Коллоидный журнал, 2023, T. 85, № 4, стр. 410-423
Влияние содержания магнетита и специфичности ионов никеля(II) на электрокинетические свойства композитов на основе пористых кремнеземных частиц
А. В. Волкова 1, *, Е. С. Лопатина 1, Е. В. Соловьева 1, Л. Э. Ермакова 1
1 Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет
199034 Санкт-Петербург,
Университетская наб. 7-9, Россия
* E-mail: anna.volkova@spbu.ru
Поступила в редакцию 02.05.2023
После доработки 27.05.2023
Принята к публикации 30.05.2023
- EDN: ALPSDK
- DOI: 10.31857/S0023291223600323
Аннотация
Получены порошки магнетита и его композитов на основе частиц макропористого высококремнеземного стекла с различным содержанием Fe3O4. Методами РФА, РФЭС и спектроскопии КРС подтверждено образование фазы магнетита во всех железосодержащих образцах. Методами СЭМ и ЭДС исследована морфология и элементный состав поверхности композитных пористых частиц. Установлено, что наблюдается различная степень модифицирования внешней поверхности пористых кремнеземных частиц. Показано, что в растворах индифферентного электролита положение изоэлектрической точки (ИЭТ) и значения дзета-потенциала композитов совпадают. Для композитных частиц наблюдаются две изоэлектрические точки на зависимостях дзета-потенциала от рН растворов хлорида никеля. В разбавленных растворах, содержащих специфически сорбирующийся ион никеля, и значениях рН меньше рНИЭТ-2 на электрокинетические свойства композитных частиц в первую очередь оказывает влияние содержание фазы магнетита в композитном порошке, а при достаточно высоких концентрациях ионов Ni2+ их специфичность по отношению к оксидным поверхностям.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Решение требующих все более пристального внимания природоохранных задач, таких как очистка водных ресурсов от различного рода загрязнителей (органических соединений, ионов тяжелых металлов), насущных проблем медицины и биохимии, разноплановых аналитических задач определяет потребность в получении новых универсальных и экологически безопасных материалов, которые могут быть использованы в качестве сорбентов, химических и биологических сенсоров, фотокатализаторов, материалов для адресной доставки лекарственных веществ и т.д. Среди получаемых материалов для решения существующих проблем оксидные наночастицы и их дисперсии вызывают повышенный и неослабевающий интерес. Однако, несмотря на то, что функциональность индивидуальных наночастиц достаточно высока, ее существенно ограничивает их склонность к агрегации в жидких средах. Этот недостаток может быть устранен путем иммобилизации наночастиц на различных матрицах, часто пористых ввиду высоких значений удельной поверхности.
В качестве неорганических матриц наиболее востребованы пористые материалы на основе диоксида кремния (в основном в виде частиц – силикагель, мезопористые кремнеземы и т.д.), что обусловлено уникальным комплексом свойств SiO2: химической устойчивостью в широком диапазоне рН, биосовместимостью, низкой токсичностью и стоимостью [1–3]. Возможность направленного модифицирования диоксида кремния широким рядом химических соединений и биомолекул увеличивает селективность композитов, наличие свободного порового пространства позволяет, например, использовать пористые частицы оксида кремния как носители лекарственных средств, что значительно расширяет возможности применения композитов на их основе для решения задач аналитики, биотехнологий, медицины. В качестве пористой кремнеземной матрицы успешно используются и пористые стекла (ПС) – продукты химической проработки двухфазных щелочноборосиликатных (ЩБС) стекол [4–6]. ПС обладают всеми необходимыми для матрицы характеристиками, такими как механическая прочность, химическая, термическая и микробиологическая устойчивость, стабильность свойств во времени, способность к регенерации, большой объем сквозных разветвленных наноразмерных пор (от единиц до сотен нанометров) [7–9].
В последние годы большое внимание уделяется магнитным наночастицам, повышенный интерес среди которых вызывают частицы магнетита Fe3O4 благодаря их низкой токсичности, биосовместимости, хорошим сорбционным свойствам в сочетании с суперпарамагнитизмом, что дает возможность управлять их перемещением под действием постоянного магнитного поля. Наночастицы Fe3O4 находят широкое практическое применение в качестве сорбентов для очистки воды от ионов тяжелых металлов [10] и различных органических соединений (красителей, лекарственных средств, пестицидов и т.д.) [11], катализатора в гетерогенном Фентон-процессе (в том числе, фото-Фентон процессе) [1, 12, 13], в биомедицинских приложениях, таких как гипертермия при лечении рака, селективное разделение белков, клеток, ДНК, адресная доставка лекарств, в качестве контрастного агента для магнитно-резонансной томографии [14–17], для решения аналитических задач (определения, концентрирования, выделения анализируемых соединений), в том числе с помощью активно развивающегося метода магнитной твердофазной экстракции (МТФЭ), в котором отделение наносорбента происходит с помощью внешнего магнитного поля вместо традиционного центрифугирования и фильтрования, что значительно упрощает, ускоряет и удешевляет процесс [15].
Получение композиционных материалов на основе пористых кремнеземных частиц и магнетита позволяет не только решить проблему агрегации последних в жидких средах, но и получить композиты с улучшенными или новыми функциональными свойствами по сравнению с исходными материалами, что обуславливает перспективность их успешного практического применения в качестве магнитных высокоэффективных сорбентов [18–21], катализаторов [22], носителей лекарственных средств, контрастных агентов [23, 24] и т.д.
Наиболее часто композиционные магнетитсодержащие материалы на основе пористых кремнеземных частиц получают кристаллизацией частиц Fe3O4 непосредственно в порах [25–29]. Основным методом получения таких композитов является пропитка мезопористой матрицы водными растворами или расплавами солей железа(III) с последующим термолизом и частичным восстановлением оксида железа(III) до оксида железа(II). При этом морфология синтезируемых в порах частиц определяется параметрами пористой структуры. Как видно, в таких системах магнитная компонента введена в пористую матрицу, а на поверхности композитной частицы содержатся только силанольные группы, наличие которых отвечает за возможность функционализации поверхности различными органическими соединениями, определяет функциональные свойства таких материалов в жидких средах.
