Геотектоника, 2023, № 4, стр. 32-55
Строение литосферы и условия формирования подводных поднятий приантарктического сектора Южной Атлантики на основе плотностного и физического моделирования
Е. П. Дубинин 1, 2, Д. А. Рыжова 1, 2, *, А. И. Чупахина 1, А. Л. Грохольский 1, А. А. Булычев 2
1 Научно-учебный Музей Землеведения МГУ им. М.В. Ломоносова
119991 Москва,
д. 1, Ленинские горы, Россия
2 Московский государственный университет имени М.В. Ломоносова,
геологический факультет
119991 Москва, д. 1, Ленинские горы, Россия
* E-mail: dasha_0292r@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 21.04.2023
После доработки 03.06.2023
Принята к публикации 16.06.2023
- EDN: UAVGWX
- DOI: 10.31857/S0016853X23040057
Аннотация
Кинематическая реорганизация границ плит, сопровождаемая отмиранием старых и формированием новых центров спрединга и проявлениями плюмовой магматической активности в юго-восточной части антарктического сектора Южной Атлантики, привела к формированию сложного структурного плана региона. Следствием этих процессов стало образование системы хребтов, поднятий и плато, имеющих различную морфологическую выраженность и различные геофизические характеристики. Результаты плотностного моделирования строения коры и тектоносферы по профилям, протягивающимся от Фолклендского плато до Мозамбикского хребта и пересекающим серию поднятий и хребтов, разделенных глубоководными котловинами, показали, что поднятия имеют различное строение коры, что свидетельствует о различном их происхождении. Условия формирования подводных поднятий разных типов, были изучены на основании физического моделирования. Построена новая экспериментальная модель формирования литосферы и подводных поднятий региона, важную роль в которой сыграли раскол крупной магматической провинции Агульяс на собственно плато Агульяс и поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия, аккреция океанической коры на спрединговом хребте Агульяс и последующий перескок оси спредингового хребта Агульяс, приведший к прекращению спрединга на этом хребте и формированию южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта и сопряженных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас. Перескоки осей спрединга, сопровождаемые периодической активностью горячих точек сыграли важную роль в формировании подводных поднятий разных генетических типов, что в свою очередь предопределило различное строение их коры.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Южная Атлантика и прилегающая юго-западная часть Индийского океана характеризуются общей историей развития, которая началась с раскола юго-западной части суперконтинента Гондваны около 190‒180 млн лет назад и связана с отделением Африки и Южной Америки от Антарктиды и раскрытием Атлантического и Индийского океанов. Район исследований представляет собой литосферный клин между литосферой Атлантического и Индийского океанов, ограниченный крупными разломными системами Агульяс‒Фолклендским, Дю-Туа–Эндрю Бейн–Принц Эдуард.
Дно рассматриваемой акватории сформировано сложным сочетанием океанических котловин (Африкано-Антарктической, Мозамбикской, Агульяс, Транскей, Капской и др.), сегментов современных (Юго-западный Индийский хребет (ЮЗИХ), Срединно-Атлантический хребет (САХ)) и палео-спрединговых хребтов (хребет Агульяс), внутриокеанических поднятий (Мод, Северо-Восточная Георгия, Айлос Оркадас, Метеор, Мозамбикский хребет и др.), краевых плато (Фолклендское, Агульяс), микроконтинентов (поднятия Бейра и Мориса Юинга) (рис. 1).
Рис. 1.
Рельеф дна антарктического сектора Южной Атлантики (по данным [54], с дополнениями). Хребты: САХ – Срединно-Атлантический хребет; ААХ – Американо-Антарктический хребет; КХ – Китовый хребет; МадХ – Мадагаскарский хребет; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; ХА – хребет Агульяс; ХШ – хребет Шона; ЮЗИХ ‒ Юго-Западный Индийский хребет; ЮСАХ – Южный сектор Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Поднятия: ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПБ – поднятие Бейра; ПДК – поднятие Дель Кано; ПК – поднятие Крозе; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПМо – поднятие Мод; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия. Бассейны: БН – бассейн Натал; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн. Плато: ПА – плато Агульяс; ФП – Фолклендское плато. Котловины: КГ – котловина Георгия; КТ – котловина Транскей; МадК ‒ Мадагаскарская котловина; МозК – Мозамбикская котловина. Горячая точка: ГТБ – Буве; ГТД – Дискавери; ГТК – Крозе; ГТМ – Марион; ГТШ – Шона. Обозначено: ТСБ – тройное соединение Буве; БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; ГД – подводные горы Дискавери; АФРЗ – Агульяс-Фолклендская разломная зона. 1 – ось срединно-океанических хребтов; 2 – ось палеоспредингового хребта Агульяс (ПХА); 3 – горячие точки; 4 – положение профилей
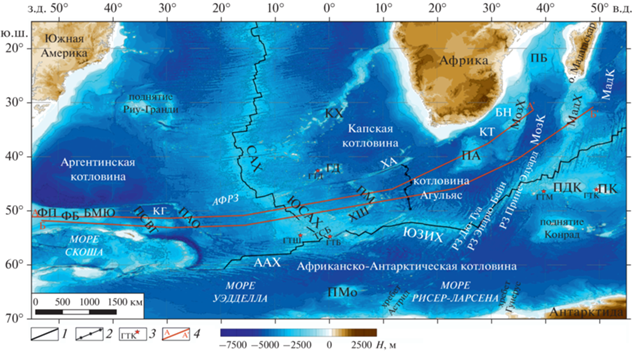
Рельеф крупнейших морфоструктур осложнен многочисленными неравномерно распределенными по акватории небольшими поднятиями, подводными горами, трогами разломных и шовных зон разного генезиса.
Разнообразие структур и картина геофизических полей, отражают гетерогенное строение коры и литосферы и свидетельствуют о ее сложной эволюции, для которой были характерны неоднократные кинематические реорганизации геометрии границ плит, осложненные активной деятельностью горячих точек Шона, Буве, Дискавери. Кинематические перестройки сопровождались перескоками осей спрединга, приводящими к отмиранию одних спрединговых хребтов и образованию других, что, в свою очередь, отражалось в аномальных геофизических полях и, в частности, в нарушении последовательности и простирания линейных магнитных аномалий и плотностной структуры литосферы.
Целью настоящей работы является установление особенностей глубинного строения коры и литосферы подводных поднятий вдоль ее трансатлантического сечения на основе плотностного моделирования и выявление с помощью физического моделирования геодинамических условий формирования поднятий разных генетических типов.
ГЕОЛОГО-ГЕОФИЗИЧЕСКАЯ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКА ПОДВОДНЫХ ПОДНЯТИЙ ПРИАНТАРКТИЧЕСКОГО СЕКТОРА ЮЖНОЙ АТЛАНТИКИ
Представленные в данном регионе подводные поднятия различаются по своей морфологии. Многие из них приурочены к палео- и современным границам плит и располагаются вблизи срединно-океанических хребтов, трансформных разломов и шовных зон палеограниц плит, разделяющих разновозрастные блоки литосферы.
Большой объем доступных геолого-геофизических материалов свидетельствуют о разной выраженности подводных поднятий в геофизических полях и разном глубинном строении исследуемых структур, их различном происхождении и помогает восстановить условия их формирования и развития в свете пространственно-временнóй эволюции литосферы всего региона (рис. 2).
Рис. 2.
Геофизическая характеристика антарктического сектора Южной Атлантики. (а) – карта аномального поля силы тяжести в свободном воздухе ∆gсв.в, (по данным [54]); (б) – карта аномального поля силы тяжести в редукции Буге ∆gБ; (в) – аномальное магнитное поле ∆Та (по данным [44]); (г) – графики аномального поля силы тяжести в свободном воздухе, в редукции Буге и рельефа дна вдоль трансатлантического Профиля-1. Хребт-ы: САХ – Срединно-Атлантический хребет; ААХ – Американо-Антарктический хребет; КХ – Китовый хребет; МадХ – Мадагаскарский хребет; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; ХА – хребет Агульяс; ХШ – хребет Шона; ЮЗИХ ‒ Юго-Западный Индийский хребет; ЮСАХ – Южный сектор Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Поднятия: ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПБ – поднятие Бейра; ПДК – поднятие Дель Кано; ПК – поднятие Крозе; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПМо – поднятие Мод; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия. Бассейны: БН – бассейн Натал; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн. Плато: ПА – плато Агульяс; ФП – Фолклендское плато. Котловины: КГ – котловина Георгия; КТ – котловина Транскей; МадК ‒ Мадагаскарская котловина; МозК – Мозамбикская котловина. Горячая точка: ГТБ – Буве; ГТД – Дискавери; ГТК – Крозе; ГТМ – Марион; ГТШ – Шона. Обозначено: ТСБ – тройное сочление Буве; БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; ГД – подводные горы Дискавери; АФРЗ – Агульяс-Фолклендская разломная зона. 1 – ось срединно-океанических хребтов; 2 – ось палеоспредингового хребта Агульяс (ПХА); 3 – горячие точки; 4 – положение профилей
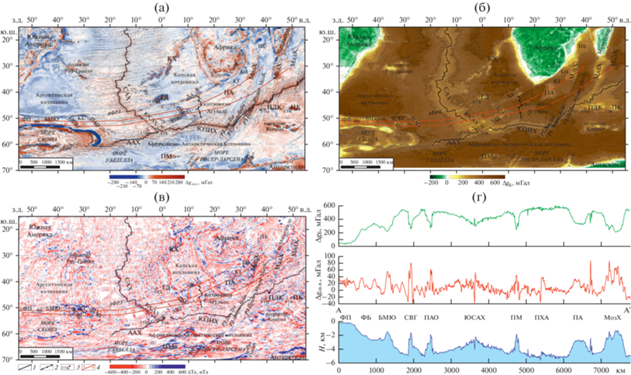
В работе были использованы:
‒ батиметрические данные (Global Predicted Bathymetry) [54];
‒ аномалии силы тяжести в свободном воздухе [54], полученные по спутниковым данным;
‒ модель аномального магнитного поля EMAG2v3 [44];
‒ модель сейсмотомографии SL2013sv [55];
‒ данные о возрасте океанического дна, полученные на основе анализа аномального магнитного поля [47].
Палеоспрединговый хребет Агульяс
Палеоспрединговый хребет Агульяс располагается в центральной части котловины Агульяс и ограничивается с севера Агульяс-Фолклендской разломной зоной. Ограничение хребта с юга трудно определимо вследствие сложной морфологии дна в результате деятельности горячей точки Шона (см. рис. 1). Хребет пересекают четыре палеотрансформных разлома, сформированные в процессе спрединга. В рельефе дна палеоспрединговый хребет слабо выражен.
Океаническая кора, сформированная на спрединговом хребте Агульяс ранее входила в состав плиты Мальвинес.
La Brecque and et al. [35] первыми предположили существование плиты Мальвинес в западной части бассейна Агульяс, формирование ее коры проходило между хронами 34 и 31. Считается, что спрединг на хребте Агульяс начался ~96 млн лет [40]. Отмечалась асимметрия плиты, а именно ‒ различие в размерах плиты к западу и востоку от палеоспредингового хребта [35].
Marks and et al. [40] в исследованиях, основанных на данных детального изучения линейных магнитных аномалий в бассейне Агульяс, показали, что асимметричное строение плиты обусловлено бо́льшей скоростью спрединга в восточной части плиты Мальвинес. Скорости на начальных стадиях на востоке оцениваются в 4.33 см/год, на западе – 2.38 см/год. После хрона 33 спрединг имел симметричный характер [40].
Мы полагаем, что наряду с асимметричным спредингом, объяснение асимметрии котловины Агульяс связано с прекращением спрединга на хребте Агульяс, перескоком спрединговой оси к западу и формированием Южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта (ЮСАХ), на древней литосфере котловины Агульяс, часть которой (котловина Георгия) в результате этого процесса оказалась западнее современного ЮСАХ.
