения: ВЭЖХ – высокоэффективная жидкостная хроматография; ГХ – газовая хроматография; ВЭТСХ – высокоэффективная тонкослойная хроматография; МНЧ – магнитная наночастица; ПИД – пламенно-ионизационный детектор; ПФД – пламенно-фотометрический детектор; УНТ – углеродные нанотрубки; ИКФС – инфракрасная Фурье-спектроскопия.
Авторами работы [72] предпринята попытка иммобилизации без носителя импринтированной липазы, продуцируемой Candida rugosa, для сохранения свойств в водных средах. Биоимпринтинг осуществляли по известной методике [73] с использованием олеиновой кислоты в качестве молекул шаблона, полиэтиленимина как коагрегатора фермента, глутарового альдегида – для ковалентной сшивки. Проведение “биоимпринтинга” и ковалентной сшивки липазы способствовало увеличению ее каталитической активности в реакции гидролиза в 10.4 раза по сравнению с нативной, а также увеличению термостабильности и возможности пятикратного использования без существенного снижения производительности.
Сочетание биоимпринтинга и иммобилизации ферментов открывает возможность выделения фермента после проведения реакции и таким образом его многократного использования; как результат, увеличивается чистота и снижается стоимость целевого продукта [74, 75]. Кроме того, иммобилизированные импринтированные ферменты менее подвержены денатурации, что способствует повышению стабильности при нагревании, по отношению к органическим растворителям и физическому воздействию. Повышенная стабильность ферментов обусловлена увеличением структурной жесткости белка, предотвращающей конформационные изменения, потенциально способные приводить к его инактивации [70].
Влияние иммобилизации на различных носителях (хитозан, полипропиленовые гранулы, полипропиленовый порошок, Accurel MP-1000, Nanomer I.44P, Immobead 150) на активность и стабильность биоимпринтированной рекомбинантной липазы LipC12 в органическом растворителе (н-гептан) изучено в работе [60]. Биоимпринтинг липазы LipC12 проводили по одностадийной методике [48], в качестве молекулы-шаблона использовали олеиновую кислоту. Увеличение биокаталитической эффективности биоимпринтированной липазы LipC12 в реакции этерификации олеиновой кислоты и 1-пентанола наблюдали для всех исследуемых носителей. Наибольшее увеличение активности наблюдалось для подложек, обладающих гидрофобными свойствами. Это может быть обусловлено проявлением у олеиновой кислоты свойств поверхностно-активного вещества и, как следствие, улучшением контакта иммобилизационной среды с носителем. Показана возможность многократного использования импринтированной липазы LipC12, иммобилизованной на подложке Immobead 150, при сохранении ферментативной активности (>95% после восьми циклов).
Биоимпринтинг рекомбинантной липазы B, полученной из Candida antarctica и экспрессированной в дрожжи семейства Pichia pastoris, описан в работе [76]. Биоимпринтинг осуществляли инкубацией предварительно иммобилизованных поперечно-сшитых ферментных агрегатов в присутствии олванила в качестве молекул шаблона. Показано увеличение ферментативной активности липазы B в 1.6 раза по сравнению с неимпринтированным аналогом и в два раза по сравнению с коммерческими образцами перекрестно-сшитой липазы.
Известны примеры иммобилизации биоимпринтированных молекул на носителях, характеризующихся высокоразвитой удельной поверхностью, таких как мультикапилляры [71] и наночастицы [69, 77]. Адсорбция на магнитных наночастицах липазы, полученной из Burkholderia cepacia, биоимпринтированной винилацетатом, позволила увеличить активность фермента более чем на 10%, повысить выход энантиомера (от 77.4 до 98.8%) и сократить время реакции (с 60 до 20 мин) [77]. Иммобилизованная биоимпринтированная липаза показала высокую стабильность работы и возможность многократного использования (не менее восьми циклов) в реакции энантиоселективной переэтерификации между рацемическим 1-фенилэтанолом и винилацетатом в гексане и гептане. Пример гиперактивации фосфолипазы D представлен в работе [69]. Биоимпринтинг фосфолипазы D и ее последующая иммобилизация на поверхности диоксида кремния (рис. 3) позволили в 14 раз увеличить активность белка (166 953 U/г) по сравнению со свободной формой (11 922 U/г), а также обеспечить сохранение конформационных изменений при работе в водных средах.