По сравнению с количеством работ по получению частиц магнетита в порах кремнеземных матриц лишь единичные работы посвящены синтезу композитных частиц на основе Fe3O4 и пористых силикатов по типу “ядро–оболочка”, полученных локализацией наночастиц магнетита на поверхности пористых частиц SiO2. Такого типа материалы обычно получают либо добавлением порошков пористых кременеземов к дисперсиям предварительно синтезированных наночастиц магнетита [30, 31], либо в процессе совместного гидролиза солей железа(II) и (III) в щелочной среде в присутствии пористых частиц SiO2 [32]. При этом вопрос о влиянии соотношения компонентов на степень модифицирования поверхности кремнеземных частиц, а, следовательно, и на их электроповерхностные свойства в жидких средах, которые в значительной мере определяют функциональные свойства подобных материалов, не обсуждается и остается открытым.
Следует также учитывать, что электроповерхностные свойства, помимо состава и структуры синтезируемых материалов, определяются составом дисперсионной среды, в том числе растворов электролитов, содержащих многозарядные неорганические или органические ионы, способные к специфической сорбции. Так, например, при использовании частиц в качестве сорбентов ионов тяжелых металлов (никеля(II), свинца(II), железа(III) и т.д.) при подборе оптимальных условий сорбции необходимо учитывать влияние концентрации и специфичности этих ионов на положение изоэлектрической точки (ИЭТ) и точки нулевого заряда (ТНЗ), величину и знак дзета-потенциала и заряда поверхности. В связи с вышесказанным представляет как фундаментальный, так и практический интерес исследование комплексного влияния состава поверхности композитных частиц и специфичности многозарядного катиона на примере ионов никеля на электроповерхностные свойства частиц SiO2–Fe3O4.
Таким образом, целью работы было получение магнетитсодержащих материалов на основе частиц пористого стекла по типу “ядро–оболочка” и исследование влияния содержания железосодержащей фазы (степени покрытия пористых кремнеземных частиц магнетитом) и специфичности катиона на их электрокинетические свойства в растворах хлорида натрия и никеля в широкой области значений рН и ионной силы электролита.
ЭСПЕРИМЕНТАЛЬНАЯ ЧАСТЬ
В качестве пористой кремнеземной матрицы для синтеза магнетитсодержащих композитов был выбран порошок макропористого стекла, полученного из двухфазного щелочноборосиликатного стекла марки ДВ-1 (7Na2O–23B2O3–70SiO2 (мол. %)). Порошок магнетита был получен гидролизом смеси 5 × 10−3 М раствора хлорида железа(II) FeCl2 ⋅ H2O (≥98%, Carl Roth) и 10−2 М раствора хлорида железа(III) FeCl3 ⋅ 6H2O (≥99%, Sigma Aldrich), взятых в стехиометрическом соотношении 1 : 2 в щелочной среде (рН изменяли, добавляя по каплям раствор гидроксида аммония до достижения неизменного значения pH 10–11). Синтез проводился при комнатной температуре при постоянном перемешивании с помощью механической мешалки. После достижения постоянного значения рН дисперсию магнетита перемешивали в течение 60 мин. Далее полученную дисперсию отмывали деионизированной водой до нейтрального значения рН (5.6–5.8), сушили при 80°С до полного испарения воды и последовательно термообрабатывали в течение 1 часа при температурах 120 и 200°С по аналогии с режимом сушки пористого стекла. Практический выход магнетита составил 1.2 г/л. Для получения композитных порошков с содержанием магнетита 5, 10 и 20 мас. % (FeПС-5, FeПС-10, FeПС-20, соответственно) с учетом практического выхода по Fe3O4 к раствору хлоридов железа(II) и (III) до начала гидролиза были при перемешивании добавлены соответствующие по массе навески пористого стекла. Полученная дисперсия перемешивалась при помощи механической мешалки в течение 30 мин. Далее процедура синтеза композитов была аналогична получению порошка магнетита. Таким образом, при различных массовых соотношениях оксидов вследствие гетероадагуляции синтезируемых нанодисперсных частиц магнетита на поверхности пористых частиц SiO2 были получены композиционные материалы по типу “ядро–оболочка”.
Общая пористость (W) исходного ПС определялась весовым методом. Для этого навеска порошка ПС (mc), высушенного при 200°С, заливалась водой. По прошествии двух дней воду сливали, а избыток воды с порошка убирали фильтровальной бумагой. Полученный таким образом влажный образец взвешивали (mм). Величину общей пористости рассчитывали по формуле (1):
(1)
${W = \frac{{{{m}_{{\text{м}}}} - {{m}_{{\text{с}}}}}}{{{{m}_{{\text{м}}}} - {{m}_{{\text{с}}}} + {{m}_{{\text{с}}}}{\text{/}}{{\rho }_{{{\text{ст}}}}}}}},$Удельная поверхность исследованных образцов S0 была определена методом БЭТ по тепловой десорбции азота с хроматографической регистрацией. Из значений S0 были также найдены величины средних радиусов пор ПС по формуле (2):
и среднего размера частиц магнетита по формуле (3): где плотность магнетита ρ принималась равной 5.2 г/см3.Морфология и структура полученных материалов были изучены методом сканирующей электронной микроскопии (СЭМ). Содержание и распределение атомов железа в композитных порошках были определены методом энергодисперсионной рентгеновской спектроскопии (ЭДС). В этих исследованиях, проводившихся в Междисциплинарном ресурсном центре по направлению “Нанотехнологии” Научного парка СПбГУ, использовался сканирующий электронный микроскоп Carl Zeiss Merlin (Carl Zeiss Merlin, Германия) с системой энергодисперсионного рентгеновского микроанализа Oxford Instruments INCAx-act (Великобритания).