Ось палеоспредингового хребта Агульяс фиксируется в аномалиях гравитационного поля в свободном воздухе интенсивным (до –40 мГал) минимумом, а в аномалиях в редукции Буге хребет отмечается слабозаметной линейной аномалией амплитудой до 560 мГал (см. рис. 2, а, б).
Южный сегмент Срединно-Атлантического хребта
Южный сегмент Срединно-Атлантического хребта (ЮСАХ) протягивается от 48° ю.ш. до 55° ю.ш. на расстояние около 800 км между Агульяс-Фолклендской разломной зоной и зоной тройного сочленения Буве (ТСБ). Скорость спрединга на этом отрезке ЮСАХ составляет 3.2–3.6 см/год [3, 9]. Для данного сегмента характерна симметричная картина линейных магнитных аномалий, начиная с хроны С30.
Южный сегмент САХ имеет строение, характерное для медленно-спрединговых хребтов Атлантики. Однако структурная сегментация и морфологическая выраженность его осевой зоны меняются вдоль простирания хребта с севера на юг.
На севере хребет имеет характерную морфологию рифтовой долины с глубиной дна достигающей 3000 м, в центральной части отмечается максимальная глубина до 4000 м, в южной части наблюдается повышение уровня дна осевой зоны до 2000 м и местами ‒ до 1000 м и морфология южной части хребта принимает вид осевых поднятий (см. рис. 1).
В северной части сегмента осевая зона смещается на несколько десятков километров поперечными трансформными разломами. Угол между простиранием хребта и направлением растяжения составляет ~70°, т.е. для данного участка характерен косой спрединг.
По мере приближения к тройному сочленению Буве трансформные разломы исчезают, а их место занимают нетрансформные смещения оси спрединга, разбивающие рифтовую ось на более короткие сегменты с меньшей величиной смещения. По всей видимости, это связано с влиянием термической аномалии, создаваемой горячими точками Буве и Шона, которое уменьшает прочность литосферы [10, 11].
Гравитационное поле в свободном воздухе хорошо коррелируется с морфологией хребта. Южный сегмент САХ проявляется положительными значениями поля силы тяжести в свободном воздухе, амплитудой до 50 мГал (см. рис. 2, а). Осевая часть с хорошо выраженной рифтовой долиной фиксируется отрицательной аномалией гравитационного поля (до –40 мГал), зоны разломов также проявляются отрицательными значениями поля (–10…–35 мГал). Участки на юге сегмента с морфологией осевого поднятия отмечаются положительными аномалиями.
В гравитационном поле в редукции Буге хорошо отражена степень прогретости осевой литосферы и подлитосферной мантии. ЮСАХ проявлен повышенными значениями поля силы тяжести в редукции Буге (250–320 мГал) (см. рис. 2, б). Для южного окончания хребта, которое находится в зоне влияния горячих точек, характерен минимум аномального гравитационного поля, амплитуда которого варьирует от 10 до 130 мГал.
В магнитном поле Южный сегмент САХ обладает характером аномалий, типичным для спрединговых хребтов (см. рис. 2, в). Он отмечается симметричными относительно его оси линейно-вытянутыми аномалиями северо-западного простирания, целостность которых нарушается в зонах разломов. В южной части ЮСАХ, по сравнению с северным участком, интенсивность осевой аномалии выше и варьирует от –440 нТл до 360 нТл, к периферии амплитуда аномалий уменьшается до –40–50 нТл.
Поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас (сопряженные структуры)
Поднятия Айлос Оркадас и Метеор являются сопряженными асейсмическими хребтами, образованными в позднем мелу–раннем палеоцене в результате продвижения к югу рифтовой зоны ЮСАХ [3, 34, 50] (см. рис. 1). При возникновении они представляли собой единую структуру, сформированную магматической активностью горячей точки Шона, и впоследствии оказались разнесенными на 2500 км друг от друга в результате рифтогенного раскола литосферы плиты Мальвинес ~62‒59 млн лет назад, а также смещения к западу литосферного блока Фолклендского плато [16, 30, 35, 38].
Сопряженные поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадос расположены:
‒ поднятие Метеор ‒ между 3° и 12° в.д. (к востоку от оси САХ);
‒ поднятие Айлос Оркадас ‒ между 30° и 21° з.д. (к западу от оси САХ).
В рельефе данные структуры имеют сходное строение и выражены в форме локальных поднятий субмеридионального простирания высотой 2000–2500 м и шириной 150‒200 км (см. рис. 2, г).
Вулканическая активность, связанная с деятельностью горячей точки Шона, больше проявлялась в южных частях поднятий и, судя по строению рельефа, была более интенсивной в районе поднятия Метеор [35, 38, 61].
Различия в структуре фундамента двух поднятий и пространственное распределение вулканизма свидетельствуют о некоторой асимметрии в процессах рифтогенеза, в которых формировались поднятия.
Ciesielskian et al. [18] считают, что оба поднятия были сформированы в течение короткого интервала времени в раннем палеоцене во время формирования Южного сегмента САХ.
Поднятие Метеор отделяет позднемеловую кору, сформированную на хребте Агульяс от более молодой позднепалеоценовой коры, формирующей молодой восточный фланг Южного сегмента САХ [22].
В аномальном гравитационном поле в свободном воздухе поднятие Метеор выделяется линейно-вытянутой интенсивно положительной аномалией (до 70 мГал), которая оконтурена отрицательными значениями поля (до –50 мГал) (см. рис. 2, а, г).
В аномальном гравитационном поле в редукции Буге поднятие Метеор характеризуется аномалией, вытянутой в северо-западном направлении, амплитуда которой варьирует от 200 до 385 мГал (см. рис. 2, б, г).
Поднятие Айлос Оркадас прилегает к коре котловины Георгия среднемелового возраста [17] (см. рис. 1). В северной части поднятие Айлос Оркадас ограничивается Агульяс-Фолклендской разломной зоной, в центральной части образует относительно ровное плато. Возраст поднятия Айлос Оркадас по данным глубоководного морского бурения (скважина 702 ODP) составляет около 62 млн лет [16].
В поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе поднятие Айлос Оркадас характеризуются положительными значениями до 50 мГал в северо-западном направлении (см. рис. 2, а, г).
Аномалии силы тяжести в редукции Буге над поднятием Айлос Оркадас вытянуты в северо-западном направлении и характеризуется амплитудой в диапазоне от 220 до 420 мГал (см. рис. 2, б, г).
По форме, направлению и амплитуде аномалий поля силы тяжести в свободном воздухе поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас имеют очень схожую структуру (см. рис. 2). Поднятие Метеор характеризуется чуть большими значениями поля по сравнению с поднятием Айлос Оркадас (разница в 20 мГал). Такая небольшая разница может быть связана с различием в толщине коры, определяемая интенсивностью магматической активности горячей точки Шона.
Котловины, окружающие поднятия, также имеют схожие значения аномалий, амплитуда которых достигает 600 мГал.
В магнитном поле данные структуры выделяются разнознаковыми аномалиями, которые в южной части имеют хаотичное простирание (см. рис. 2, в).
К западу от поднятия Айлос Оркадас и к востоку от поднятия Метеор аномалии формируют сходную картину поля и характеризуются интенсивными положительными значениями до 300 нТл, подтверждающими, что данные участки сложены океанической корой, имеющей сходное строение и единое происхождение на палеоспрединговом хребте Агульяс.
Плато Агульяс
Плато Агульяс расположено вблизи южной оконечности Африки. Оно покрывает территорию более чем на 3‒4 км2 и возвышается на 2500 м над океанским дном [25] (см. рис. 1). По сейсмическим данным средняя мощность земной коры в районе плато Агульяс составляет 20 км, с максимальными значениями в 24 км [48].
В строении коры выделяют три основных сейсмических комплекса [49]:
‒ верхний комплекс определен как серия многочисленных вулканических потоков на плато, составляющих его верхнюю часть, для которой характерна скорость 4.1 км/с;
‒ средний комплекс представляет собой утолщенную за счет магматических интрузий океаническую кору со скоростью 6.0 км/с;
‒ нижний комплекс мощностью до 10 км, характеризуется высокими сейсмическими скоростями – ~7.0–7.6 км/с.
Такая глубинно-скоростная модель интерпретируется как переуплотненная и утолщенная океаническая кора, характерная и для других крупных магматичских провинций, такие как плато Онтонг-Джава или северная провинция плато Кергелен.
Некоторые участки нижней коры (нижнего сейсмического комплекса) имеют более низкие скорости прохождения сейсмических волн, чем окружающие ее области. Это может свидетельствовать о континентальном строении этих фрагментов. Исследования пород, взятых из выступов фундамента, свидетельствуют, как аргумент в пользу того, что кора плато Агульяс может быть частично континентальной [64].
Плато Агульяс в аномальном гравитационном поле в свободном воздухе проявляется положительной вытянутой в меридиональном направлении аномалией, невысокой амплитуды до 55 мГал (см. рис. 2, а).
В северо-западной части наблюдаются группа линейных отрицательных и положительных аномалии, интенсивность которых меняется в пределах от –95 до 100 мГал.
С западной, восточной и северо-восточной стороны от плато Агульяс поле силы тяжести характеризуется спокойными значениями аномалий (от –30 до 10 мГал), которые приурочены к котловине Агульяс и бассейну Транскей.
В аномальном гравитационном поле в редукции Буге плато проявляется широкой вытянутой в южном направлении аномалией (см. рис. 2, б, г).
Интенсивность аномалии варьирует от 260 до 410 мГал, что может быть признаком ее магматической природы.
В аномальном магнитном поле плато Агульяс характеризуется линейно-вытянутыми знакопеременными аномалиями субширотного направления (см. рис. 2, в).
Интенсивность аномалий уменьшается с севера на юг. В северной части амплитуда аномалий изменяется от –360 нТл до 585 нТл, в южной варьирует от –100 нТл до 155 нТл.
Поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия
Поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия образует океаническое плато в юго-западной части Атлантического океана между 30° и 38° з.д. и 48° и 56° ю.ш. в котловине Георгия, разделяя ее на восточную и западную части (см. рис. 1). Западная часть поднятия образует дугообразный хребет, вытянутый в северном направлении, при этом восточная сторона поднятия представляет собой более широкую структуру.
Labrecque and et al. [35] полгагают, что формирование поднятия Северо-Восточная Георгия связано с конвергенцией в конце мелового периода между Южно-Американской плитой и плитой Мальвинес.
Kristoffersen и Labrecque [33] несколько позже, по результатам бурения ODP 114 (скв. №№ 698, 699, 700) предположили, что часть поднятия Северо-Восточной Георгия образовалась в центре спрединга.
В скважине № 698 на глубине ~219 м ниже морского дна были подняты пробы керна с сильно выветренным базальтом, в котором исходные железомарганцевые минералы полностью изменены до гематита, с некоторыми микробрекчиями, содержащими фрагменты серпентинитов [18].
Скважина № 699, пробуренная на северо-восточном склоне поднятия Северо-Восточная Георгия, выявила кору, которая образована ранее поднятий Айлос Оркадас и Метеор.
На глубине ~516 м ниже морского дна были отобраны образцы керна с содержанием гранитного гравия и переотложенного вулканического кварцевого песка неопределенного возраста [18].
Такое разнообразие пород, полученных по результатам бурения, предполагает некоторую неоднозначность в условиях формирования этого поднятия, допускающую его вероятное магматическое происхождение с возможным влиянием серпентинизации и наличием остатков континентальной коры.
В поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия характеризуется линейной аномалией, вытянутой в северо-западном направлении с повышенными значениями поля до 70 мГал (см. рис. 2, а, г).
