Агрохимия, 2023, № 5, стр. 77-82
Способ получения, исследование структуры и механических свойств композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титан” сельскохозяйственного назначения
А. С. Баикин 1, *, А. А. Мельникова 1, А. В. Михайлова 1, 2, М. А. Каплан 1, Е. О. Насакина 1, К. В. Сергиенко 1, С. В. Конушкин 1, Е. П. Севостьянова 2, Е. В. Степанова 2, С. В. Железова 2, А. П. Глинушкин 2, М. А. Севостьянов 1, 2
1 Институт металлургии и материаловедения им. А.А. Байкова РАН
119332 Москва, Ленинский просп., 49, Россия
2 Всероссийский научно-исследовательский институт фитопатологии
143050 Московская обл., Одинцовский р.-н, р.п. Большие Вяземы, ул. Институт, влад. 5, Россия
* E-mail: imet@imet.ac.ru
Поступила в редакцию 09.12.2022
После доработки 09.01.2023
Принята к публикации 16.02.2023
- EDN: URMUFA
- DOI: 10.31857/S0002188123050034
Аннотация
Биопротекторные материалы для сельского хозяйства являются важной частью современного мира. Для их разработки используют широкий спектр различных соединений. Например, диоксид титана помимо защитных свойств положительно влияет на усваиваемость питательных веществ, улучшает эффективность удобрений и, соответственно, позволяет снизить их потребление, что особенно важно в современном мире. Однако прямое введение диоксида титана является малоэффективным из-за процессов его потери. Наилучшим вариантом является пролонгированное выделение, обеспечивающее требуемую для растения концентрацию диоксида титана в почве. Введение в полимерную матрицу диоксида титана может решить эту задачу за счет постепенного высвобождения. В свою очередь к такой полимерной матрице предъявляется целый ряд требований их свойств. Возможным решением может быть хитозан – нетоксичный, неиммуногенный, антимикробный, биологически безопасный и биодеградируемый материал. В работе рассмотрено получение композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана” в гранулярной форме. Исследована эффективность материала с массовыми соотношениями хитозана к диоксиду титана 1 : 1, 2 : 1 и 3 : 1, а также хитозана без диоксида титана. Исследована структура и механические свойства полученных композиционных материалов.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Удобрения являются основным методом повышения плодородия почв. Из-за высокой растворимости, низкой термической стабильности и небольшого молекулярного веса обычных удобрений бóльшая часть питательных веществ теряется в окружающей среде из-за поверхностного стока, денитрификации, выщелачивания и улетучивания, что приводит к низкой эффективности удобрений [1]. Кроме того, использование обычных удобрений является дорогостоящим из-за низкой эффективности использования питательных веществ [2]. Таким образом, поиск новых видов/поколений/вариантов модификации удобрений является актуальной темой в последние десятилетия. Широкий круг исследований приходится на разработку инкапсулированных удобрений, обладающих возможностью длительного высвобождения активных агентов и обеспечивающих повышение эффективности удобрений за счет снижения растворимости питательных веществ, в то же время сохраняя требуемое питание для роста растений [3]. Достаточно подробный обзор таких материалов произведен в работе [4]. Однако эти исследования направлены исключительно на введение этих материалов в состав удобрения, и на данный момент существует очень широкий круг удобрений пролонгированного действия, основанных на различных принципах.
Большой областью исследований стало внедрение нанотехнологий в разработку и использование инновационных удобрений. Благодаря уникальным свойствам наноматериалов, это направление обладает большим потенциалом. Текущее состояние развития наноудобрений хорошо обобщено и обсуждено в нескольких недавних обзорных статьях [6–8].