Качественный и количественный анализы, изучение электронной структуры и валентно-координационного состояния железа на поверхности частиц магнетита и железосодержащих композитов были выполнены методом рентгеновской фотоэлектронной спектроскопии (РФЭС) с использованием комплексного фотоэлектронного и растрового оже-электронного спектрометра Thermo Fisher Scientific Escalab 250Xi (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Великобритания) в Ресурсном центре Научного парка СПбГУ “Физические методы исследования поверхности”.
Рентгенофазовый (РФА) и рентгеноструктурный анализы (РСА) полученных железосодержащих материалов были выполнены в Ресурсном центре Научного парка СПбГУ “Рентгенодифракционные методы исследования” с использованием настольного порошкового дифрактометра Bruker “D2 Phaser” (Bruker AXS, Германия) и программного обеспечения TOPAS и PDXL 2.0.
Спектры комбинационного рассеяния (КР) зарегистрированы на спектрометре LabRam-HR 800 (Horiba Jobin-Yvon, Франция) в Ресурсном центре Научного парка СПбГУ “Оптические и лазерные методы исследования вещества”. Для возбуждения спектров была использована линия с длиной волны 632.8 нм He-Ne лазера. Мощность лазерного излучения на образце составляла 1 мВт.
Определение электрокинетических свойств частиц полученных порошков (электрофоретическая подвижность (Ue) и дзета-потенциал (ζ)) было выполнено методом лазерного допплеровского электрофореза на анализаторе Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments, Великобритания) при предварительном термостатировании в течение 2 мин при 20°С в универсальной капиллярной U-образной кювете (DTS1070) с интегрированными позолоченными электродами. В первом приближении электрокинетический потенциал частиц рассчитывался по уравнению Смолуховского:
(4)
${{\zeta }^{S}} = \frac{{{\eta }}}{{\varepsilon {{\varepsilon }_{{\text{0}}}}}}{{U}_{{\text{e}}}},$Для синтеза железосодержащих образцов и приготовления растворов электролитов использовалась деионизированная вода, удельная электропроводность которой не превышала 1.5 × 10−6 Ом−1 см−1 (система очистки воды Аквалаб AL Plus). рН растворов электролитов задавали с помощью 3 × 10−2 и 10−1 М растворов соляной кислоты и гидроксида натрия. Определение рН среды проводили на рН-метре SevenMulti (Mettler Toledo).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ИХ ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Структура, морфология, элементный и фазовый состав исследуемых материалов
СЭМ изображения исходного пористого стекла приведены на рис 1. Как видно из рис. 1а и 1б, порошок ПС полидисперсен, средний размер частиц варьируется от 150 нм до 200 мкм. Результаты определения структурных характеристик частиц пористого стекла показали, что объемная пористость составила 0.76, величина удельной поверхности 100 м2/г, а средний радиус пор, рассчитанный по уравнению (2), составил 29 нм. Полученные данные согласуются с результатами исследования структуры методом сканирующей электронной микроскопии (рис. 1в).
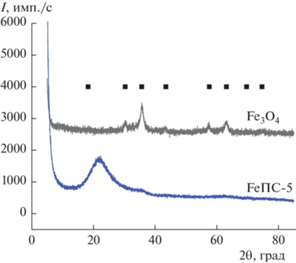
Результаты рентгенофазового анализа некомпозитного железосодержащего порошка свидетельствовали об образовании фазы магнетита (рис. 2). Средний размер кристаллита Fe3O4, определенный методом рентгеноструктурного анализа, составил 6.7 нм. Рентгенограммы композитных образцов (в качестве примера на рис. 2 приведена рентгенограмма для композита FeПС-5 соответствуют рентгеноаморфным образцам, что, по-видимому, свидетельствует о том, что размер частиц железосодержащей фазы в композитах менее 5 нм. Следует, однако, отметить, что при значениях 2θ = 35.68° (относительная интенсивность пика магнетита 100%) на рентгенограммах композитных образцов наблюдаются слабые пики, отвечающие за наличие в них железосодержащей фазы.
Рис. 2.
Рентгенограмма полученных образцов магнетита и композита на основе ПС, содержащего 5 мас. % железосодержащей фазы.
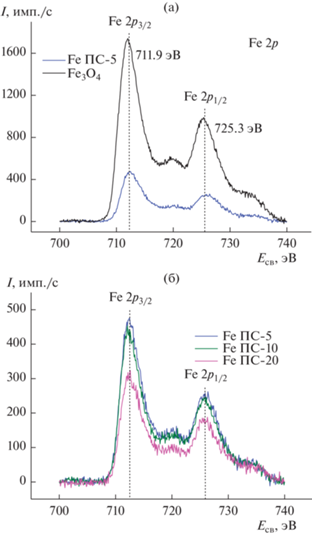
На рис. 3 приведен рентгеновский фотоэлектронный спектр Fe2p для синтезированного Fe3O4, представляющий собой типичный для фазы магнетита асимметричный дублет с максимальными значениями энергии связи 2р3/2 и 2р1/2 711.9 и 725.3 эВ, соответственно, что хорошо согласуется с литературными данными [33, 24 ]. Результаты аппроксимации пиков с помощью функции Гаусса показали, что в Fe2p спектре помимо пиков, соответствующих состояниям Fe3+ и Fe2+ в магнетите, наблюдаются сателлитные пики Fe3+, что, по-видимому, свидетельствует о наличии на поверхности магнетита примесного количества фазы Fe2O3 вследствие частичного окисления Fe2+.