В поле силы тяжести в редукции Буге поднятие характеризуется повышенными значениями поля, аномальные значения которого варьируют от 180 мГал до 420 мГал и выделяется двумя аномалиями (см. рис. 2, б, г):
‒ первая аномалия имеет линейно-вытянутую форму и северо-западное простирание, центральная часть аномалии осложнена пониженными значениями до 280 мГал, которые могут быть связаны с наличием утоненной континентальной коры в его структуре;
‒ вторая аномалия характеризуется изометричной формой, амплитудой до 350 мГал, что может свидетельствовать о наличии более плотных магматических пород в структуре поднятия.
В аномальном магнитном поле поднятие проявляется хаотичным распределением разнознаковых аномалий (см. рис. 2, в). Интенсивность аномалий варьирует в пределах –300–450 нТл.
Мозамбикский хребет, поднятие Бейра, Мадагаскарский хребет
Мозамбикский хребет простирается в субмеридиональном направлении почти параллельно береговой линии юго-восточной части Африки между 25° и 35° ю.ш. Морфологически хребет представляет линейную структуру длиной ~1100 км и шириной 160 км на севере и 350 км на юге и является формальным продолжением африканского континента. Наименьшая глубина составляет 1200 м, средняя глубина достигает 2900 м. Хребет состоит из северного, центрального и юго-западного погруженных блоков, возвышающихся до 3500‒4000 м над дном прилегающей котловины, расположенном на глубине ~5000 м [29]. Блоки разделены долинами и депрессиями субширотного простирания.
Мозамбикский хребет отделяется от Африки бассейном Натал. В северной части бассейн выражен не так ярко, как на юге, его глубина в северной части составляет 1500‒2000 м, в южной части глубина бассейна достигает максимальной отметки почти в 4000 м.
Бассейн Натал в поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе характеризуется отрицательными значениями (от –30 до –5 мГал), в редукции Буге – повышенными значениями (от 200 до 415 мГал). В южной части бассейна в магнитном поле фиксируются линейные знакопеременные аномалии, которые подтверждают океанический тип коры. К востоку от Мозамбикского хребта располагается Мозамбикская котловина, которая отделяется Мадагаскарским хребтом от Мадагаскарской котловины. Мозамбикская и Мадагаскарская котловины в потенциальных полях отображаются значениями, типичными для океанической коры.
В магнитном поле они выделяются знакопеременными линейными аномалиями, в поле силы тяжести в редукции Буге – повышенными до 400 мГал значениями поля, в свободном воздухе – средними значениями от –18 до –3 мГал.
Исследования строения Мозамбикского хребта начались в 1970-х гг. Были сделаны первые предположения о том, что Мозамбикский хребет сложен утоненной континентальной корой [36]. Веские доказательства вулканической природы хребта были получены в исследованиях Симпсона [60], который изучил толеитовые базальты и установил их меловой возраст. Геофизические, в частности, геомагнитные данные также позволили оценить возраст его происхождения между 140 и 122 млн лет назад [32, 46]. Ряд исследователей предполагали, что Мозамбикский хребет является микроконтинентом, отделенным от африканского материка [40, 41].
Современные исследования показали, что северо-восточная часть хребта представляет собой утоненную континентальную кору, покрытую осадочным чехлом, в то время как в строении его южной части значительную роль играют магматические породы [23, 43].
Этот факт, включая данные сейсмических исследований, подтверждает возможность океанического происхождения южной части Мозамбикского хребта, которая имеет геохимическое сходство с плато, образованными под действием горячих точек в Южной Атлантике [15, 25, 29, 62].
Мозамбикский и Мадагаскарский хребты в поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе характеризуются положительными значениями (см. рис. 2, а).
В поле силы тяжести в редукции Буге характеризуются пониженными значениями по сравнению с прилегающими котловинами (см. рис. 2, б).
В аномальном магнитном поле ∆T структуры Мозамбикского и Мадагаскарского хребтов представляют собой хаотичное распределение разнознаковых аномалий, не имеющих какого-либо выраженного простирания (рис. 2, в).
Анализ результатов сейсмотомографии обнаруживает зону повышенных скоростей продольных волн в районе Мозамбикского хребта на глубине 50 км, что может свидетельствовать о континентальном типе коры в его пределах [59].
Однако Мадагаскарский хребет в данных сейсмотомографии не проявляется на этой глубине, что может свидетельствовать о разном генезисе двух структур и их различном глубинном строении.
К северу от Мозамбикского хребта располагается поднятие Бейра, которое морфологически представляет собой выступ фундамента, расположенный примерно в 70 км от побережья Африки [46]. Эта структура имеет 300 км в длину и 120 км в ширину и ориентирована субпараллельно окраине континента (см. рис. 1). Данные сейсмических и гравиметрических исследований показывают, что поднятие Бейра подстилается утоненной сильно растянутой континентальной корой мощностью 20–23 км. От африканского континента поднятие отделяется древней океанической корой или максимально утоненной континентальной коры мощностью 7–10 км. Юго-восточная окраина поднятия Бейра контактирует с нормальной океанической корой Мозамбикского бассейна.
Таким образом, характеристики аномальных геофизических полей, свидетельствуют о различном строении подводных поднятий в приантарктическом секторе Южной Атлантики (см. рис. 2, г).
В поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе положительными значениями по сравнению с окружающей корой характеризуются структурные формы спрединговых и палеоспрединговых хребтов, трансформные разломы и океанические плато (см. рис. 2, а).
Также четко выделяются структуры поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, маркирующие контакты между разновозрастными участками океанической коры.
В магнитном поле также отражается сложное и гетерогенное строение коры (см. рис. 2, в).
В большинстве случаев в котловинах магнитные аномалии расположены последовательно, однако в определенных местах их хронология и простирание нарушаются. Структуры Мозамбикского и Мадагаскарского хребтов, а также поднятий Агульяс и Северо-Восточной Георгии представляют собой хаотичное распределение разнознаковых аномалий без какого-либо выраженного простирания. Изменения хронологии в картине линейных магнитных аномалий также является следствием перестроек осей спрединга и термического влияния горячих точек, за которыми следует перемагничивание пород коры вследствие ее прогрева.
Такими особенностями характеризуется кора на границах плиты Мальвинес, а также в районе границ плато Агульяс, поднятий Мод и Северо-Восточной Георгии. Картину линейных магнитных аномалий осложняют также следы крупных трансформных разломов и шовных зон палеограниц плит, по которым наблюдается смещение аномалий, нарушение их хронологической последовательности и изменения в простирании.
СТРОЕНИЕ КОРЫ ПО РЕЗУЛЬТАТАМ ПЛОТНОСТНОГО МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЯ
Для выявления вариаций в строении коры подводных поднятий было проведено плотностное моделирование строения литосферы по двум региональным трансатлантическим профилям, пересекающим южную часть Атлантического океана от Фолклендского плато до Мозамбикского хребта (см. рис. 1; рис. 3).
Плотностная модель тектоносферы до глубины 100 км представлена пятью основными слоями, гравитационный эффект от которых, исходя из анализа структуры аномального гравитационного поля, имеет разные частотные и амплитудные характеристики:
– водный слой с плотностью 1.03 г/см3;
– слой осадочных пород со средней плотностью 2.1 г/см3;
– слой океанической коры с переменными значениями плотности (2.70–2.88 г/см3);
‒ слой подкоровой литосферной мантии, который имеет переменную плотность в зависимости от возраста литосферы: от 3.21 г/см3 под осью спредингового хребта до 3.31 г/см3 при возрасте старше 100 млн лет;
– астеносферный слой так же с переменной плотностью в зависимости от возраста и расстояния от центра спрединга: 3.19 г/см3 под осью спрединга и до 3.29 г/см3 при возрасте старше 100 млн лет.
Плотность в слоях модели задавались постоянными в пределах отдельных блоков, а не менялись градиентно по глубине.
Такое распределение значений плотности можно допустить для блоков земной коры, но не для слоя подкоровой литосферы и астеносферы, которые по структуре и составу значительно более однородны. Дискретное назначение плотности не меняет картины аномального распределения масс в разрезе для регионального моделирования, которое проводилось в этом исследовании.
Профиль А–А' с запада на восток пересекает Фолклендское плато, банку Мориса Юинга, котловину Георгия, поднятия Северо-Восточная Георгия, Айлос Оркадас, центральный сегмент ЮСАХ, поднятие Метеор, палеоспрединговый хребет Агульяс, котловину и плато Агульяс и Мозамбикский хребет (см. рис. 1, профиль А–А'; см. рис. 3, а ).
Протяженность профиля А–А′ составляет более 7500 км. Рельеф дна меняется от 1.2 км, на таких поднятиях как банка Мориса Юинга и Мозамбикский хребет, до 5.3 в котловине Агульяс. Через центральный сегмент ЮСАХ рельеф от оси спрединга к его флангам изменяется от 2.5 до 3.8 км. Глубина оси спрединга достигает 3.9 км.
По результатам анализа модели сейсмотомографии [55] показано, что на глубине 25‒50 км, почти на всем протяжении профиля значения скорости не изменяются. На этой глубине наблюдается резкое уменьшение скорости только в районе Фолклендского плато, что может свидетельствовать о наличии утоненной континентальной коры. С 50 км и до 200 км наблюдается падение скоростей в области спредингового хребта ЮСАХ. Это обусловлено тем, что под хребтом располагается разогретое частично расплавленное вещество астеносферы.
С запада и востока от ЮСАХ, в районе поднятий Айлос Оркадас и Метеор происходит контакт разновозрастных блоков литосферы. Такая же картина наблюдается в районе плато Агульяс и Мозамбикского хребта, Фолклендского плато и банки Мориса Юинга.
Рис. 3.
Структурно-плотностная и сейсмотектоническая модель литосферы (по данным [55]). (а) ‒ профиль А‒А'; (б) ‒ профиль Б‒Б'. Хребты: МадХ – Мадагаскарский хребет; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; ХШ – хребет Шона; ЮСАХ – Южный сектор Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Поднятия: ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия. Плато: ПА – плато Агульяс; ФП – Фолклендское плато. Обозначено: БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн. Показаны (цифры на профилях) значения плотности, г/см3. На разрезах (оттенки цвета) отображается изменение плотности в слоях: чем темнее цвет, тем выше значение плотности, изолинии сейсмических скоростей (линии серым), (по данным [55]), чем светлее цвет, тем ниже скорость, пунктирная линия – нулевая.Графики: наблюденное поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе (∆gсв.в., мГал) (синий); рассчитанное поле силы тяжести в свободном воздухе (красный); поле силы тяжести в редукции Буге (∆gБ., мГал) (зеленый); аномальное магнитное поле (∆Та, нТл) (фиолетовый)
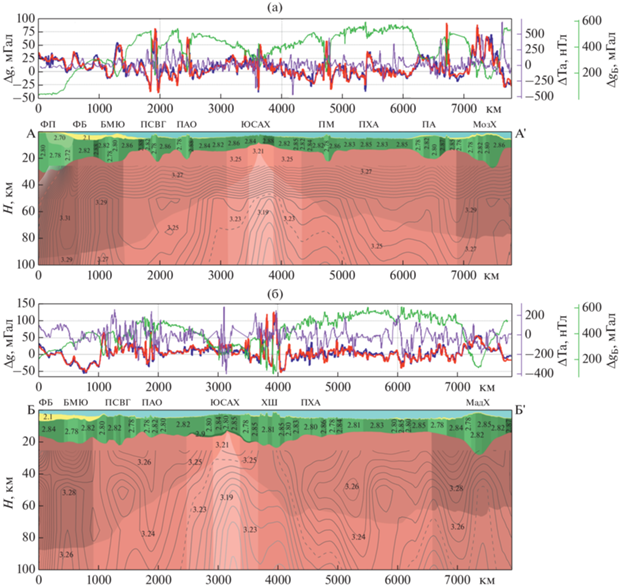
Плотность пород коры в центральной части профиля А–А′ (возраст дна от 0 до 20 млн лет) изменяется как по латерали, так и по глубине. Мощность земной коры западного фланга ЮСАХ составляет ~13 км, при этом мощность его восточного фланга немного больше и составляет ~15 км.