Приведенные данные показывают, что сочетание современных протоколов импринтинга ферментов с возможностью иммобилизации на поверхности носителей позволяет существенно повысить их ферментативную активность. При этом важное значение имеет величина ИФ полученных систем, которая в данном случае оценивается как отношение ферментативной активности импринтированного и неимпринтированного ферментов (табл. 2). Наиболее высокие значения ИФ отмечены для биоимпринтированных ферментов, иммобилизированных на поверхности носителя [69]. В связи с этим подобные системы импринтированных белков выглядят наиболее перспективными в качестве рецепторных элементов при разработке биомиметических сенсорных си-стем.
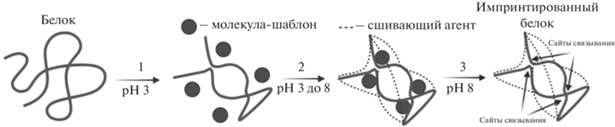
Рецепторные системы. Оригинальная методика “биоимпринтинга” овальбумина для придания ему ферментативных свойств глутатион-пероксидазы предложена Лиу в 2004 г. [26] и может считаться предвестником современного применения ИБ как рецепторных систем в аналитической химии. Основными особенностями предложенного подхода являются проведение импринтирования белка в водной среде и использование для фиксации полученной белковой структуры сшивающего агента – глутарового альдегида (рис. 4). Рассматривая этот процесс с точки зрения молекулярного импринтинга, можно сказать, что белковая молекула выступает в роли крупного функционального ко-мономера, а глутаровый альдегид – в роли сшивающего – матричного мономера. Это позволяет отнести такой тип биоимпринтинга к классическому молекулярному импринтингу и использовать его терминологию.
Описанный подход получил развитие для решения задач аналитической химии, начиная с 2016 г. [14], в том числе в работах нашей группы [54, 55, 71]. Аналитические характеристики разработанных систем представлены в табл. 3.
Таблица 3.
Рецепторные системы на основе импринтированных белковых молекул
| Белок | Молекула-шаблон | Носитель | Метод исследования | cmin, мкг/л | ДОС, мкг/л | ИФ | Литература | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Овальбумин | Афлатоксин B1 | Золотой электрод | ЦВА | 0.002 | 1–1000 | 1.62 | [14] | |
| БСА | ||||||||
| БСА | Зеараленон | МТП | ИБ-ИФА | 4 | 8–500 | 2.24 | [54] | |
| Овальбумин | н/д | н/д | 1.80 | |||||
| ГЛУ | н/д | н/д | 1.32 | |||||
| БСА | Зеараленон | МТП | ИБ-МФА | 5 | 10–290 | 2.32 | [24] | |
| Дезоксиниваленол | 35 | 55–420 | ||||||
| Овальбумин | Зеараленон | МОВ, МК | ИБ-ИФА | 0.12 | 1–8 | 2.05 | [74] | |
| Фруктозамин | Липосахариды | E. coli | ФК | Дифракция | 0.87 | н/д | н/д | [77] |
| P. aeruginosa | 1.22 | |||||||
| Овальбумин | Квакхурин | МТП | ИБ-ИФА | 4 мг/л | 4.7– 75.0 мг/л | 1.5 | [25] | |
| Моноклональные антитела против глицирризина | МТП | ИБ-ИФА | 0.8 мг/л | 2.3– 37.5 мг/л | 3.12 | |||
| ГО | Овальбумин | МТП | ИБ-МФА | 6 | 10–2000 | 4.7 | [29] | |
Используемые сокращения: ЦВА – циклическая вольтамперометрия; ГЛУ – гемоцианин лимфы улитки; МТП – микро титровальный планшет; ИБ-ИФА – иммуноферментный анализ на основе ИБ; ИБ-МФА – иммунофлуоресцентный анализ на основе ИБ; МОВ – микроструктурный оптический волновод; МК – мультикапилляр; ФК – фотонный кристалл.