Об образовании фазы магнетита в композитных порошках также свидетельствуют результаты рентгеновской фотоэлектронной спектроскопии. Видно (рис. 4), что спектры Fe2p для композитных материалов полностью соответствуют таковому для синтезированного порошка магнетита. Анализ результатов деконволюции пика O1s РФЭ спектра композита FeПС-5 (рис. 5а) и сравнение O1s спектров для всех композиционных образцов (рис. 5б) также свидетельствуют о наличии фазы магнетита в композитах. Энергия связи 530.9 эВ (малиновый пик для FeПС-5 и черный для магнетита (рис. 5а)) соответствует значению связи (Eсв) Fe–O в магнетите [33, 34]. Пики при энергиях 533.0 и 533.6 эВ, по всей видимости, соответствуют энергиям связи Si–O–Si и Si–O–H соответственно [35, 36].
Рис. 4.
Спектр РФЭС 2р-электронов железа в магнетите (а) и его композитах на основе ПС с содержанием Fe3O4: 5 а, б), 10 (б) и 20 мас. % (б).
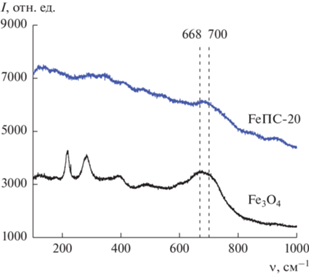
Формирование фазы магнетита во всех железосодержащих образцах было также подтверждено с помощью спектроскопии комбинационного рассеяния, являющейся высокоинформативным методом идентификации оксидов железа и их различных кристаллических модификаций. Из полученных спектров КР (рис. 6) магнетита и композита FeПС-20 (аналогичного спектрам FeПС-5 и FeПС-10) видно, что об образовании фазы магнетита в образцах свидетельствует характеристичная полоса 668 см−1, которая является его главным маркером [37, 38]. При этом полоса 700 см−1 говорит о наличии маггемита (γ-Fe2O3) на поверхности железосодержащих частиц. Вероятно, именно он является той примесной фазой железа, окисленного до Fe3+, которая определена в спектрах РФЭС. Следует отметить, что более интенсивная базовая линия в спектре FeПС-20 в сравнении со спектром Fe3O4 говорит о меньшем размере железосодержащих частиц в композите, так как рэлеевское рассеяние, определяющее фоновый сигнал, проявляется сильнее. Это подтверждает данные рентгенофазового и рентгеноструктурного анализoв. Следует также отметить, что в спектре синтезированного Fe3O4 присутствуют две интенсивные компоненты в области 200–300 см−1, соответствующие фазе гематита. Подобный фазовый переход характерен для магнетита, подверженного длительному лазерному воздействию в процессе съемки спектров КР, вследствие нагрева образца [39].
Рис. 6.
КР спектры полученных образцов магнетита и композита на основе ПС, содержащего 20 мас. % железосодержащей фазы.
Результаты определения удельной поверхности всех исследованных образцов показали (табл. 1), что значения удельной поверхности композиционных материалов FeПС лежат между величинами S0 для исходного стекла (100 м2/г) и магнетита (197 м2/г) и растут по мере увеличения содержания фазы Fe3O4 в композите. Из величины удельной поверхности магнетита был рассчитан средний размер частиц по формуле (3), который составил 5.8 нм. Данное значение хорошо согласуется с размерами частиц, определенными методами рентгеноструктурного анализа, а также сканирующей электронной микроскопии (рис. 7а).
Таблица 1.
Удельная поверхность всех исследованных образцов
| Образец | S0, м2/г |
|---|---|
| ПС | 100 |
| FeПС-5 | 116 |
| FeПС-10 | 138 |
| FeПС-20 | 153 |
| Fe3O4 | 197 |
Рис. 7.
СЭМ изображения полученных образцов: магнетит (а); внешняя поверхность композитных частиц FeПС с различным общим содержанием железосодержащей фазы в порошках: 5 (б), 10 (в), 20 мас. % (г).
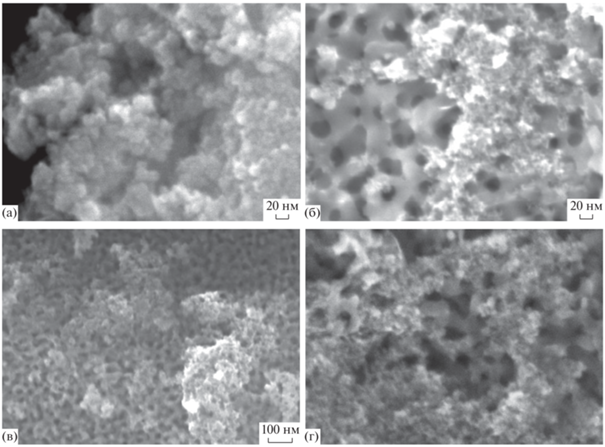
На рис. 7б–7г приведены СЭМ изображения поверхности частиц пористого стекла, модифицированного магнетитом, при различном содержании железосодержащей фазы в композитных порошках. Видно, что частицы магнетита находятся, главным образом, на внешней поверхности пористых частиц, которая, в свою очередь, покрыта ими неравномерно. Методом СЭМ было установлено, что в композиционных порошках, независимо от содержания Fe3O4, степень покрытия частиц ПС различна – от практически немодифицированной поверхности до практически полностью покрытой магнитной фазой. Это подтверждали и результаты ЭДС анализа (табл. 2), и визуально определенное различие в скорости движения частиц композитов в постоянном магнитном поле. Анализ всех полученных СЭМ изображений образцов FeПС показал, что синтезируемая железосодержащая фаза преимущественно покрывает внешнюю поверхность частиц пористого стекла. Следует отметить, что отдельных агрегатов магнетита в порошках методами СЭМ и ЭДС обнаружено не было.
Таблица 2.