Плотность блоков коры на восточном фланге ниже, по сравнению с западным, и варьируют от 2.82 г/см3 до 2.85 г/см3.
Мы полагаем, что это связано с термическим разуплотнением коры в окрестности горячих точек. Поднятия Айлос Оркадас, Метеор, Северо-Восточная Георгия и плато Агульяс имеют сходную плотностную характеристику, где плотность блоков коры изменяется от 2.78 г/см3 до 2.82 г/см3. Мощность земной коры поднятий составляет ~20 км.
В рассматриваемых поднятиях наблюдается изменение скорости сейсмических волн свидетельствует о различии их строения [55]. Котловина Агульяс, в которой располагается одноименный палеоспрединговый хребет, характеризуется типичными значениями плотности, для котловин с океаническим типом коры. Мощность коры не превышает 14 км.
Фолклендское плато, банка Мориса Юинга и Мозамбикский хребет характеризуются повышенными значениями плотности в подкоровой мантии и астеносферном слое, что свидетельствует о присутствии разновозрастных блоков на профиле. Фолклендское плато сложено утоненной континентальной корой, о чем свидетельствует разуплотненный блок коры (2.70 г/см3), мощностью ~12 км.
Профиль Б–Б′, протяженностью более 7500 км, также имеет субширотное простирание и расположен несколько южнее Профиля А–А′ (см. рис. 1). Профиль Б–Б′ пересекает с запада на восток южную часть Фолклендского плато и банки Мориса Юинга, поднятий Северо-Восточная Георгия и Айлос Оркадас, южную часть Южного сектора САХ, и южное окончание Мадагаскарского хребта.
В рельефе дна океана едва наблюдается ось спредингового хребта ЮСАХ, глубина которого изменяется от 2.5 км до 3.3 км. Причем его восточный фланг приподнят примерно на 1 км, относительно западного фланга. Рельеф дна оставшейся части изменяется от 1.1 км, на Мадагаскарском хребте, до 5.5 км в Мозамбикской котловине.
На модели сейсмотомографии начиная с глубины 25 км и до 200 км наблюдается гетерогенность тектоносферы вдоль всего профиля. В приосевой части ЮСАХ и на его восточном фланге наблюдается понижение сейсмических скоростей, что свидетельствует о сильном прогреве мантийного вещества.
На плотностной модели южного профиля наблюдается увеличение мощности земной коры под ЮСАХ до 15 км и выделяется более плотный блок небольшой мощности (2.9 г/см3), возможно связанного с частично серпентизированной мантией (см. рис. 3, б).
Восточный фланг хребта осложнен вулканической постройкой – хребтом Шона, мощность коры под котором достигает 24 км. Наблюдается разуплотнение блоков коры (2.80–2.85 г/см3), которое связано с близким расположением горячих точек Буве и Шона. Поднятия Айлос Оркадас и Северо-Восточная Георгия почти сливаются в единую структуру, плотностная характеристика которых также схожа (2.78–2.84 г/см3). Мощность земной коры поднятия Айлос Оркадас уменьшается до 17 км.
В котловине Агульяс отмечается увеличение мощности земной коры с восточной стороны от палеоспредингового хребта Агульяс (до 17 км), ближе к Мозамбикской котловине она составляет около 12 км. Плотность блоков в районе палеохребта возрастает до 2.85 г/см3. Мадагаскарский хребет характеризуется увеличенной плотностью в слое подкоровой мантии и астеносферном слое, а также мощностью земной коры (~30 км). Плотность блоков коры Мадагаскарского хребта изменяется от 2.78 г/см3 до 2.85 г/см3.
Таким образом, плотностные модели разреза тектоносферы по трансатлантическим профилям, которые пересекают гетерогенные структуры при всем своем сходстве имеют некоторые отличия. В аномальном гравитационном поле в свободном воздухе средняя амплитуда аномалий над северным профилем ниже на 10 мГал, чем над южным (15 и 25 мГал, соответственно).
В области оси спрединга южного профиля наблюдаются высокоамплитудные магнитные аномалии, которые связаны с плюмовой активностью горячих точек Буве и Шона, приводящая к увеличению мощности магнитоактивного слоя. В поле силы тяжести в редукции Буге ЮСАХ характеризуется широкой аномалией пониженных значений. Это также связано с прогретостью мантийного вещества под действием близкого расположения горячих точек.
Нами представлены обобщенные характеристики коры подводных поднятий, полученные на основании плотностного моделирования, анализ которых позволяет выделить основные типы коры (табл. 1).
Таблица 1.
Параметры строения литосферы вдоль трансатлантических профилей.
| Название, параметры | Фолклендское плато | Банка Мориса Юинга | Поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия | Поднятие Айлос Оркадас | ЮСАХ | Поднятие Метеор | Хребет Шона | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| север | юг | север | юг | север | юг | север | юг | ||||
| Тип коры | утоненная континентальная | утоненная континен- тальная осложненная магматизмом | утоненная континентальная осложненная магматизмом | утолщенная океаническая | утолщенная океаническая | океаническая | утолщенная океаническая | ||||
| Глубина дна, км | 0.4‒2.8 | 1.4‒2.5 | 2.9‒3.2 | 1.7‒2.8 | 2.4‒3.5 | 1.9‒3.3 | 2.4–3.9 | 2.3‒3.6 | 1.7‒3.3 | 1.8‒3.6 | 0.7‒3.5 |
| Мощность земной коры, км (вместе с осадочными толщами) | 18‒30 | 16‒22 | 16‒20 | 17‒22 | 16‒21 | 15‒20 | 14–16 | 7‒13 | 11‒17 | 15‒22 | 17‒22 |
| Плотность, г/см3 | 2.70‒2.80 | 2.78‒ 2.82 | 2.78‒2.84 | 2.78‒2.86 | 2.80‒2.82 | 2.78‒2.88 | 2.78–2.82 | 2.82‒2.88 | 2.80‒2.90 | 2.78‒2.86 | 2.81‒2.85 |
| Название, параметры | Котловина Агульяс | Палеохребет Агульяс | Плато Агульяс | Мозамбикский хребет | Мозамбикская котловина | Мадагаскарский хребет | |||||
| север | юг | север | юг | ||||||||
| Тип коры | океаническая | утоненная континентальная осложненная магматизмом | океаническая | утолщенная океаническая | |||||||
| Глубина дна, км | 4.1‒5.3 | 3.9‒5.6 | 4.6‒5.4 | 4.2‒5.0 | 2.5‒3.9 | 1.2‒3.8 | 4.2‒5.7 | 1.0‒3.4 | |||
| Мощность земной коры, км (вместе с осадочными толщами) | 12‒14 | 12‒16 | 12‒13 | 14‒16 | 15‒20 | 16‒27 | 12‒15 | 16‒28 | |||
| Плотность, г/см3 | 2.83‒2.86 | 2.78‒2.86 | 2.83‒2.85 | 2.80‒2.83 | 2.78‒2.87 | 2.78‒2.82 | 2.78‒2.85 | 2.78‒2.85 | |||
Разное строение коры поднятий, по всей видимости, связано с разными геодинамическими условиями формирования этих структур. Пространственно-временны́е реконструкции эволюции литосферы юго-восточной части Атлантики позволяют идентифицировать временны́е рамки реорганизации границ плит и проявления магматической активности горячих точек, что, в свою очередь, позволяет восстановить условия формирования подводных поднятий разных типов.
ЭТАПЫ РАСКРЫТИЯ ЮГО-ВОСТОЧНОЙ АТЛАНТИКИ
Развитие спрединга морского дна в результате относительного движения Африки, Южной Америки и Антарктиды является ключом к процессу формирования сложного морфоструктурного плана и гетерогенного строения литосферы приантарктического сектора Южной Атлантики. На сегодняшний день существует немало моделей реконструкции литосферы Западной Гондваны и отдельных поднятий, основанных на геолого-геофизических данных [3, 7, 8, 19, 21, 26, 32, 34, 37, 39, 40, 46, 48, 51, 52, 65 ] . Тем не менее, многие вопросы строения и эволюции подводных поднятий остаются открытыми к обсуждению и-сследователей.
В границах рассматриваемой акватории можно выделить четыре крупных сектора океанической коры, сформированной при распаде гондванских материков:
‒ Сектор I, где кора сформирована в центральной части ЮЗИХ в створе континентальных окраин Мозамбика и Антарктиды в районе моря Риссер-Ларсена;
‒ Сектор II, где кора сформирована на САХ в створе Капской и Аргентинской континентальных окраин;
‒ Сектор III, где образована кора клиновидного в плане сектора, отделенного от них демаркационными разломными системами Агульяс-Фолклендской и Дю-Туа – Эндрю-Бейн – Принц-Эдуард;
‒ Сектор IV, где образована кора сектора моря Уэдделла, который расположен южнее Американо-Антарктического хребта.
Генезис и эволюция структур секторов I и II изучены относительно хорошо. Формирование океанического дна здесь происходило в процессе равномерного наращивания коры на спрединговых хребтах.
Развитие структур секторов III и IV предстоит во многом исследовать. Здесь формирование коры и структур океанического дна сопровождалось неоднократными кинематическими перестройками и перескоками осей спрединга, отмиранием спрединговых хребтов и проявлениями плюмового магматизма. Строение коры осложнено рядом океанических поднятий, подстилаемых корой противоречивого генезиса.
В пределах литосферы клиновидного сектора III можно выделить несколько провинций сложенных корой, сформированной на различных спрединговых хребтах и подверженной магматическому воздействию горячих точек:
‒ провинции с корой, сформированной на спрединговых хребтах Агульяс, ЮЗИХ, а также в ходе предполагаемого спрединга в котловине Транскей;
‒ провинция с корой, сформированной в ходе спрединга на прямолинейном отрезке ЮЗИХ.
‒ провинция с корой, сформированной в ходе спрединга на спрединговом хребте моря Уэдделла с неоднократно менявшимся направлением спрединга, преимущественно северо-западного‒юго-восточного направления.
Границы провинций, имеющих кору, сформированную на разных спрединговых хребтах, прослеживаются в рельефе дна, магнитном и гравитационном полях и ропредставляют собой псевдоразломы, шовные зоны и следы различных исторических генераций тройного сочленения Буве.
Началу спрединга в западной части Гондваны предшествовал рифтогенный раскол континентальной литосферы инициируемым воздействием плюма Кару (178‒188 млн лет назад). Возраст наиболее древних даек в бассейне реки Лимпопо ~174 млн лет, а в южной Африке и Антарктике – 180 млн лет и более. Они фиксируют начало магматической активизации, вызванное растяжением литосферы по широкой площади, сопровождаемым последующим излиянием расплавов и формированием высокоскоростных тел в нижней коре [27, 39, 45].
История спрединга на акватории этого сектора включает несколько этапов.
• Первый этап (≈174‒150 млн лет назад) ‒ за рифтогенным расколом континентальной литосферы последовал спрединг и формирование океанической коры в створе континентальных окраин Мозамбика и моря Риссер-Ларсена. Здесь прослеживается наиболее древняя аномалия М25, возникшая ~155–156 млн лет назад. Формирование Мозамбикского бассейна, привело к обособлению Мозамбикского хребта и образованию многочисленных магматических поднятий. В это же время 166‒154 млн лет назад сформировалась океаническая кора мощностью ~20 км в Фолклендском бассейне между банкой Мориса Юинга и Фолклендским плато [56].
• Второй этап (150–135 млн лет назад) ‒ начинается спрединг в субмеридиональном направлении в акватории современного моря Уэдделла. Этот спрединговый центр примыкал к континентальной коре Северного Мозамбикского хребта и Северной долины Натал и стремился соединиться с функционирующим, начиная со времени в 155–157 млн лет назад, спрединговым центром в Мозамбикской котловине [46] (рис. 4, а).
Рис. 4.