Методика синтеза импринтированного овальбумина для определения микотоксина афлатоксина B1 разработана Матиассоном и сотр. [14]. Синтез импринтированного белка включал стадии (1) обратимой денатурации в растворе HCl (pH 3.0, 10 мин), (2) импринтинга белка в присутствии молекул шаблона (10 мин), (3) ренатурации белка в щелочной среде (при добавлении NaOH до pH 8.0), (4) закрепления полученной структуры белковой молекулы в присутствии сшивающего агента (глутаровый альдегид, 4°С, 12 ч). Молекулы шаблона удаляли из синтезированных ИБ диализом против фосфатно-солевого буферного раствора (10 мМ, pH 7.4, 48 ч). Полученный импринтированный овальбумин успешно использовали для сенсорного определения афлотоксина В1 методом циклической вольтамперометрии. Иммобилизацию ИБ проводили на золотом электроде, предварительно модифицированном самоорганизующимся монослоем альфа липоевой кислоты и активированном N-этил-N'-(3-диметиламинопропил)карбодиимидом.
Синтез ИБ, специфичных к микотоксину зеараленону, с использованием различных белков (БСА, овальбумина и гемоцианин лимфы улитки) изучен в работе [55]. Сравнение сорбционных характеристик ИБ показало, что наибольшим ИФ (2.2) характеризуется БСА. Иммобилизация ИБ на поверхности микропланшета позволила разработать методику определения зеараленона в формате иммуноанализа и показать возможность использования ИБ для замены антител. Валидация разработанной методики проведена на примере искусственно загрязненных образцов пшеницы и кукурузы с использованием ВЭЖХ-МС/МС. Аналитические характеристики сопоставимы с коммерческими тест-системами на основе антител. В дальнейшем работа получила продолжение [24]. Авторами предложен подход к одновременному определению зеараленона и дезоксиниваленола в формате иммунофлуоресцентного анализа на основе ИБ и применению в качестве меток люминесцентных нанокристаллов (квантовых точек) с разными длинами волн испускания (547 и 632 нм). Предложенный подход успешно апробирован при одновременном определении микотоксинов в образцах пшеницы и кукурузы. Аналитические характеристики позволяют контролировать присутствие микотоксинов на уровнях, рекомендованным Европейской Комиссией (ЕК 401/2006).
Нами показана возможность использования ИБ для модификации внутренней поверхности стеклянных микроструктурных оптических волноводов и мультикаппиляров [71]. В качестве белка-носителя использовали овальбумин, молекулы шаблона – зеараленон. Показано, что использование высокоэффективных оптических платформ и систем с развитой поверхностью позволяет снизить cmin в 33 раза по сравнению с результатами, полученными на микропланшете.
Определенный интерес в плане применения возможностей ИБ в аналитической химии представляет работа [25]. Авторами проведено систематическое изучение влияния природы белка на свойства ИБ с использованием в качестве молекулы шаблона квакхурин. Установлено, что наилучшие сорбционные и аналитические характеристики достигаются при импринтировании моноклональных антител. Этот факт подтверждает концепцию Полинга по in vitro синтезу антител [49–51]. Возможность направленной смены специфичности моноклональных антител с учетом поставленной задачи является перспективным направлением современной биотехнологии. В то же время использование для импринтинга моноклональных антител приводит к увеличению стоимости анализа.