Результаты ЭДС анализа спиртовых дисперсий композитов с различным содержанием магнетита (кремниевая подложка, содержание элементов в ат. %)
| FeПС-5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Спектр | C | O | Fe |
| 1 | 20.93 | 72.76 | 6.30 | |
| 2 | 18.83 | 76.98 | 4.19 | |
| 3 | 15.32 | 84.68 | 0.00 | |
| 4 | 22.67 | 71.98 | 5.36 | |
| 5 | 21.18 | 73.05 | 5.77 | |
| 6 | 14.37 | 85.63 | – | |
| 7 | 9.28 | 90.72 | – | |
| 8 | 12.45 | 87.55 | – | |
| FeПС-10 | ||||
 |
Спектр | C | O | Fe |
| 1 | 28.27 | 56.60 | 15.14 | |
| 2 | 22.94 | 66.64 | 10.42 | |
| 3 | 23.96 | 62.32 | 13.72 | |
| 4 | 21.41 | 70.04 | 8.55 | |
| 5 | 21.98 | 72.18 | 5.83 | |
| 6 | 16.37 | 80.06 | 3.57 | |
| 7 | 21.48 | 70.76 | 7.76 | |
| FeПС-20 | ||||
 |
Спектр | C | O | Fe |
| 1 | 28.15 | 67.08 | 4.77 | |
| 2 | 29.18 | 64.53 | 6.30 | |
| 3 | 22.24 | 77.76 | – | |
| 4 | 24.08 | 75.92 | – | |
| 5 | 23.23 | 76.77 | – | |
Электрокинетические свойства частиц магнетита, ПС и композитов на их основе
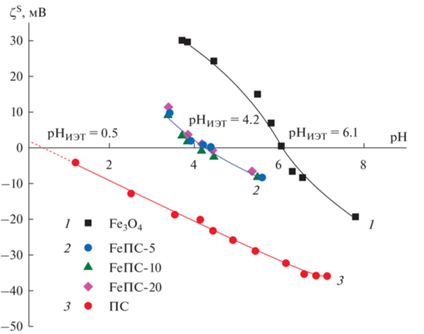
Зависимости величин электрокинетического потенциала частиц всех исследуемых образцов от рН на фоне 10−2 М растворов хлорида натрия приведены на рис. 8. Видно, что значение ИЭТ (рНИЭТ = 4.2 ± 0.1) практически не зависит от содержания в композитах железосодержащей фазы и занимает промежуточное положение между рНИЭТ для ПС (рНИЭТ ≅ 0.5) и магнетита (рНИЭТ = 6.1 ± 0.1). Видно также, что в растворе индифферентного электролита абсолютные величины дзета-потенциала частиц композитных образцов совпадают в пределах погрешности эксперимента во всем исследованном интервале рН. Следует отметить, что в электрофоретическом движении участвовала только самая высокодисперсная фракция исходных и композитных пористых частиц с размером не более 1 мкм.
Рис. 8.
Зависимость электрокинетического потенциала ζS частиц всех исследованных образцов от pH на фоне 10–2 M раствора NaCl.
Из рис. 9 видно, при постоянной ионной силе раствора электролита (10−2 М) высокая специфичность катиона Ni2+ по сравнению с ионом натрия приводит к появлению более сложных зависимостей дзета-потенциала частиц всех исследуемых образцов от рН. Как известно, специфическая сорбция катионов смещает положение ТНЗ в сторону меньших, а ИЭТ – в сторону больших значений рН по сравнению с их значениями в индифферентном электролите. Высокой специфичностью иона никеля к поверхности магнетита и сдвигом ИЭТ от значения 6.1 ед. рН в более щелочную область, видимо, и обусловлено наблюдаемое постоянство достаточно высоких положительных значений дзета-потенциала частиц магнетита во всей исследованной области рН (рис. 9, кривая 1).
Рис. 9.
Зависимость электрокинетического потенциала частиц исследованных образцов от pH при ионной силе 10–2 M раствора NiCl2 (закрашенные точки – средние значения дзета-потенциала, незакрашенные точки – значения пиков на кривой распределения дзета-потенциала).
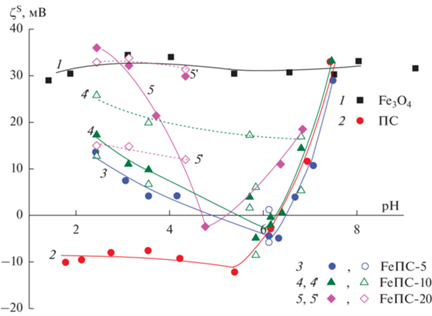
Согласно данным работы [40], для натриевоборосиликатных ПС в растворах хлорида никеля характерно наличие двух изоэлектрических точек. ИЭТ-1 лежит в области рН 0.5–1.5 и соответствует положению изоэлектрической точки для ПС в растворах индифферентных электролитов, что согласуется с данными, приведенными на рис. 8 для исследуемого в данной работе ПС. По-видимому, в области малых значений поверхностного заряда двухзарядный ион не проявляет своей специфичности и ведет себя как индифферентный. Как видно из рис. 9 (кривая 2), при рН > pHИЭТ-1 наблюдается область отрицательных значений дзета-потенциала. Однако по мере роста рН растет значение заряда поверхности и, по-видимому, специфичность ионов Ni2+ к силикатной поверхности, что, в свою очередь, приводит к перезарядке в слое Штерна и появлению ИЭТ-2 при рН = 6.3 ± 0.1.
Для композитов “пористое стекло–магнетит” также характерно наличие двух изоэлектрических точек на зависимостях средних значений дзета-потенциала композитных частиц от рН при I (NiCl2) = 10−2 М, значения которых приведены в табл. 3. Из данных табл. 3 также видно, что с увеличением содержания магнетита значение ΔрНИЭТ (ΔрНИЭТ = рНИЭТ-2 – рНИЭТ-1), т.е. область отрицательных значений дзета-потенциала уменьшается, по-видимому, вследствие более полного покрытия поверхности частиц ПС, участвующих в электрофоретическом движении, железосодержащей фазой. Из рис. 9 также видно, что при рН < рНИЭТ-2 средние значения абсолютной величины электрокинетического потенциала занимают, как правило, промежуточное положение между таковыми для исходного ПС и магнетита, причем при рН < рНИЭТ-1, чем выше содержание магнетита в композите, тем больше положительное значение дзета-потенциала при рН = const. Следует отметить, что для композита FeПС-20 при рН ≤ 3.2 значения дзетаS-потенциала совпадают в пределах погрешности эксперимента с таковыми для магнетита.