Палеореконструкции плит для интервала от 133 млн лет до 33 млн лет (по [65 ] , с изменениями и дополнениями). (а) ‒ формирование Сомалийского и Мозамбикского бассейнов; (б) ‒ раскрытие Южной Атлантики, формирование спредингового хребта Агульяс; (в) ‒ формирование плато Агульяс; (г) ‒ раскол плато Агульяс на три блока – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия, плато Агульяс и поднятие Мод; (д) ‒ продвижение к югу САХ и прекращение спрединга на хр. Агульяс; (е) ‒ аккреция новой коры на южном сегменте САХ и формирование поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас. Хребты: МадХ – Мадагаскарский хребет; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; Поднятия: ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПМо – поднятие Мод; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия. Плато: ПА – плато Агульяс; ФП – Фолклендское плато. Обозначено: БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн. 1‒3 ‒ кора: 1 – континентальная, 2 – утоненная континентальная, 3 – океаническая; 4 – подводные поднятия; 5 – ось спрединговых хребтов; 6 – разломные зоны; 7 – палеохребет; 8 – направления раздвижения плит; 9 – горячие точки
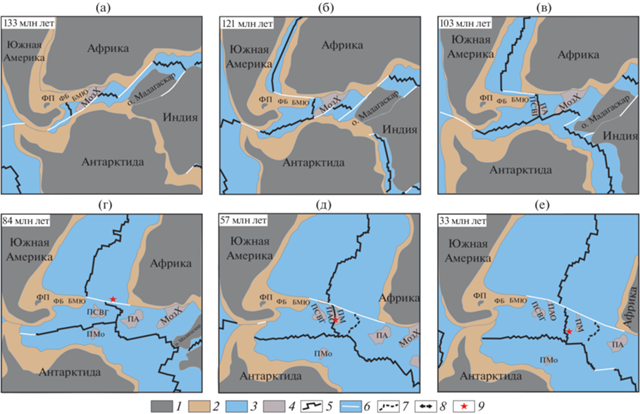
Продолжающееся движение Антарктиды на юг относительно Африки стало причиной отделения Фолклендского плато от Антарктиды. Ко времени хрона М20 (147 млн лет назад), океаническая кора образовалась между Южной Америкой и Антарктидой в южной части моря Уэдделла [31]. Рифтинг между Южной Америкой и Африкой начался138 млн лет назад [49].
• Третий этап ‒ начиная с интервала ~130–135 млн лет назад, спрединг в северо-восточного‒юго-западного направлении развивается в южной долине Натал и затем ‒ в котловине Транскей, соединенной в то время с бассейном, расположенным к востоку от банки Мориса Юинга. Возможно, в это время происходит отделение банки Мориса Юинга от Северного Мозамбикского хребта и формируется тройное сочленение Буве-1 [3]. В период 131–125 млн лет назад на океанической коре формируются массивы магматических поднятий Южного Мозамбикского хребта и, возможно, ‒ поднятия Астрид [46].
• Четвертый этап ‒ на протяжении интервала 125‒105 млн лет назад продолжался спрединг в котловине Транскей. Начался спрединг в Южной Атлантике, важным индикатором которого считается аномалия M5n (~126 млн лет) [63] (см. рис. 4, б).
Продвигающаяся к югу рифтовая зона САХ в Южной Атлантике подошла к Фолклендскому плато с мощной континентальной литосферой, которая послужила структурным барьером на пути рифта. Это привело к существенной кинематической перестройке границ плит ‒ образованию крупного Агульяс‒Фолклендского трансформного разлома длиной более 1110 км, разделяющего Африканскую плиту с юга и Фолклендское плато (Южноамериканская плита) с севера, а также соединяющего сегмент САХ и спрединговый хребет в бассейне Тренскей.
• Пятый этап ‒ период нормального магнитного поля, в районе южной оконечности Африки сформировалась крупная магматическая провинция, морфоструктурным выражением которой явилось плато Агульяс (см. рис. 4, в; рис. 5, а).
Рис. 5.
Тектонические реконструкции формирования подводных поднятий. (а)‒(г) ‒ палеореконструкции положения спрединговых хребтов и эволюции плато Агульяс в интервале времени 120–94 млн лет, (по [48] с дополнениями): (а) ‒ спрединг в Южной Атлантике и в бассейне Транскей; (б) ‒ продвижение Фолклендского плато на запад и формирование крупной Агульяс-Фолклендской разломной зоны, (в) ‒ перескок спрединга и образование крупной магматической провинции Агульяс; (г) ‒ спрединг на хребте Агульяс, формирование коры одноименной котловины и разбиение крупной магматической провинции Агульяс на три фрагмента; (д)‒(ж) ‒ формирование Южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта и сопряженных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, (по [28], с дополнениями): (д) ‒ отмирание спредингового хребта Агульяс, (е) ‒ продвижение Южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта и образование единой структуры поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, (ж) ‒ аккреция океанической коры на Южном сегменте Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Обозначено: БПА – местоположение будущего плато Агульяс; БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; ПА – плато Агульяс; ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПМо – поднятие Мод; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия; ПХА – палеохребет Агульяс; САХ – Срединно-Атлантический хребет; ХА – хребет Агульяс; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн; ФП – Фолклендское плато. 1‒3 ‒ кора: 1 – континентальная, 2 – утоненная континентальная, 3 – океаническая; 4 – подводные поднятия; 5 – ось спрединговых хребтов; 6 – разломные зоны; 7 – палеохребет; 8 – направления раздвижения плит; 9 – горячие точки; 10 – область развития моря Скоша
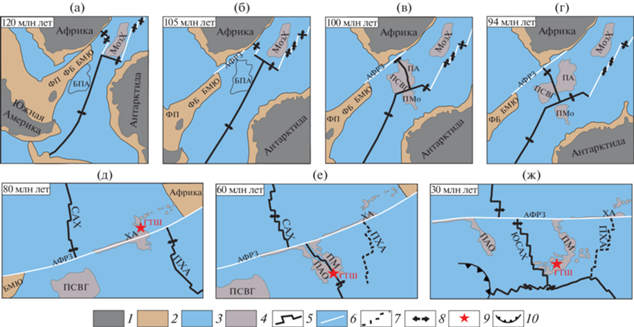
Это событие привело к перескоку оси спрединга, сопровождавшимся отмиранием спрединга в котловине Транскей и образованием нового спредингового хребта Агульяс и одноименного плато, являющегося результатом магматической деятельности горячей точки. Такая кинематическая перестройка привела к формированию тройного сочленения Буве-2, в котором соединились спрединговые хребты юго-западного‒северо-восточного простирания ‒ хр. Агульяс, ЮЗИХ и хр. Уэддельский [48].
В дальнейшем ~96 млн лет назад плато Агульяс раздробилось на фрагменты ‒ собственно, плато Агульяс, поднятие Мод и поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия, которые, перемещаясь, окажутся вблизи трех материков – Африки, Антарктиды и Южной Америки [48] (см. рис. 4, д, см. рис. 5, в).
Mueller и Jokat [46] предположили, что поднятие Мод могло быть фрагментом Южной части Мозамбикского хребта.
• Шестой этап ‒ спрединг на хребте Агульяс продолжался вплоть до хрона С29 (60–64 млн лет назад) и сформировал кору котловины Агульяс (или Мальвинес) (см. рис. 4, г). В период 60–80 млн лет назад активность горячей точки Шона в районе сочленения хребта Агульяс и Агульяс-Фолклендской разломной зоны привела к формированию приразломного хребта и ряда небольших магматических поднятий в этой котловине (см. рис. 5, д).
• Седьмой этап ‒ характеризовался прекращением спрединга на хребте Агульяс и формированием нового спредингового сегмента на южном продолжении САХ (см. рис. 4, д; см. рис. 5, е). Такая кинематическая реорганизация, вероятно, происходила под влиянием термической аномалий связанной с деятельностью горячей точки Шона, что зафиксировано в поднятиях рельефа. Продвижение нового сегмента спредингового хребта ЮСАХ к югу привело к перескоку оси спрединга хребта Агульяс на 1105 км к западу, произошедшим между хронами C31 и C26. Этот перескок сопровождался постепенным прекращением спрединга на хребте Агульяс и формированием двух сопряженных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас симметрично расположенных относительно оси ЮСАХ и фиксирующих место его заложения (см. рис. 5, е).
Новый южный спрединговый сегмент САХ начал генерировать молодую кору, которая в современном морфоструктурном плане отделяется поднятиями Метеор и Айлос Оркадас от более древней коры котловины Агульяс, сформированной на спрединговом хребте Агульяс.
В реконструкциях Marks и Tikku [41] начало формирования сопряженных шовных зон Метеор и Айлос Оркадос, как место рифтогенного раскола литосферы плиты Мальвинес датируется в 83 млн лет. В это же время началось постепенное уменьшение скорости спрединга на хребте Агульяс. Здесь в раскрытии океанических бассейнов участвовали Южно-Американская, Африканская, Антарктическая плиты и микроплита Мальвинес. Кора микроплиты Мальвинес подстилает котловину Агульяс, где в настоящее время находится одноименный палеоспрединговый хребет Агульяс, и котловину Восточная Георгия, расположенную между поднятием Айлос Оркадас и поднятием Северо-Восточная Георгия.
Когда спрединг на хребте Агульяс завершился во время хрона C27o (61.2 млн лет), плита Мальвинес вошла в состав Африканской плиты. Поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, расположенные на западном фланге плиты Мальвинес, представляют собой шовные зоны, маркирующие границы между корой плиты Мальвинес и более молодой корой Южно-Американской плиты, сформированной на ЮСАХ [3].
• Восьмой этап ‒ связан с прекращением спрединга в море Уэдделла, формированием плиты Скоша и Американо-Антарктического хребта (ААХ) [4, 20, 65 ] . Причины прекращения спрединга в акватории моря Уэдделла обсуждаются исследователями. Прекращение спрединга в море Уэдделла стало результатом столкновения спредингового центра моря Уэдделла с зоной субдукции вдоль юго-восточной окраины формировавшейся плиты Скоша (дуга Джейн).
Этот этап эволюции сопровождался рифтогенным разрушением континентального моста между Южной Америкой и Антарктидой и раскрытием моря Скоша, которое началось со спрединга в западной части моря Скоша ~26 млн лет назад, последующего столкновения Западного хребта Скоша со структурным барьером Фолклендского плато и его отмиранием [4, 13, 20, 24].
Дальнейшее изменение направления астеносферного потока в субширотном направлении привело к растяжению литосферы континентального моста в районе моря Скоша, образованию зоны субдукции вдоль восточной окраины плиты Скоша и ААХ, соединяющего южную границу плиты Скоша с тройным соединением Буве [42].
Таким образом, кинематические и структурные перестройки приантарктической части Южной Атлантики были в значительной степени стимулированы активностью горячих точек (Шона, Буве), следы магматической деятельности которых хорошо выражены в рельефе дна в виде хребтов, цепочек подводных гор и вулканических плато [28].
Причина усиленного снабжения расплавом этого региона может быть связана с обширной термальной аномалией в мантии, связанной с наличием африканского суперплюма, инициирующего магматическую активность плюма Кару-Феррар и последующую миграцию астеносферного расплава, реализующегося в магматической активности горячих точек.
Мы не исключаем возможность того, что структуры подводных поднятий могут включать фрагменты континентальной коры, отторженной от краевых частей континентов (например, поднятие Бейра и Мозамбикский хребет).
Имеющиеся модели реконструкций положения материков и аккреции океанической коры, а также восстановление основных этапов кинематических перестроек границ плит и магматической активизации горячих точек позволяют с большой вероятностью установить генезис подводных поднятий и тип слагающей их коры.
Это обстоятельство существенно дополняет выводы, полученные при интерпретации геофизической информации.