В ряде работ для определения биомолекул (биоимпринтинга) в качестве функционального мономера использованы белковые молекулы [14, 24, 25, 54, 55]. По аналогии с синтезом МИП, специфичных к клеточным структурам, предложена оригинальная методика обнаружения грамотрицательных бактерий на основе импринтированного фруктозоамина [78]. Липосахариды, выделенные из бактерий, использованы в качестве молекул-шаблонов, а фотонный кристалл на основе гидрогелей полистирола применен в качестве носителя. Обнаружение бактерий основано на измерении изменения дифракционных характеристик фотонного кристалла. Нами разработана методика синтеза импринтированной ГО, специфичной к овальбумину и ПХ [54]. Возможность прямого определения ПХ на основе хромогенной реакции с 3,3',5,5'-тетраметилбензидином использовали для оптимизации условий импринтинга, которые в дальнейшем применяли для синтеза импринтированной ГО, специфичной к овальбумину.
Представленные работы демонстрируют возможность создания сенсорных элементов на основе ИБ с использованием протоколов, известных для иммунохимических методов анализа. Основным преимуществом ИБ является возможность быстрого получения сенсорного элемента на целевые молекулы, отказа от использования лабораторных животных и сложного оборудования. Немаловажной является также возможность существенного снижения себестоимости анализа по сравнению с иммунохимическими аналогами при многосерийном производстве.
* * *
Синтез белков с молекулярными отпечатками является перспективной альтернативой методам определения и выделения на основе моноклональных и поликлональных антител в формате иммунохимического анализа. При этом возможность интеграции подходов, известных в области молекулярного импринтинга, позволяет получать ИБ, специфичные как к низко-, так и к высокомолекулярным соединениям и характеризующиеся более высокой стабильностью к изменениям температуры и кислотности среды по сравнению с природными антителами. Немаловажным является и тот факт, что ИБ полностью соответствуют принципам “зеленой химии” и теоретически могут быть использованы при проведении аналитических исследований и специфическом выделении молекул-мишеней как в in vitro, так и в in vivo форматах.
При получении белков с молекулярными отпечатками необходимо учитывать, что важным этапом является подбор белковой молекулы, дающей возможность импринтинга отдельно для каждой молекулы-шаблона, что может занимать значительное время. Отсутствие теоретической базы при выборе белковой матрицы не позволяет в настоящее время говорить о возможности широкого внедрения данной технологии в аналитическую практику.
Работа выполнена при поддержке Российского Научного Фонда (грант № 22–16–00102).
Список литературы
Korbakis D., Schiza C., Brinc D., Soosaipillai A., Karakosta T D., Légaré C., Sullivan R., Mullen B., Jarvi K., Diamandis E.P., Drabovich A.P. Preclinical evaluation of a TEX101 protein ELISA test for the differential diagnosis of male infertility // BMC Medicine. 2017. V. 15. № 1. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-017-0817-5
Chau C.H., Strope J.D., Figg W.D. COVID-19 clinical diagnostics and testing technology // Pharmacotherapy. 2020. V. 40. № 8. P. 857. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2439
Saushkin N.Y., Samsonova J.V., Osipov A.P., Kondakov S.E. Strip-dried blood sampling: applicability for bovine leukemia virus detection with ELISA and real-time PCR // J. Virol. Methods. 2019. V. 263. P. 101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.11.004
Поляков М.В. Адсорбционные свойства силикагеля и его структура // Журн. физ. химии. 1931. Т. 2. № 6. С. 799.
Belbruno J.J. Molecularly imprinted polymers // Chem. Rev. 2019. V. 119. № 1. P. 94. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Гендриксон О.Д., Жердев А.В., Дзантиев Б.Б. Молекулярно импринтированные полимеры и их применение в биохимическом анализе // Успехи биол. химии 2006. Т. 46. С. 149.
Mosbach K. Molecular imprinting // Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994. V. 19. № 1. P. 9.
Sellergren B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Man-Made Mimics of Antibodies and their Applications in Analytical Chemistry. (Techniques and Instrumentation in Analytical Chemistry. Netherlands: Elsevier, 2001. 558 p.