Таблица 3.
Значения рН изоэлектрических точек ПС и композитов на его основе в растворах хлорида никеля
| Образец | рНИЭТ | ΔрНИЭТ |
|---|---|---|
| ПС | 0.5 6.3 |
5.8 |
| FeПС-5 | 4.9 6.5 |
1.6 |
| FeПС-10 | 5.5 6.3 |
0.8 |
| FeПС-20 | 4.7 5.2 |
0.5 |
Видно также, что при рН > рНИЭТ-2 для FeПС-5 и FeПС-10 зависимости дзета-потенциала от рН близки к таковым для исходного ПС, тогда как для FeПС-20, как и при рН < рНИЭТ-2, занимают промежуточное значение между величинами электрокинетического потенциала частиц исходного ПС и магнетита. По-видимому, при рН > рНИЭТ-2 и содержании Fe3O4 до 10 мас. % электрокинетическое поведение композитных частиц определяется уже, главным образом, специфичностью ионов никеля к силикатной поверхности, а не содержанием железосодержащей фазы на поверхности частиц. Следует отметить, что при рН ~ 7 значения дзета-потенциала частиц магнетита, ПС и композитов совпадает в пределах погрешности эксперимента.
Анализ экспериментальных данных также показал, что на кривых распределения дзета-потенциала частиц композитных образцов в ряде случаев наблюдались два максимума, значения которых приведены на рис. 9 в виде незакрашенных точек. По всей видимости, это свидетельствует о различной степени покрытия поверхности пористых стеклянных частиц магнетитом, что заметным образом проявляется в электрокинетическом поведении композитных систем в растворах, содержащих специфически сорбирующийся ион никеля, при достаточно высоком содержании Fe3O4 (композиты FeПС-10 и FeПС-20, кривые 4' и 5' соответственно). Совпадение максимальных значений дзета-потенциала частиц композитного порошка FeПС-20 с таковыми для магнетита при рН < 5 может свидетельствовать как о высокой степени модифицирования поверхности части пористых частиц магнитной фазой, так и наличием в композитном порошке отдельных агрегатов наночастиц Fe3O4.
На рис. 10 приведены зависимости дзета-потенциала частиц магнетита и ПС, а также их композитов от ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля при естественном значении рН (рис. 11). Видно, что электрокинетический потенциал частиц магнетита положителен и практически не зависит от ионной силы растворов NiCl2, при этом значения рН дисперсий совпадают в пределах погрешности с таковыми для исходных растворов (за исключением I = 10−1 М). Специфичность ионов никеля к поверхности стекла приводит к изменению знака потенциала двойного электрического слоя в слое Штерна и появлению ИЭТ при ионной силе раствора хлорида никеля 3.5 × 10−3 М. Как видно из рис. 10, заметные различия в значениях дзета-потенциала частиц композитов, а именно уменьшение абсолютных величин |ζS| при увеличение содержания Fe3O4 при I = const, наблюдаются в растворах хлорида никеля с ионной силой 10−6–10−3 М. При дальнейшем увеличении ионной силы раствора NiCl2 значения дзета-потенциала частиц композитов, независимо от содержания железосодержащей фазы, практически совпадают. Изоэлектрическое состояние для композитных систем достигается при I = 5 × 10−2 М. Таким образом, видно, что при достаточно высокой концентрации ионов никеля при 3.5 × 10−3 М < I < 5 × 10−2 М значения дзета-потенциала частиц ПС и магнетита положительны, а частиц композитов – отрицательны. Принимая во внимания значения рН дисперсий (рис. 11) в исследованном интервале ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля, видно, что полученные результаты согласуются с результатами, приведенными на рис. 9.
Рис. 10.
Зависимость электрокинетического потенциала частиц исследованных образцов от ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля при естественном значении рН.
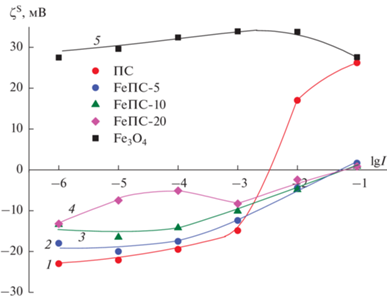
Рис. 11.
Зависимость равновесных значений рН дисперсионной среды от ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля после 30 мин их контакта с твердой фазой.
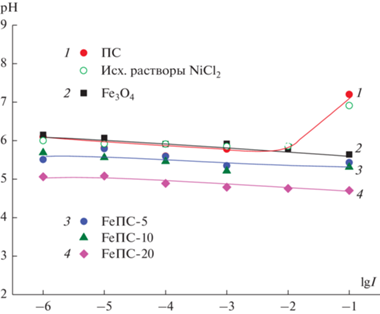
Анализ изменений рН дисперсий по сравнению с величинами рН растворов NiCl2 показывает (рис. 11), что при I = 10−1 М поверхность магнетита заряжена отрицательно (рН дисперсии меньше, чем рН фонового раствора), причем его поверхностный заряд существенно превышает по абсолютной величине заряд кремнеземной поверхности. Видно, что при одинаковом соотношении суммарной площади поверхности навески и объема фонового раствора величина рН дисперсии магнетита снизилась на единицу, тогда как рН суспензии ПС и фонового раствора практически совпадали в пределах погрешности эксперимента. Видно также, что во всей исследованной области составов растворов NiCl2 поверхностный заряд полученных композитов отрицателен, причем его абсолютная величина максимальна для композита FeПС-20. По-видимому, в растворах хлорида никеля и в области рН 5.7−5.9 магнетит заряжен отрицательно, что означает существенное смещение точки нулевого заряда Fe3O4 в кислую область по сравнению с индифферентным электролитом NaCl.