Относительно новым направлением является изучение влияния непосредственно различного вида наночастиц на рост растений, качество плодов, эффективность удобрений в целом. Многочисленные исследования показали перспективность использования биопротекторных веществ (например TiO2, Ag, SiO2, ZrO2, CeO2 и др.), позволяющих в перспективе сократить применение удобрений [9–13]. Данные вещества способны помимо биопротекторных свойств влиять на усвояемость и эффективность удобрений, позволяя в том числе сократить их требуемое количество. Ключевым звеном для создания препаратов такого типа является наличие адекватного материала, обладающего специальными свойствами, среди которых обязательными являются экологическая совместимость с окружающей средой и глобальными биосферными круговоротными циклами, т.е. разрушаемость, безопасность для живой и неживой природы; длительная (недели и месяцы) сохраняемость в природной среде и контролируемая деструкция с образованием нетоксичных продуктов; химическая совместимость с пестицидами и удобрениями; возможность переработки доступными способами, совместимыми с технологиями изготовления ядохимикатов. Среди материалов, которые могут оказаться пригодными для этих целей, – разрушаемые полимеры различного происхождения [14]. Анализ литературы свидетельствует об активном развитии работ, направленных на синтез и изучение полимеров на основе производных карбоновых кислот. Наряду с полилактидами и полигликолидами из полиэфиров, способных к биоразложению, особое место занимает хитозан [15]. Он известен своей нетоксичностью, неиммуногенностью, способностью к заживлению ран и антимикробными свойствами, что делает его подходящим кандидатом для реализации цели проекта. В структуре хитозана присутствуют активные амино- и гидроксильные функциональные группы. На них можно закреплять предлагаемые препараты, что обеспечивает их выход по мере биодеградации полимера.
В данной работе был выбран диоксид титана TiO2. Исследования показали, что в требуемых дозах TiO2 способен положительно влиять на рост растений, особенно на усваиваемость растениями фосфора [16, 17]. TiO2 активируют также биодоступность питательных микроэлементов (Zn, Cu и Fe) и Al [18]. Эти результаты свидетельствуют о том, что TiO2 имеет некоторое сродство с фосфатными соединениями и ионами металлов в почве, чтобы переводить их в растворимую форму, что увеличивает их биодоступность.
Равномерная иммобилизация диоксида титана в матрицу хитозана ведет к его минимальным потерям, повышению стабильности, предотвращению агрегации. Поэтому предполагали наибольшую эффективность диоксида титана в композиционном материале “хитозан–TiO2”. Цель работы – разработать способ получения и исследовать структуру и механические свойства композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титан” для сельскохозяйственного назначения.
МЕТОДИКА ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Для получения композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана” вначале готовили раствор, состоящий из 0.9 мл ортофосфорной кислоты (Компонент-реактив, Россия, 87 мас. %) и 18 мл дистиллированной воды. Далее, при комнатной температуре в нем растворяли навеску высокомолекулярного хитозана (Sigma-Aldrich, США) массой 0.375 г при постоянном помешивании до гомогенного состояния (среднее время растворения составляло 1 ч). В полученный раствор добавляли порошок диоксида титана массой 0.25, 0.5 или 0.75 г (с массовыми соотношениями хитозана к диоксиду титана 1 : 1, 2 : 1 и 3 : 1) и перемешивали для равномерного распределения в объеме. Так же готовили раствор хитозана без добавления диоксида титана для сравнения. Гранулы композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана” получали капельным методом. Для этого приготовленный раствор капали в избыток аммиака водного (Компонент-реактив, Россия, 87 мас. %) и оставляли минимум на 6 ч. После чего гранулы промывали дистиллированной водой. Для высушивания полученных гранул композиционного материала их сначала замораживали в течение 5 ч при температуре –19°С, далее помещали в лиофильную сушку.
Анализ структуры композиционного материала выполнили на оптическом микроскопе “Альтами МЕТ”, оснащенного специализированной цифровой видеокамерой “Альтами U3CMOS14000KA” высокого разрешения. Для анализа изображений и изучения структуры полученного композиционного материала была использована лицензионная программа Altami Studio 4.0 Pro, с фильтром “Мультифокус”, позволявшим собрать из изображений с разным фокусным расстоянием одну картинку таким образом, чтобы все ее элементы были в фокусе.
Электронно-микроскопические исследования образцов проводили при помощи сканирующего электронного микроскопа “Hitachi TM4000”. Для исследования в растровом режиме морфологии частиц образцы наклеивали на медную подложку при помощи проводящего углеродного клея.
Механические свойства изученных образцов определяли в условиях статического сжатия на универсальной испытательной машине “Instron 3382” со скоростью нагружения 0.5 мм/мин. На одну экспериментальную точку испытывали по 3–5 образцов.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ИХ ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
На рис. 1 представлен общий вид полученных гранул композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана”. Гранулы имели сферическую форму, диаметр составлял ≈5 мм. На рис. 2, 3 показана структура полученных образцов композиционных материалов “хитозан–диоксид титана” с различным соотношением компонентов композиции.
Рис. 2.
Структура полученного хитозана: слева – оптический микроскоп, справа – сканирующий электронный микроскоп (СЭМ). То же на рис. 3.