Spivak D.A., Shea K.J. Binding of nucleotide bases by imprinted polymers // Macromolecules. 1998. V. 31. № 7. P. 2160. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma971310d
Mingarro I., Abad C., Braco L. Interfacial activation-based molecular bioimprinting of lipolytic enzymes // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995. V. 92. № 8. P. 3308. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.8.3308
Peißker F., Fischer L. Crosslinking of imprinted proteases to maintain a tailor-made substrate selectivity in aqueous solutions // Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999. V. 7 № 10. P. 2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(99)00156-X
González-Navarro H., Braco L. Improving lipase activity in solvent-free media by interfacial activation-based molecular bioimprinting // J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 1997. V. 3. № 1. P. 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1177(96)00038-0
Fishman A., Cogan U. Bio-imprinting of lipases with fatty acids // J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2003. V. 22. № 3–4. P. 193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1177(03)00032-8
Gutierrez A.V., Hedström M., Mattiasson B. Bioimprinting as a tool for the detection of aflatoxin B1 using a capacitive biosensor // Biotechnol. Rep. 2016. V. 11. P. 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.05.006
Mujahid A., Iqbal N., Afzal A. Bioimprinting strategies: From soft lithography to biomimetic sensors and beyond // Biotechnol. Adv. 2013. V. 31. № 8. P. 1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.06.008
Sardaremelli S., Razmi H., Hasanzadeh M., Shadjou N. A novel bioassay for the monitoring of hydrogen peroxide in human plasma samples based on binding of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated prostate specific antigen to poly (toluidine blue) as imprinted polymer receptor // Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020. V. 145. P. 311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.195
Piletsky S., Canfarotta F., Poma A., Bossi A.M., Piletsky S. Molecularly imprinted polymers for cell recognition // Trends Biotechnol. 2020. V. 38. № 4. P. 368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.10.002
Hasanzadeh M., Shadjou N., de la Guardia M. Cytosensing of cancer cells using antibody-based molecular imprinting: A short-review // Trends Anal. Chem. 2018. V. 99. P. 129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.12.010
Bai W., Spivak D.A. A double-imprinted diffraction-grating sensor based on a virus-responsive super-aptamer hydrogel derived from an impure extract // Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014. V. 53. № 8. P. 2095. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201309462
Shoja Y., Kermanpur A., Karimzadeh F., Ghodsi J., Rafati A.A., Adhami S. Electrochemical molecularly bioimprinted siloxane biosensor on the basis of core/shell silver nanoparticles/EGFR exon 21 L858R point mutant gene/siloxane film for ultra-sensing of Gemcitabine as a lung cancer chemotherapy medication // Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019. V. 145. Article 111611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111611
Rezaei B., Boroujeni M.K., Ensafi A.A. Development of Sudan II sensor based on modified treated pencil graphite electrode with DNA, o-phenylenediamine, and gold nanoparticle bioimprinted polymer // Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2016. V. 222. P. 849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.017
Rezaei B., Boroujeni M.K., Ensafi A.A. Fabrication of DNA, o-phenylenediamine, and gold nanoparticle bioimprinted polymer electrochemical sensor for the determination of dopamine // Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015. V. 66. P. 490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.009
Qi P., Wan Y., Zhang D. Impedimetric biosensor based on cell-mediated bioimprinted films for bacterial detection // Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013. V. 39. № 1. P. 282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.07.078
Beloglazova N., Lenain P., Tessier M., Goryacheva I., Hens Z., De Saeger S. Bioimprinting for multiplex luminescent detection of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone // Talanta. 2019. V. 192. P. 169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.042
Sakamoto S., Minami K., Nuntawong P., Yusakul G., Putalun W., Tanaka H., Fujii S., Morimoto S. Bioimprinting as a receptor for detection of kwakhurin // Biomolecules. 2022. V. 12. № 8. Article 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081064