Таким образом, из анализа полученных результатов видно, что по изменению электрокинетических свойств композитных частиц по сравнению с исходными материалами можно косвенно судить о степени модифицирования поверхности, причем влияние количественного состава композита наиболее выражено в растворах, содержащих специфически сорбирующийся ион, что, несомненно, следует учитывать при возможном использовании данных композитных материалов в сорбционных и каталитических процессах очистки воды от ионов тяжелых металлов и органических загрязнителей, при решении аналитических задач по выделению, концентрированию и разделению различных органических веществ.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Получены порошки магнетита и магнетитсодержащих композитных материалов с различным содержанием железосодержащей фазы (5–20 мас. %) на основе частиц высококремнеземного макропористого стекла. Образование фазы магнетита и формирование композиционных частиц подтверждено методами РФА, РФЭС, спектроскопии КРС, СЭМ, ЭДС.
Установлено, что в растворе индифферентного электролита (NaCl) рНИЭТ = 4.2 и значения дзета-потенциала композитных частиц практически не зависят от содержания магнетита. Специфичность катиона Ni2+ к поверхности исследуемых оксидов приводит к появлению сложных зависимостей дзета-потенциала всех исследуемых частиц от рН и ионной силы растворов NiCl2. В растворах хлорида никеля электрокинетические свойства композитных частиц зависят как от общего содержания железосодержащей фазы в композите, так и степени покрытия поверхности пористых стеклянных частиц Fe3O4. На зависимостях дзета-потенциала композитных частиц от рН появляются две изоэлектрические точки. С увеличением содержания магнетита в композитном порошке область отрицательных значений дзета-потенциала сужается, по-видимому, вследствие более полного покрытия поверхности частиц ПС железосодержащей фазой. При естественном рН наблюдаемая специфичность ионов никеля к поверхности стекла приводит к перезарядке в слое Штерна и появлению ИЭТ при I = 3.5 × 10–3 М. Изоэлектрическое состояние для композитных систем, независимо от содержания, магнетита достигается в более концентрированном растворе NiCl2 (I = 5 × 10–2 М).
При значениях ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля выше 10–2 М или при рН > рНИЭТ-2 при прочих равных условиях электрокинетические свойства исходных и композитных пористых частиц определяются в первую очередь специфичностью ионов никеля к кремнеземной поверхности. Определяющее влияние содержания железосодержащей фазы на коллоидно-химические свойства композитов возрастает по мере удаления от положения рНИЭТ-2 в сторону меньших значений рН и уменьшении ионной силы растворов хлорида никеля.
Список литературы
Feijoo S., González-Rodríguez J., Fernández L. et al. Fenton and photo-Fenton nanocatalysts revisited from the perspective of life cycle assessment // Catalysts. 2020. V. 10. № 1. P. 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010023
Shariatinia Z., Esmaeilzadeh A. Hybrid silica aerogel nanocomposite adsorbents designed for Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution // Water Environment Research. 2019. V. 91. № 12. P. 1624–1637. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1162
Kondrashova N.B., Shamsutdinov A.S., Batueva T.D. et al. Preparation and properties of iron oxide doped mesoporous silica systems // Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials. 2020. V. 30. P. 2081–2088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01370-2
Viter R., Geveluk S., Smyntyna V., Doycho I. Optical properties of nanoporous glass filled with TiO2 nanostructures // Optica Applicata. 2012. V. XLII. № 2. P. 307–313. https://doi.org/10.5277/oa120208
Zapotoczny B., Dudek M.R., Guskos N. et al. FMR study of the porous silicate glasses with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles fillers // Journal of Nanomaterials. 2012. V. 2012. P. 341073. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/341073
Burak Ertuş E., Vakifahmetoglu C., Öztürk A. Enhanced methylene blue removal efficiency of TiO2 embedded porous glass // Journal of the European Ceramic Society. 2021. V. 41. № 2. P. 1530–1536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.09.047
Мазурин О.В., Роскова Г.П., Аверьянов В.И., Антропова Т.В. Двухфазные стекла: структура, свойства, применение. Ленинград: Наука, 1991. 276 с.
Enke D., Janowski F., Schwieger W. Porous glasses in the 21st century—a short review // Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 2003. V. 60. № 1–3. P. 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(03)00329-9
Inayat A., Reinhardt B., Herwig J. et al. Recent advances in the synthesis of hierarchically porous silica materials on the basis of porous glasses // New Journal of Chemistry. 2016. V. 40. № 5. P. 4095–4114. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ03591K
Konate A., He X., Zhang Z. et al. Magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles reduce heavy metals uptake and mitigate their toxicity in wheat seedling // Sustainability. 2017. V. 9. № 5. P. 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050790
Makarchuk O.V., Dontsova T.A., Astrelin I.M. Magnetic nanocomposites as efficient sorption materials for removing dyes from aqueous solutions // Nanoscale Research Letters. 2016. V. 11. P. 161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1364-2
Nidheesh P.V. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the abatement of organic pollutants from aqueous solution: A review // RSC Advances. 2015. V. 5. № 51. P. 40552–40577. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02023A
Rehman A., Daud A., Warsi M.F. et al. Nanostructured maghemite and magnetite and their nanocomposites with graphene oxide for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue // Materials Chemistry and Physics. 2020. V. 256. P. 123752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123752
Arsalani S., Guidelli E.J., Silveira M.A. et al. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by natural rubber latex as MRI contrast agent // Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 2019. V. 475. P. 458–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.11.132
Толмачева В.В, Апяри В.В., Кочук Е.В., Дмитриенко С.Г. Магнитные сорбенты на основе наночастиц оксидов железа для выделения и концентрирования органических соединений // Журнал аналитической химии. 2016. Т. 71. № 4. С. 339–356. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934816040079
Першина А.Г., Сазонов А.Э., Мильто И.В. Использование магнитных наночастиц в биомедицине // Бюллетень сибирской медицины. 2008. № 2. С. 70–78.