ФИЗИЧЕСКОЕ МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЕ УСЛОВИЙ ФОРМИРОВАНИЯ ПОДВОДНЫХ ПОДНЯТИЙ
Постановка экспериментов и методика моделирования
Для выявления геодинамической связи плюмовой активности и кинематических перестроек нами проведено физическое моделирование условий формирования структур подводных поднятий приантарктической части Южной Атлантики.
Экспериментальные исследования проводились на модельных материалах, в соответствии с условиями подобия и методиками, описанными в работах [1, 2, 14, 57, 58].
В процессе подготовки эксперимента расплавленное, однородное модельное вещество, помещенное в ванну, охлаждалось сверху. Затвердевшее до необходимой толщины оно имитировало литосферу, которая припаивалась к поршню и противоположной стенке экспериментальной ванны. Изменение длительности охлаждения при подготовке модельной плиты обеспечивает различное соотношение ее хрупкого и пластичного слоев.
В модельной плите можно задавать различные типы неоднородностей – центры локализации деформаций (разрезы – рифтовые трещины или ослабленные зоны с более тонкой литосферой в области прогрева рифта и др.) [2, 5]. После подготовки начиналось горизонтальное растяжение модели.
Особенностью региона Южной Атлантики является наличие горячих точек. Их термическое влияние в различные периоды эволюции континентального рифтинга и океанического спрединга в экспериментах воспроизводилось с помощью локального источника нагрева (ЛИН).
Приспособление ЛИН, генерирующее термическую аномалию при подготовке экспериментов, помещалось в модельную астеносферу в нужной локации и включалось в нужное время по мере развития экспериментального процесса. При необходимости возможна регулировка интенсивности его нагрева. Образующаяся при работе ЛИН термическая аномалия с более горячим модельным веществом моделировала локальное уменьшение прочности модельной литосферы и тепловое воздействие астеносферных потоков на структурообразование в ней.
Задачей экспериментов было установление влияния горячих точек на кинематические перестройки спрединговых хребтов и выявление условий формирования подводных поднятий приантарктического сектора Южной Атлантики.
Ранее нами экспериментально было показано, что наличие горячей точки (в природе Шона) вблизи молодой окраины отодвигающегося континентального блока (Фолклендское плато) могло привести к кинематической перестройке спрединговых хребтов [6]. Ее следствием являлось прекращение спрединга на хребте Агульяс, перескок оси спрединга, формирование сегмента ЮСАХ и шовных зон Метеор и Айлос Оркадас.
В настоящей работе, в соответствии с данными палеореконструкций, нами было проведено физическое моделирование условий формирования структур в Южной Атлантике. Оно учитывало наличие двух этапов магматической активизации горячих точек и кинематическую реорганизацию спрединговых хребтов.
В соответствии с имеющимися палеореконструкциями предполагалась следующая последовательность событий:
‒ формирование крупной магматической провинции Агульяс и одноименного спредингового хребта;
‒ спрединг на хребте Агульяс и формирование сопряженных парных структур плато Агульяс и поднятия Северо-Восточная Георгия в результате раскола единого плато Агульяс;
‒ аккреция океанической коры на спрединговом хребте Агульяс (формирование котловины Агульяс),
‒ перескок оси спрединга хребта Агульяс и формирование нового спредингового сегмента – ЮСАХ и сопряженных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, фиксирующих начальное место его формирования под влиянием магматической активности горячей точки Шона,
‒ аккреция океанической коры на ЮСАХ.
Подготовка экспериментов осуществлялась следующим образом. После охлаждения модельной литосферы и достижения ею толщины Н, в ней на всю глубину делался разрез, и затем начиналось ее растяжение со скоростью V (рис. 6).
Рис. 6.
Схема проведения экспериментов. (а) ‒ формирование крупной магматической провинции Агульяс и одноименного спредингового хребта; (б) ‒ аккреция океанической коры на спрединговом хребте Агульяс (формирование котловины Агульяс); (в) ‒ перескок оси спрединга, формирование Южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта и сопряженных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас; (г) ‒ аккреция океанической коры на Южном сегменте Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Обозначены (римские цифры) стадии магматической активизации горячих точек. 1 – модельная плита; 2 – ослабленная зона; 3 – поршень установки; 4 – разрез; 5 – область влияния ЛИН (пониженная толщина и прочность литосферы); 6 – новообразованная литосфера первого этапа аккреции (после формирования магматической провинции и ее раскола); 7 ‒ новообразованная литосфера второго этапа аккреции (после формирования магматической провинции); 8 – направление растяжения
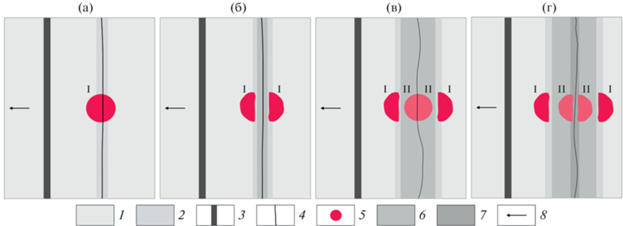
После формирования полосы новой модельной литосферы первый раз включался ЛИН, действие которого приводило к образованию магматической провинции (см. рис. 6, а). Далее ЛИН выключался и при продолжающемся растяжении модели происходил раскол магматической провинции на два блока, между которыми продолжалась аккреция коры на спрединговом хребте (котловина Агульяс) (см. рис. 6, б).
Затем делался перерыв в растяжении, имитирующий прекращение спрединга на хребте Агульяс и вторично включался ЛИН, имитирующий активность второй горячей точки (в природе Шона) в пределах литосферы котловины Агульяс (см. рис. 6, в).
После формирования новой вулканической провинции, ЛИН выключался и начиналось растяжение (рис. 6, г).
Результаты моделирования
В подготовленной модельной плите был сделан разрез, имитирующий спрединговый хребет Агульяс (рис. 7, а, (I)).
Рис. 7.
Экспериментальная модель формирования вулканических провинций Южной Атлантики в два этапа активности горячих точек Н = 3 × 10–3 м; V = 3.75 × 10–5 м/с–1. (I)‒(V) – стадии эксперимента: (а) ‒ модель (вид сверху); (б) – структурные схемы; (в) – схематичное строение литосферы вдоль профиля А‒А'. 1 – континентальная модельная литосфера; 2 – модельная океаническая кора, образованная на первом этапе спрединга (в природе ‒ на хребте Агульяс); 3 – модельная океаническая кора, образованная на втором этапе спрединга после перескока оси (в природе ‒ на ЮСАХ); 4 – активность первой (а) и второй (б) горячих точек и образование магматических провинций (в природе ‒ плато Агульяс (а) и поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас (б)); 5 – границы между аккреционными валами; 6 – спрединговая ось; 7 – палеоспрединговая ось; 8 – поперечные смещения оси; 9 – направление растяжения; 10 – модельная литосферная мантия; 11 – расплав модельного вещества, имитирующий астеносферу
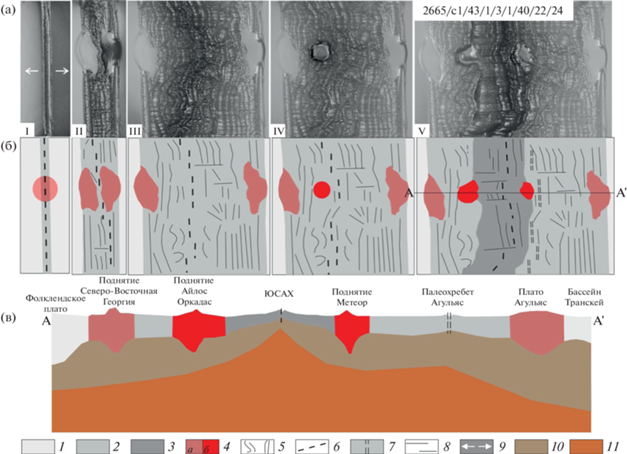
После этого началось растяжение и в течение небольшого периода времени происходило наращивание модельной коры. Затем в первый раз включался ЛИН. В области его действия модельная литосфера проплавлялась и расплав изливался на поверхность плиты, формируя аналог природной магматической провинции (см. рис. 7, а, б, (I)).
В процессе дальнейшего растяжения расплав застывал и в это ослабление перескакивала спрединговая ось раскалывая магматическую провинцию на две части (природные аналоги плато Агульяс и блока Северо-Восточная Георгия) (см. рис. 7, а, б, (II)).
На модельном спрединговом хребте Агульяс продолжалось симметричное наращивание новой коры (см. рис. 7, а, б, (III)).
Далее, между спрединговой осью и левой частью разделенной магматической провинции во второй раз был включен ЛИН (см. рис. 7, а, б, (IV)).
Его действие привело к образованию в модели второй магматической провинции. В эту область опять произошел перескок оси спрединга. Дальнейший спрединг на этом сегменте разделил новую магматическую провинцию на две части (природные аналоги поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас) (см. рис. 7, а, б, (V)).
После этого в модели продолжилось наращивание коры на новом спрединговом хребте (природный аналог ЮСАХ). В экспериментах этой серии, на отдельных участках модели, в результате растягивающих и сдвиговых деформаций, с одной стороны, и значительных вертикальных подвижек, с другой, наблюдалось излияние расплава по разломам ограничивающих отдельные блоки модельной литосферы.
В соответствии с результатами эксперимента № 2665 был построен схематичный профиль через основные структуры (см. рис. 7, в). Профиль показывает соответствие образовавшихся структур экспериментальной модели реальным структурам региона южной Атлантики.
Проведенное моделирование показало вероятный сценарий формирования магматических провинций южной Атлантики в течение двух этапов активизации действия горячих точек. На каждом из этапов ее действие приводило к термомеханическому ослаблению литосферы, формированию магматической провинции и перескоку спрединговой оси в сторону ослабленной литосферы.
Следствием перескока было отмирание одного спредингового хребта, заложение нового и формирование двух пар сопряженных подводных поднятий магматического генезиса: плато Агульяс – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия и поднятий Метеор – Айлос Оркадас.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Приантарктический сектор южной части Атлантического океана отличается сложным строением и историей своего развития, что связано с перемещением трех гондванских материков Африки, Южной Америки и Антарктиды и активностью горячих точек Шона, Буве.
Проведенный нами анализ геолого-геофизической информации позволил определить закономерности характеристик аномальных геофизических полей подводных поднятий и установить диапазоны значений характерные для разных типов структур.
Значительные различия в наблюдаемых батиметрических и геофизических характеристиках отмечаются между океаническими котловинами разного возраста, предполагаемыми блоками с континентальной корой (Фолклендское плато, банка Мориса Юинга), современными и палеоспрединговыми хребтами. Близкие характеристики имеют внутриплитные подводные понятия и плато магматического генезиса.
Проведенное нами плотностное моделирование строения литосферы вдоль двух трансатлантических профилей, пересекающих различные подводные поднятия и котловины, позволило выделить глубинное строение поднятий и предположить вероятные типы слагающей их коры:
‒ утоненная континентальная кора микроконтинентов (поднятие Бейра) [53];
‒ утоненная континентальная кора поднятий, не полностью отделенных от материка (северная часть Мозамбикского хребта);
‒ утоненная континентальная кора осложненная плюмовым магматизмом (южная часть Мозамбикского хребта [12];
‒ кора, утолщенная за счет андеплейтинга вызванного плюмовым магматизмом (плато Агульяс [48], поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия, поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас).
Нами представлена структурная схема региона и трансатлантический профиль глубинного строения литосферы, построенные на основании анализа геолого-геофизической информации, плотностного и физического моделирования (рис. 8).
Рис. 8.