Liu J., Zhang K., Ren X., Luo G., Shen J. Bioimprinted protein exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity // Anal. Chim. Acta. 2004. V. 504. № 1. P. 185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00763-3
Gao J., Yin L., Feng K., Zhou L., Ma L., He Y., Wang L., Jiang Y. Lipase Immobilization through the combination of bioimprinting and cross-linked protein-coated microcrystal technology for biodiesel production // Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016. V. 55 № 42. P. 11037. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b03273
Mukherjee J., Gupta M.N. Dual bioimprinting of Ther-momyces lanuginosus lipase for synthesis of biodiesel // Biotechnol. Rep. 2016. V. 10. P. 38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.02.005
Fan Y., Ke C., Su F., Li K., Yan Y. Various types of lipases immobilized on dendrimer-functionalized magnetic nanocomposite and application in biodiesel preparation // Energy and Fuels. 2017. V. 31. № 4. P. 4372. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00036
Keyes M.H., Albert D.E., Saraswathi S. Enzyme semisynthesis by conformational modification of proteins // Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1987. V. 501 № 1. P. 201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb45709.x
Russell A.J., Klibanov A.M. Inhibitor-induced enzyme activation in organic solvents // J. Biol. Chem. 1988. V. 263. № 24. P. 11624. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)37828-1
Ohya Y., Miyaoka J., Ouchi T. Recruitment of enzyme activity in albumin by molecular imprinting // Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1996. V. 17. № 12. P. 871. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.1996.030171205
Slade C.J., Vulfson E.N. Induction of catalytic activity in proteins by lyophilization in the presence of a transition state analogue // Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998. V. 57. № 2. P. 211. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19980120)57: 2<211::AID-BIT9>3.0.CO;2-Q
Дмитриенко Е.В., Пышная И.А., Мартьянов О.Н., Пышный Д.В. Молекулярно импринтированные полимеры для биомедицинских и биотехнологических применений // Успехи химии. 2016. Т. 85. № 5. С. 513. https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4542
Medlock J., Das A.A.K., Madden L.A., Allsup D.J., Paunov V.N. Cancer bioimprinting and cell shape recognition for diagnosis and targeted treatment // Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017. V. 46. № 16. P. 5110. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00179g
Filby B.W., Hardman M.J., Paunov V.N. Antibody-free bioimprint aided sandwich ELISA technique for cell recognition and rapid screening for bacteria // Nano Select. 2020. V. 1. № 6. P. 673. https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202000113
Remaud P., Medlock J., Das A.A.K., Allsup D.J., Madden L.A., Nees D., Weldrick P.J., Paunov V.N. Targeted removal of blood cancer cells from mixed cell populations by cell recognition with matching particle imprints // Mater. Chem. Front. 2020. V. 4. № 1. P. 197. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9qm00531e
Sardaremelli S., Hasanzadeh M., Razmi H. Chemical binding of horseradish peroxidase enzyme with poly beta-cyclodextrin and its application as molecularly imprinted polymer for the monitoring of H2O2 in human plasma samples // J. Mol. Recognit. 2021. V. 34. № 5. Article e2884. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2884
Cai W., Li H.H., Lu Z.X., Collinson M.M. Bacteria assisted protein imprinting in sol-gel derived films // Analyst. 2018. V. 143. № 2. P. 555. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an01509g
Pelle M., Das A.A.K., Madden L.A., Paunov V.N. Bioimprint mediated label-free isolation of pancreatic tumor cells from a healthy peripheral blood cell population // Adv. Biosyst. 2020. V. 4. № 11. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202000054
Sarwar M., Evans J.J. Bioimprinting: bringing together 2D and 3D in dissecting cancer biology // BioTechniques. 2021. V. 71. № 5. P. 543. https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2021-0058
Hashemi A., Nock V., Alkaisi M., Ali A. Enhancing the resolution of bioimprinted casein microdevices // Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2018. V. 15. № 8. P. 676–682. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJNT.2018.098433