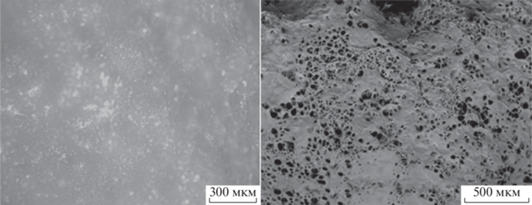
Рис. 3.
Структура композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана”, с отношением компонентов: (а) – 3 : 1, (б) – 2 : 1, (в) – 1 : 1.
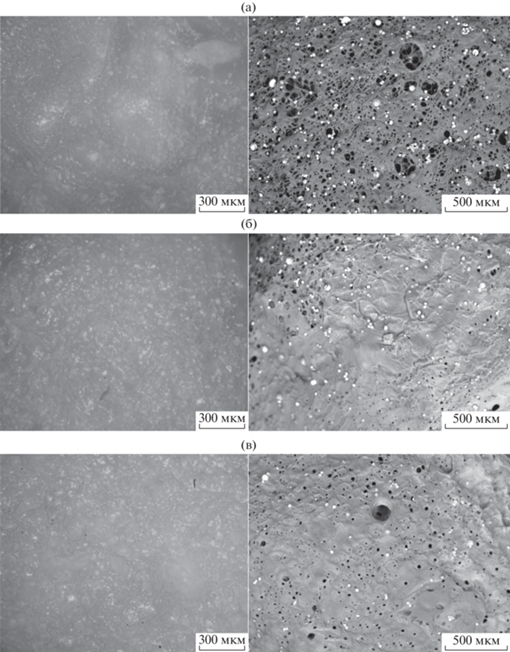
Анализируя полученные изображения, можно отметить относительно равномерное распределение частиц диоксида титана. Они располагаются как на поверхности хитозана, так и внутри полученной матрицы. Их размер варьируется от 10 до 100 мкм. Частицы имеют сферическую форму. Можно отметить, что сферические частицы диоксида титана в некоторых местах имеют разломы. По данным разломам видно, что сферические частицы диоксида титана образованы вытянутыми стержнями. Такая структура скорее всего объясняется процессом сшивки хитозана в аммиаке и последующей сушкой. Композиционный материал вне зависимости от концентрации диоксида титана обладает пористой структурой, что достигается выбранным способом лиофильной сушки.
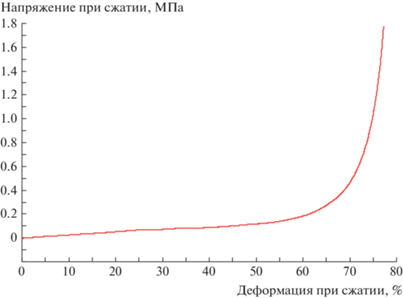
На рис. 4 представлена зависимость напряжения при сжатии от деформации. Напряжение при сжатии рассчитывали по формуле: σ = F/dгр, где σ – напряжение при сжатии, МПа, F – сила, приложенная к образцу, при сжатии, dгр – диаметр гранулы, м2. Исходя из структурного исследования композиционного материала, можно обозначить 2 составляющие, определяющие механизм сопротивления сжатию (механические характеристики): непосредственно материал гранулы (хитозан или хитозан–диоксид титана) и каркас пор, образованных этим материалом. Механизм деформирования гранул можно разделить на 3 этапа. На первом этапе (от 0 до 50–60% деформации при сжатии) работа деформирования переходит в разрушение каркаса пор и незначительное сжатие материала каркаса. На 2-м этапе (от 50–60 до 65–75% деформации при сжатии) преобладает сжатие материала гранул и остаточное уплотнение пор вплоть до их полного закрытия. Дальнейшая деформация ведет к прессованию материала гранул. Данная зависимость характерна для всех полученных образцов, внесение диоксида титана во всех изученных концентрациях не влияло на этот процесс.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Таким образом, в работе рассмотрен способ получения композиционного материала “хитозан–диоксид титана” с различным содержанием диоксида титана. Показана структура полученных образцов композиционного материала. Отмечена пористая структура с равномерным распределением частиц диоксида титана во всех рассмотренных вариантах концентраций диоксида титана.
Введение диоксида титана не приводило к заметному изменению механических свойств при сжатии полученного композиционного материала. Деформация при сжатии достигала порядка 70–75%, после чего начиналось прессование материала.