Структурная схема приантарктиеского сектора Южной Атлантики (а) и глубинное строение литосферы вдоль трансатлантического профиля (б). Обозначено: ТСБ – тройное сочленение Буве; БМЮ – банка Мориса Юинга; АФРЗ – Агульяс-Фолклендская разломная зона; ПХА – палеохребет Агульяс. Хребты: САХ – Срединно-Атлантический хребет; ААХ – Американо-Антарктический хребет; МадХ – Мадагаскарский хребет; МозХ – Мозамбикский хребет; ХА – хребет Агульяс; ХШ – хребет Шона; ЮЗИХ – Юго-Западный Индийский хребет; ЮСАХ – Южный сектор Срединно-Атлантического хребта. Подняти-я: ПАО – поднятие Айлос Оркадас; ПБ – поднятие Бейра; ПМ – поднятие Метеор; ПМо – поднятие Мод; ПСВГ – поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия. Бассейны: БН – бассейн Натал; БТр – бассейн Транскей; ФБ – Фолклендский бассейн. Плато: ПА – плато Агульяс; ФП – Фолклендское плато. Котловины: КТ – котловина Транскей; МадК ‒ Мадагаскарская котловина; МозК – Мозамбикская котловина. Горячая точка: ГТБ – Буве; ГТД – Дискавери; ГТШ – Шона. 1‒8 ‒ земная кора, сформированная на спрединговых хребтах: 1 – континентальная, 2 – утоненная континентальная, 3 – моря Скоша, 4 – океаническая САХ, 5 – океаническая ЮЗИХ, 6 – океаническая палеохребта Агульяс, 7 – океаническая ЮСАХ; 8 – океаническая ААХ и моря Уэдделла; 9‒11 ‒ поднятия, сформированные: 9 – на океанической коре (магматические), 10 – на палеохребте Агульяс, 11 – на ЮСАХ; 12 – модельная литосферная мантия; 13 – расплав модельного вещества, имитирующий астеносферу; 14‒15 ‒ хребты: 14 – спрединговые, 15 – палеоспрединговые; 16 – следы трансформных разломов; 17 – демаркационные разломы, ограничивающие район исследования; 18 – расположение горячих точек
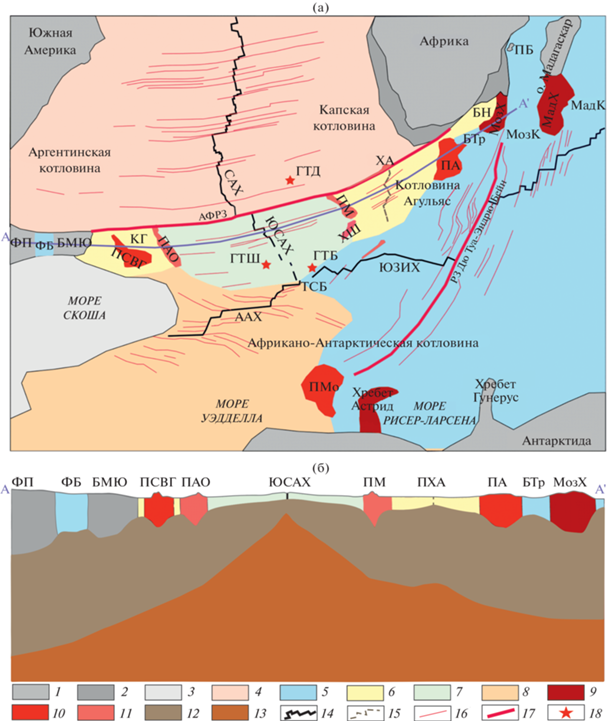
На схеме и на глубинном профиле показаны гетерогенные блоки литосферы, сформированные на разных спрединговых хребтах (Юго-Западном Индийском, Срединно-Атлантическом, Американо-Антарктическом, Уэддельском и хребте Агульяс) и разделенные подводными поднятиями разной морфологической выраженности и разного строения.
Границами между блоками являются следы трансформных разломов или палеодивергентные шовные зоны. Последние, представляют собой либо палеоспрединговые хребты (хребет Агульяс, Уэддельский хребет), либо шовные зоны, сформированные в результате перескоков осей спрединга, как правило, выраженные в поднятиях (Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, Северо-Восточная Георгия и плато Агульяс) и разделяющие разновозрастные блоки литосферы, либо псевдоразломы – следы продвижения спредингового хребта в пределы старой океанической литосферы (Юго-Западного Индийского хребта – к западу и Американо-Антарктического хребта – к востоку).
Все это создает сложный морфоструктурный план, на формирование которого и эволюцию л-итосферы этого региона решающее влияние оказали следующие факторы:
‒ пространственно-временнáя миграция Южно-Американской, Африканской и Антарктической литосферных плит, разделенных разными спрединговыми хребтами соединяющихся в зонах тройных сочленений;
‒ существование континентального блока Фолклендского плато в пределах Южно-Американской плиты, которое могло служить структурным барьером на пути продвигающейся с севера в южном направлении рифтовой оси сегмента САХ;
‒ наличие плюмовой магматической активности, сформировавшей структуру плато Агульяс, в месте соединения трех рифтовых ветвей, а именно ‒ восточной (ЮЗИХ), северной (хребет Агульяс, упирающийся в разломную зону Агульяс) и юго-западной (спрединговый хребет, уходящий в сторону моря Уэдделла), при этом, каждая рифтовая ветвь генерировала свою кору, разделившую единое плато Агульяс на три блока ‒ собственно, плато Агульяс, поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия и поднятие Мод (см. рис. 8, а);
‒ наличие горячей точки (в природе Шона) на океанической коре котловины Агульяс, вблизи окраины Фолклендского плато, могло стимулировать продвижение к югу сегмента САХ.
Следствием этого был перескок оси спрединга, выразившийся в отмирании спредингового хребта Агульяс, формировании сегмента ЮСАХ и шовных зон Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, фиксирующих место его первоначального заложения и разделяющих разновозрастные блоки литосферы, сформированные на палеохребте Агульяс и ЮСАХ.
Процесс перескока оси спрединга не являлся одномоментным явлением, а заключался в постепенном прекращении спрединга на хребте Агульяс и ростом скорости спрединга на новом активном южном сегменте САХ. Такая кинематическая реструктуризация спрединговых хребтов продолжалась на протяжении от 83 до 60.9 млн лет и характеризовалась существованием микроплиты Мальвинес [40].
В результате перескока существенно сократилась активная часть Агульяс-Фолклендского трансформного разлома, а ЮЗИХ начал стремительно продвигаться к западу до его соединения с молодым южным сегментом САХ в зоне современного ТСБ, в то время как Уэдделльский хребет вступил в фазу своего отмирания и прекращения спрединга.
Близкое положение горячей точки Шона привело к формированию поднятия Шона. Южная часть сегмента САХ и западная часть ЮЗИХ были подвержены термическому влиянию горячей точки Буве, что повлияло на структурную сегментацию и осевую морфологию хребтов.
Северная часть ЮСАХ характеризуется наличием трансформных разломов, узкой отчетливой осевой рифтовой долиной.
Вся южная часть ЮСАХ отражает влияние термической аномалии на сегментацию и морфологическую выраженность южного участка спредингого хребта, где наблюдается рассеянный спрединг, отсутствуют трансформные разломы и преобладают нетрансформные смещения.
На основании физического моделирования структурообразующих деформаций в районе исследования построена экспериментальная модель, которая позволила выявить особенности эволюции литосферы данного региона. Исследованы условия образования подводных поднятий южного сектора приантарктической части Южной Атлантики в результате реорганизации геометрии границ плит, приведшей к неоднократным перескокам оси спрединга.
Следствием кинематических перестроек, часто связанных с проявлениями плюмовой магматической активности стал раскол на три блока крупного плато Агульяс ‒ собственно плато Агульяс, поднятие Северо-Восточная Георгия и поднятие Мод, формирование спредингового хребта Агульяс и одноименной котловины, последующее отмирание спредингового хребта Агульяс и формирование ЮСАХ, генерирующего новую молодую океаническую кору, отделенную от более древней коры и литосферы котловины Агульяс сопряженными симметрично расположенными относительно оси ЮСАХ хребтами Метеор и Айлос Оркадас.
ВЫВОДЫ
Таким образом, анализ геолого-геофизической информации, результаты плотностного и физического моделирования позволяют выявить основные генетические типы подводных поднятий в данном регионе и установить геодинамические условия их формирования.
1. Современные спрединговые хребты (южный сегмент Срединно-Атлантического хребта – сформированный в результате продвижения оси Срединно-Атлантического хребта к югу под влиянием горячей точки Шона; Юго-Западный Индийский хребет – сформированный в результате продвижения к западу и соединения с южным сегментом Срединно-Атлантического хребта в области современного положения тройного сочленения Буве; Американо-Антарктический хребет – сформированный в результате необходимости кинематического урегулирования замкнутости границ плит между Южно-Американской и Антарктической плитами и плитой Скоша).
2. Палеоспрединговый хребет Агульяс, сформированный в результате формирования южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта, в результате чего произошло прекращение спрединга на хребте Агульяс.
3. Асейсмические хребты, частично отделенные от континента и подстилаемые утоненной континентальной корой (Мозамбикский хребет).
4. Хребты, сформированные в результате плюмового магматизма, сложенные утолщенной за счет андерплейтинга океанической корой (Мадагаскарский хребет).
5. Поднятия Метеор и Айлос Оркадас, образованные при формировании южного сегмента Срединно-Атлантического хребта на старой океанической литосфере в результате перескока оси спрединга вызванного активной деятельностью горячей точки.
6. Погруженные плато и поднятия (Агульяс, Северо-Восточная Георгия, Мод), представляющие собой фрагменты крупной единой магматической провинции.
7. Микроконтинент Бейра, представляющий собой отторженный блок с утоненной континентальной корой.
Благодарности. Авторы благодарят рецензента А.А. Пейве (ГИН РАН, г.Москва, Россия) и анонимного рецензента за конструктивные замечания и признательны редактору М.Н. Шуплецовой (ГИН РАН, г. Москва, Россия) за тщательное редактирование.
Финансирование. Работа выполнена при поддержке Российского научного фонда (проект № 22-27-00110).
Список литературы
Грохольский А.Л., Дубинин Е.П. Аналоговое моделирование структурообразующих деформаций литосферы в рифтовых зонах срединно-океанических хребтов // Геотектоника. 2006. № 1. С. 76‒94.
Дубинин Е.П., Грохольский А.Л., Макушкина А.И. Физическое моделирование условий образования микроконтинентов и краевых плато континентальных окраин // Физика Земли. 2018. № 1. С. 69‒82.
Дубинин Е.П., Сущевская Н.М., Грохольский А.Л. История развития спрединговых хребтов Южной Атлантики и пространственно-временнóе положение тройного соединения Буве // Российский журнал наук о Земле. 1999. Т. 1. № 5. С. 423‒443.
Дубинин Е.П., Кохан А.В., Тетерин Д.Е., Грохольский А.Л., Курбатова Е.С., Сущевская Н.М. Тектоническое строение и типы рифтогенных бассейнов моря Скотия, Южная Атлантика // Геотектоника. 2016. № 1. С. 41‒61.
Дубинин Е.П., Грохольский А.Л. Особенности структурообразования в процессе развития литосферы Аденского залива (физическое моделирование) // Геодинамика и тектонофизика. 2020. Т. 11. № 3. С. 522‒547.
Дубинин Е.П., Чупахина А.И., Грохольский А.Л. Физическое моделирование условий формирования подводных поднятий Метеор и Айлос Оркадас (Южная Атлантика) // Океанология. 2023. Т. 63. № 3. С. 482‒491.
Лейченков Г.Л., Гусева Ю.Б., Гандюхин В.В., Иванов С.В. Строение земной коры и история геологического развития осадочных бассейнов индоокеанской акватории Антарктики. ‒ С-Пб: ИЦ “Академия”, 2015. 200 с.
Лейченков Г.Л., Сущевская Н.М., Беляцкий Б.В. Геодинамика атлантического и индийского секторов Южного океана // ДАН. 2003. Т. 391. № 5. С. 675–678.