Ansari S., Masoum S. Molecularly imprinted polymers for capturing and sensing proteins: current progress and future implications // Trends Anal Chem. 2019. V. 114. P. 29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.02.008
Abbasy L., Mohammadzadeh A., Hasanzadeh M., Razmi N. Development of a reliable bioanalytical method based on prostate specific antigen trapping on the cavity of molecular imprinted polymer towards sensing of PSA using binding affinity of PSA-MIP receptor: A novel biosensor // J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020. V. 188. Article 113447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113447
Teke M., Sezgintürk M.K., Dinçkaya E., Telefoncu A. A bio-imprinted urease biosensor: Improved thermal and operational stabilities // Talanta. 2008. V. 74. № 4. P. 661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.06.031
Piletsky S. Molecular Imprinting of Polymers. CRC Press, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781498713542
Whitty A. Cooperativity and biological complexity // Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008. V. 4. № 8. P. 435. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio0808-435
Brandão L.M.S., Barbosa M.S., Souza R.L., Pereira M.M., Lima Á.S., Soares C.M. Lipase activation by molecular bioimprinting: The role of interactions between fatty acids and enzyme active site // Biotechnol. Prog. 2021. V. 37 № 1. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.3064
Pauling L. A theory of the formation of antibodies // J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940. V. 372. № 62. P. 2643.
Pauling L., Campbell D.H. The production of antibodies in vitro // Science. 1942. V. 95. № 2469. P. 440. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.95.2469.440
Pauling L., Campbell D.H. The manufacture of antibodies in vitro // J. Exp. Med. 1942. V. 76. № 2. P. 211. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.76.2.211
Dickey F.H. The preparation of specific adsorbents. // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1949.V. 35. № 5. P. 227. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.35.5.227
Li Z., Liu H., Zhao G., Wang P., Wang L., Wu H., Fang X., Sun X., Wu X., Zheng Z. Enhancing the performance of a phospholipase A1 for oil degumming by bio-imprinting and immobilization // J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2016. V. 123. P. 122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.11.018
Pidenko P., Presnyakov K., Beloglazova N., Burmistrova N. Imprinted proteins for determination of ovalbumin // Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04009-3
Pidenko P., Zhang H., Lenain P., Goryacheva I., De Saeger S., Beloglazova N. Imprinted proteins as a receptor for detection of zearalenone // Anal. Chim. Acta. 2018. V. 1040. P. 99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.07.062
Yin Y., Dong Z., Luo Q., Liu J. Biomimetic catalysts designed on macromolecular scaffolds // Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012. V. 37. № 11. P. 1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.04.001
Klibanov A.M. Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents // Nature. 2001. V. 409. № 6817. P. 241. https://doi.org/10.1038/35051719
Zaks A., Klibanov A.M. Enzyme-catalyzed processes in organic solvents // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1985. V. 82. № 10. Article 31923196. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.82.10.3192
Zaks A., Klibanov A.M. Enzymatic catalysis in nonaqueous solvents // J. Biol. Chem. 1988. V. 263. № 7. P. 3194. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)69054-4
Sánchez D.A., Alnoch R.C., Tonetto G.M., Krieger N., Ferreira M.L. Immobilization and bioimprinting strategies to enhance the performance in organic medium of the metagenomic lipase LipC12 // J. Biotechnol. 2021. V. 342. P. 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.09.022
Mustafa A., Niikura F., Pastore C., Allam H.A., Hassan O.B., Mustafa M., Inayat A., Salah S.A., Salam A.A., Mohsen R. Selective synthesis of alpha monoglycerides by a clean method: Techno-economic and environmental assessment // Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022. V. 27. Article 100690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100690
Almeida F.L.C., Castro M.P.J., Travália B.M., Forte M.B.S. Trends in lipase immobilization: Bibliometric review and patent analysis // Process Biochem. 2021. V. 110. P. 37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.07.005
Joyce P., Gustafsson H., Prestidge C.A. Engineering intelligent particle-lipid composites that control lipase-mediated digestion // Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018. V. 260. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2018.08.001