Zhao D.L., Zhang H.L., Zeng X.W. et al. Inductive heat property of Fe3O4/polymer composite nanoparticles in an ac magnetic field for localized hyperthermia // Biomed. Materials. 2006. V. 1 № 4. P. 198–201. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/1/4/004
Yiu H.H.P., Keane M.A., Lethbridge Z.A.D. et al. Synthesis of novel magnetic iron metal-silica (Fe-SBA-15) and magnetite-silica (Fe3O4-SBA-15) nanocomposites with a high iron content using temperature-programed reduction // Nanotechnology. 2008. V. 19. № 25. P. 255606. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/25/255606
Juang R.-S., Chien C.-C., Yao C.-L. et al. Preparation of magnetically recoverable mesoporous silica nanocomposites for effective adsorption of urea in simulated serum // Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers. 2018. V. 91. P. 22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.05.022
Kim J.H., Cha B.J., Kim Y.D., Seo H.O. Kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption on the Fe-oxide nanoparticles embedded in the mesoporous SiO2 // Advanced Powder Technology. 2020. V. 31. № 2. P. 816–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.11.036
Hong Y., Cha B.J., Kim Y.D., Seo H.O. Mesoporous SiO2 particles combined with Fe oxide nanoparticles as a regenerative methylene blue adsorbent // ACS Omega. 2019. V. 4. № 6. P. 9745−9755. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00726
Mazilu I., Ciotonea C., Chirieac A. et al. Synthesis of highly dispersed iron species within mesoporous (Al‑)SBA-15 silica as efficient heterogeneous Fenton-type catalysts // Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017. V. 241. P. 326–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.12.024
Tao C., Zhu Y. Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for potential delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and hyperthermia // Dalton Transactions. 2014. V. 43. № 41. P. 15482–15490. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4dt01984a
El-Boubbou K., Ali R., Al-Zahrani H. et al. Preparation of iron oxide mesoporous magnetic microparticles as novel multidrug carriers for synergistic anticancer therapy and deep tumor penetration // Scientific Reports. 2019. V. 9. P. 9481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46007-z
Huang H., Ji Y., Qiao Z. et al. Preparation, characterization, and application of magnetic Fe-SBA-15 mesoporous silica molecular sieves // J. Autom. Methods Manage. Chem. 2010. V. 2010. P. 323509. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/323509
Стовпяга Е.Ю., Еуров Д.А., Курдюков Д.А. и др. Синтез кластеров оксидов железа в мезопорах монодисперсных сферических частиц кремнезема // Физика твердого тела. 2017. Т. 59. № 8. С. 1598–1603.
Surowieca Z., Wiertel M., Budzynski M. et al. Magnetite nanowires in MCM-41 type mesoporous silica templates // Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 2008. V. 354. № 35−39. P. 4271–4274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.06.032
Napolsky K., Eliseev A., Knotko A. Preparation of ordered magnetic iron nanowires in the mesoporous silica matrix // Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2003. V. 23. № 1−2. P. 151–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-4931(02)00252-7
Cuello N.I., Oliva M.I., Rodriguez Torres C.E. et al. Study on magnetite nanoparticles embedded in mesoporous silica obtained by a straightforward and biocompatible method // Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 2020. V. 145. P. 109535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109535
Карсакова Ю.В., Тихомирова Т.И. Магнитные сорбенты на основе химически модифицированных кремнеземов: получение и свойства // Сорбционные и хроматографические процессы. 2018. Т. 18. № 6. С. 846–852. https://doi.org/10.17308/sorpchrom.2018.18/612
Munasir N., Setyaningsih S., Yanasin et al. Phase and magnetic properties of Fe3O4/SiO2 natural materials-based using polyethylene glycol media // IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2019. V. 515. № 1. P. 012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/515/1/012017
Богачев Ю.В., Гареев К.Г., Матюшкин Л.Б. и др. Исследование суспензии наночастиц магнетита методами фотометрии и ЯМР-релаксометрии // Физика твердого тела. 2013. Т. 55. № 12. С. 2313–2317.
Elmi Ch., Brigatti M.F., Guggenheim S. et al. Crystal chemistry and surface configurations of two polylithionite-1M crystals // American Mineralogist. 2014. V. 99. № 10. P. 2049–2059. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2014-4908
Zhu Y., Yue M., Natarajan V. et al. Efficient activation of persulfate by Fe3O4@β-cyclodextrin nanocomposite for removal of bisphenol A // RSC Advances. 2018. V. 8. № 27. P. 14879–14887. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01696H
Chi Y., Yuan Q., Li Y. et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2-Ag magnetic nanocomposite based on small-sized and highly dispersed silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol // Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 2012. V. 383. № 1. P. 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.06.027
Choi Y., Kim T., Lee H. et al. Bottom-up plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of SiO2 by utilizing growth inhibition using NH3 plasma pre-treatment for seamless gap-fill process // Scientific Reports. 2022. V. 12. P. 15756. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20201-y
Shebanova O.N., Lazor P. Raman spectroscopic study of magnetite (FeFe2O4): A new assignment for the vibrational spectrum // Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 2003. V. 174. № 2. P. 424–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-4596(03)00294-9
Slavov L., Abrashev M.V., Merodiisk T. et al. Raman spectroscopy investigation of magnetite nanoparticles in ferrofluids // Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 2010. V. 322. № 14. P. 1904–1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.01.005
Testa-Anta M., Ramos-Docampo M.A., Comesana-Hermo M.A. et al. Raman spectroscopy to unravel the magnetic properties of iron oxide nanocrystals for biorelated applications // Nanoscale Advances. 2019. V. 1. № 6. P. 2086–2103. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NA00064J
Ермакова Л.Э., Кузнецова А.С., Антропова Т.В., Волкова А.В. Структурные и электрокинетические характеристики высококремнеземных пористых стекол в растворах хлорида никеля // Коллоидный журнал. 2021 Т. 83. № 4. С. 394–403. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0023291221030046
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Коллоидный журнал