Список литературы
Stanley N., Mahanty B. Preparation and characterization of biogenic CaCO3-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol-alginate hydrogel as controlled-release urea formulation // Polym. Bull. 2019. V. 77. P. 529–540.
Vishwakarma K., Upadhyay N., Kumar N., Tripathi D.K., Chauhan D.K., Sharma S., Sahi S. Potential applications and avenues of nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture // Academic Press. 2018. V. 1. P. 473–500.
Babadi F.E., Yunus R., Rashid S.A., Salleh M.M., Ali S. New coating formulation for the slow release of urea using a mixture of gypsum and dolomitic limestone // Particuology. 2015. V. 23. P. 62–67.
Sim D.H.H., Tan I.A.W., Lim L.L.P., Hameed B.H. Encapsulated biochar-based sustained release fertilizer for precision agriculture. A review // J. Cleaner Product. 20 June 2021. V. 303. 127018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127018
Liu R., Lal R. Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions // Sci. Total Environ. 2015. V. 514. P. 131–139.
Dimkpa C.O., Bindraban P.S. Nanofertilizers: new products for the industry? // J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02150
Kah M., Kookana R.S., Gogos A., Bucheli T.D. A critical evaluation of nanopesticides and nanofertilizers against their conventional analogues // Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0131-1
Raliya R., Saharan V., Dimkpa C., Biswas P. Nanofertilizer for precision and sustainable agriculture: current state and future perspectives // J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02178
Sangeeta Chavan, Vishwas Sarangdhar, Vigneshwaran Nadanathangam. Toxicological effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on plant growth promoting soil bacteria // Emerg. Contamin. 2020. V. 6. P. 87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2020.01.003
Selma M.H., Jawad A.L., Taha Ali A., Salim M.M. Synthesis and characterization of pure and Fe doped TiO2 thin films for antimicrobial activity // Optik. 2017. V. 142. P. 42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.05.048
Sreeja S., Shetty K.V. Photocatalytic water disinfection under solar irradiation by Ag@TiO2 core-shell structured nanoparticles // Solar Energy. 2017. V. 157. P. 236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.07.057
Grégori D., Benchenaa I., Chaput F., Thérias S., Gardette J.-L., Léonard D., Guillard C., Parola S. Mechanically stable and photocatalytically active TiO2/SiO2 hybrid films on flexible organic substrates // J. Mater. Chem. 2014. V. 2. P. 20096–20104. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03826F
Vladkova T., Angelov O., Stoyanova D., Gospodinova D., Gomes L., Soares A., Mergulhao F., Ivanova I. Magnetron co-sputtered TiO2/SiO2/Ag nanocomposite thin coatings inhibiting bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation // Surface Coat. Technol. 2020. V. 384. Iss. 125322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125322
Xing Y., Yang H., Guo X., Bi X., Liu X., Xu Q., Wang Q., Li W., Li X., Shui Y., Chen C., Zheng Y. Effect of chitosan/Nano-TiO2 composite coatings on the postharvest quality and physicochemical characteristics of mango fruits // Sci. Horticult. 2020. V. 263. Iss. 109135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.109135
González-Saucedo A., Barrera-Necha L.L., Ventura-Aguilar R.I., Correa-Pacheco Z.N., Bautista-Baños S., Hernández-López M. Extension of the postharvest quality of bell pepper by applying nanostructured coatings of chitosan with Byrsonima crassifolia (L.) Kunth extract // Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019. V. 149. P. 74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.11.019
Waani S.P.T., Irum S., Gul I., Yaqoob K., Khalid M.U., Ali M.A., Manzoor U., Noor T., Ali S., Rizwan M., Arshad M. TiO2 nanoparticles dose, application method and phosphorous levels influence genotoxicity in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), soil enzymatic activities and plant growth // Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021. V. 213. Iss. 111977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111977
Bakshi M., Liné C., Bedolla D.E., Stein R.J., Kaegi R., Sarret G., Pradas del Real A.E., Castillo-Michel H., Abhilash P.C., Larue C. Assessing the impacts of sewage sludge amendment containing nano-TiO2 on tomato plants: A life cycle study // J. Hazard. Material. 2019. V. 369. P. 191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.036
Ullah S., Adeel M., Zain M., Rizwan M., Irshad M.K., Jilani G., Hameed A., Khan A., Arshad M., Raza A., Baluch M.A., Rui Y. Physiological and biochemical response of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to TiO2 nanoparticles in phosphorous amended soil: A full life cycle study // J. Environ. Manag. 2020. V. 263. Iss. 110365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110365
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.