Bordes F., Cambon E., Dossat-Létisse V., An dré I., Croux C., Nicaud J.M., Narty A. Improvement of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase enantioselectivity by using mutagenesis targeted to the substrate binding site // Chem Bio Chem 2009. V. 10. № 10. P. 1705. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200900215
Yan Y., Zhang X., Chen D. Enhanced catalysis of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase LIP2 immobilized on macroporous resin and its application in enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids // Bioresour. Technol. 2013. V. 131. P. 179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.092
Matsumoto M., Matsui E. Enhanced activities and thermostability of lipase pretreated with carboxylic and perflurocarboxylic acids in transesterification // J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018. V. 93. № 11. P. 3219. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5678
Matsumoto M., Nakao K., Tahara Y. Effects of imprinting and water activity on transesterification and thermostability with lipases in ionic liquid // Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2021. V. 35. № 1. P. 57. https://doi.org/10.15255/CABEQ.2020.1899
Matsumoto M., Hasegawa Y. Enzymatic kinetics of solvent-free esterification with bio-imprinted lipase // Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2020. V. 33. № 4. P. 495. https://doi.org/10.15255/CABEQ.2019.1692
Li B., Duan D., Wang J., Li H., Zhang X., Zhao B. Improving phospholipase D activity and selectivity by bio-imprinting-immobilization to produce phosphatidylglycerol // J. Biotechnol. 2018. V. 281. P. 67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.06.343
Mateo C., Palomo J.M., Fernandez-Lorente G., Guisan J.M., Fernandez-Lafuente R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques // Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007. V. 40. № 6. P. 1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.01.018
Burmistrova N.A., Pidenko P.S., Pidenko S.A., Zacharevich A.M., Skibina Y.S., Beloglazova N.V., Goryacheva I.Y. Soft glass multi-channel capillaries as a platform for bioimprinting // Talanta. 2020. V. 208. Article 120445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120445
Sampath C., Belur P.D., Iyyasami R. Enhancement of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid glycerides in sardine oil by a bioimprinted cross-linked Candida rugosa lipase // Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2018. V. 110. P. 20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.12.003
Kahveci D., Xu X. Enhancement of activity and selectivity of Candida rugosa lipase and Candida antarctica lipase A by bioimprinting and/or immobilization for application in the selective ethanolysis of fish oil // Biotechnol. Lett. 2011. V. 33. № 10. P. 2065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0671-z
Sheldon R.A., van Pelt S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how // Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013. V. 42. № 15. P. 6223. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60075k
Cui J.D., Zhang S., Sun L.M. Cross-Linked enzyme aggregates of phenylalanine ammonia lyase: Novel biocatalysts for synthesis of L-phenylalanine // Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012. V. 167. № 4. P. 835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9738-0
Diaz-Vidal T., Armenta-Perez V.P., Rosales-Rivera L.C., Mateos-Díaz J.C., Rodríguez J.A. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates of recombinant Candida antarctica lipase B for the efficient synthesis of olvanil, a nonpungent capsaicin analogue // Biotechnol. Prog. 2019. V. 35. № 4. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2807
Li K., Wang J., He Y., Cui G., Abdulrazaq M.A., Yan Y. Enhancing enzyme activity and enantioselectivity of Burkholderia cepacia lipase via immobilization on melamine-glutaraldehyde dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles // Chem. Eng. J. 2018. V. 351. P. 258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.086
Murtaza G., Rizvi A.S., Irfan M., Yan D., Khan R.U., Rafique B., Xue M., Meng Z.S. Glycated albumin based photonic crystal sensors for detection of lipopolysaccharides and discrimination of gram-negative bacteria // Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020. V. 1117. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.018
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Журнал аналитической химии