Пейве А.А., Зителлини Н., Перфильев А.С., Мазарович А.О., Разницин Ю.Н., Турко Н.Н., Симонов В.А., Аверьянов С.Б., Бортолуци Д., Булычев А.А., Гасперини Л., Гилод Д.А., Гладун В.А., Евграфов Л.М., Ефимов В.Н. и др. Строение Срединно-Атлантического хребта в районе тройного сочленения Буве // ДАН. 1994. Т. 338. № 5. С. 645‒648.
Пейве А.А., Перфильев А.С., Пущаровский Ю.М., Симонов В.А., Турко Н.Н., Разницин Ю.Н. Строение района южного окончания Срединно-Атлантического хребта (тройное сочленение Буве) // Геотектоника. 1995. № 1. С. 51‒68.
Пущаровский Ю.М. Тектоника и геодинамика спрединговых хребтов Южной Атлантики // Геотектоника. 1998. № 4. С. 41‒52.
Рыжова Д.А., Коснырева М.В., Дубинин Е.П., Булычев А.А. Строение тектоносферы Мозамбикского и Мадагаскарского хребтов по геофизическим данным // Вестн. МГУ. Сер.4. Геология. 2021. № 6. С. 20‒29.
Удинцев Г.Б., Береснев А.Ф., Куренцова Н.А. и др. Пролив Дрейка и море Скоша – океанские ворота Западной Антарктики. ‒ В кн.: Строение и история развития литосферы. ‒ Т. 4 ‒ Вклад России в Международный Полярный год. ‒ М.: Paulsen, 2010. С. 66‒90.
Шеменда А.Н. Критерии подобия при механическом моделировании тектонических процессов // Геология и геофизика. 1983. № 10. С. 10‒19.
Ben-Avraham Z., Hartnady C.J.H., le Roex A.P. Neotectonic activity on continental fragments in the Southwest Indian Ocean: Agulhas Plateau and Mozambique Ridge // J. Geophys. Res. 1995. Vol. 100. B4. P. 6199‒ 6111.
Bradford M.C., Hailwood E.A. Magnetostratigraphy of Sediments from Sites 701 and 702. ‒ In: SubAntarctic South Atlantic. ‒ Proceedings of Scientific Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. College Station, TX. 1991. Vol. 114). P. 359‒366.
Brenner C., La Brecque J.L. Bathymetry of the Georgia Basin and environs. ‒ In: Sub-Antarctic South Atlantic. ‒ Proc. Sci. Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. College Station, TX. 1988. Vol. 114). P. 23‒26.
Ciesielski P.R., Kristoffersen Y., Hailwood E.A., et al. Site 698. – In: SubAntarctic South Atlantic. ‒ Proc. Sci. Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. College Station, TX. 1988. Vol. 114). P. 87‒ 254.
Cox K.G. Karoo igneous activity, and the early stages of the break-up of Gondwanaland. ‒ In: Magmatism and the Causes of Continental Break-Up. ‒ Ed.by B.C. Storey, T.Alabaster, R.J. Pankhurst ‒ (Geol. Soc., London, Spec. Publ. 1992. Vol. 68). P. 137‒148.
Eagles G., Jokat W. Tectonic reconstructions for paleobathymetry in Drake Passage // Tectonophysics. 2014. Vol. 611. P. 28‒50.
Eagles G., König M. A model of plate kinematics in Gondwana breakup // Geophys. J. Int. 2008. Vol. 173. P. 703–717.
Evans H.F., Westerhold T., Channell J.E.T. ODP Site 1092: Revised Composite Depth Section has Implications for Upper Miocene 'Cryptochrons' // Geophys. J. Int. 2004. Vol. 156. No. 2. P. 195‒199.
Fischer M.D., Uenzelmann-Neben G., Jacques G., Werner R. The Mozambique Ridge: A document of massive multistage magmatism // Geophys. J. Int. 2017. Vol. 208. No. 1. P. 449‒467.
Galindo-Zaldivar J., Balanya J., Bohoyo F., Jabaloy A. Active crustal fragmentation along the Scotia–Antarctic plate boundary east of the South Orkney Microcontinent (Antarctica) // Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002. Vol. 204. P. 33‒46.
Gohl K., Uenzelmann-Neben G. The crustal role of the Aguhlas Plateau, southwest Indian Ocean: Evidence from seismic profiling // Geophys. J. Int. 2001. Vol. 144. P. 632‒646.
Hanyu T., Nogi Y., Fujii M. Crustal formation and evolution processes in the Natal Valley and Mozambique Ridge, off South Africa // Polar Science. 2017. Vol. 13. P. 66‒81.
Hastie W.W., Watkeys M.K., Aubourg C. Magma flow in dyke swarms of the Karoo LIP: implications for the mantle plume hypothesis. // Gondwana Research. 2014. Vol. 25. P. 736‒755.
Hoernle K., Schwindrofska A., Werner R., van den Bogaard P., Hauff F., Uenzelmann-Neben G., Garbe-Schönberg D.D. Tectonic dissection and displacement of parts of Shona hotspot volcano 3500 km along the Agulhas-Falkland Fracture Zone // Geology. 2016. Vol. 44. No. 4. P. 263‒266.
Jacques G., Hauff F., Hoernle K. et al. Nature and origin of the Mozambique Ridge, SW Indian Ocean // Chem. Geol. 2019. Vol. 507. P. 9‒22.
Kent D.V., Gradstein F.M. A Jurassic to recent chronology. ‒ In: The Western North Atlantic Region. ‒ (GSA. 1986. Vol. M). P. 45‒50.
König M., Jokat W. The Mesozoic breakup of the Weddell Sea // J. Geophys. Res. 2006. Vol. 111. P. 1‒28.
König M., Jokat W. Advanced insights into magmatism and volcanism of the Mozambique Ridge and Mozambique Basin in the view of new potential field data // Geophys. J. Int. 2010. Vol. 180. No. 1. P. 158‒180.
Kristoffersen Y., Labrecque J. On the tectonic history and origin of the Northeast Georgia Rise. ‒ In: SubAntarctic South Atlantic. ‒ Proc. Sci. Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. College Station, TX. 1991. Vol. 114). P. 23‒38.
Labrecque J.L., Ciesielski P.F., Clement B. Sub-Antarctic South Atlantic. ‒ in: Proceedings of Scientific Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. 1987. Vol. 114), p. 135.
Labrecque J.L., Hayes D.E. Seafloor spreading history of the Agulhas Basin // Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979. Vol. 45. No. 2. P. 411‒428.
Laughton A.S., Matthews D.H., Fisher R.L. The structure of the Indian Ocean. ‒ In: The Sea; Ideas and Observations. ‒ Ed.by M. Hill, (NY, USA. 1970. Vol. 4. Is. 2). P. 543‒586.
Lawver L.A., Gahagan L.M., Dalziel I.W.D. A tight fit-early Mesozoic Gondwana: A plate reconstruction perspective // Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Spec. 1998. Iss. 53. P. 214‒229.
Le Roex A., Class C., O’Connor J., Jokat W. Shona and discovery aseismic ridge systems, South Atlantic: Trace element evidence for enriched mantle sources // J. Petrol. 2010. Vol. 51. No. 10. P. 2089‒2120.
Leinweber V.T., Jokat W. The Jurassic history of the Africa-Antarctica corridor – new constraints from magnetic data on the conjugate continental margins // Tectonophysics. 2012. Vol. 530–531. P. 87‒101.
Marks K.M., Stock J.M. Evolution of the Malvinas Plate south of Africa // Marin. Geophys. Res. 2001. Vol. 22. P. 289‒302.
Marks K.M., Tikku A.A. Cretaceous reconstructions of East Antarctica, Africa and Madagascar // Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001. Vol. 186. P. 479‒495.
Martos Y.M., Galindo-Zaldívar J., Catalán M., Bohoyo F., Maldonado A. Asthenospheric Pacific-Atlantic flow barriers and the West Scotia Ridge extinction // J. Geophys. Res. 2014. Vol. 41. P. 43‒49.
Matsinhe N.D., Tang Y., Li CF. et al. The crustal nature of the northern Mozambique Ridge, Southwest Indian Ocean // Acta Oceanologica Sinica. 2021. Vol. 40. No. 7. P. 170‒182.
Meyer B., Chulliat A., Saltus R. Derivation and Error Analysis of the Earth Magnetic Anomaly Grid at 2 arc min Resolution Version 3 (EMAG2v3) // Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017. Vol. 18. P. 4522‒4537.
Mueller C.O., Jokat W., Schreckenberger B. The crustal structure of Beira High, central Mozambique—Combined investigation of wide-angle seismic and potential field data // Tectonophysics. 2016. Vol. 683. P. 233‒ 254.
Mueller C.O., Jokat W. The initial Gondwana break-up: A synthesis based on new potential field data of the Africa-Antarctica Corridor // Tectonophysics. 2019. Vol. 750. P. 301‒328.
Muller R.D., Sdrolias M., Gaina C., Roest W.R. Age, spreading rates, and spreading asymmetry of the world’s ocean crust // Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008. Vol. 9. No. 4. P. 1‒19.
Parsiegla N., Gohl K., Uenzelmann-Neben G. The Agulhas Plateau: Structure and evolution of a large igneous province // Geophys. J. Int. 2008. Vol. 174. P. 336‒350.
Pérez Díaz L, Eagles G. Constraining South Atlantic growth with seafloor spreading data // Tectonics. 2014. Vol. 33. No. 9. P. 1848‒1873.
Raymond C.A., LaBrecque J.L., Kristoffersen Y. Islas Orcadas Rise and Meteor Rise: The tectonic and depositional history of two aseismic plateaus from sites 702, 703, and 704. – In: Sub-Antarctic South Atlantic. ‒ Proc. Sci. Results ODP, Leg. 114. ‒ (Ocean Drilling Program, Sci. Prospects. College Station, TX. 1991. Vol. 114). P. 5‒22.
Reeves C. V. et al. Insight into the Eastern Margin of Africa from a new tectonic model of the Indian Ocean // Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ .2016. Vol. 431. No. 1. P. 299‒323.
Reeves C.V., de Wit M.J. Making ends meet in Gondwana: retracing the transforms of the Indian Ocean and reconnecting continental shear zones // Terra Nova. 2000. Vol. 12. No. 6. P. 272‒282.
Riley T.R., Leat P.T., Curtis M.L., Millar L.L., Fazel A. Early-Middle Jurassic dolerite dykes from western Dronning Maud Land (Antarctica): Identifying mantle sources in the Karoo large igneous province // J. Petrol. 2005. Vol. 46. P. 1489‒1524.
Sandwell D.T., Müller D., Smith W.H.F., Garcia E., Francis R. New global marine gravity from CryoSat-2 and Jason-1 reveals buried tectonic structure // Science. 2014. Vol. 346. No. 6205. P. 65‒67.
Schaeffer A.J., Lebedev S. Global shear speed structure of the upper mantle and transition zone // Geophys. J. Int. 2013. Vol. 194. P. 417‒449.
Schimschal C.M., Jokat W. The Falkland Plateau in the context of Gondwana breakup // Gondwana Research. 2019. Vol. 68. P. 108‒115.
Shemenda A.I., Grokholsky A.L. A formation and evolution of overlapping spreading centers (constrained on the basis of physical modeling) // Tectonophysics. 1991 Vol. 199. P. 389‒404.
Shemenda A.I., Grocholsky A.L. Physical modeling of slow seafloor spreading // J. Geophys. Res. 1994. Vol. 99. P. 9137‒9153.
Simmons N.A., Myers S.C., Johannesson G., Matzel E. LLNL-G3Dv3: Global P wave tomography model for improved regional and teleseismic travel time prediction // J. Geophys. Res. 2012. Vol. 117. No. B10. P. 1‒28.
Simpson E.S.W., Schlich R., et al. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. ‒ (Washington, U.S. Govern. Print. Office. 1974. Vol. 25). P. 1‒873.
Sleep N.H. Ridge-crossing mantle plumes and gaps in tracks // Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2002. Vol. 3. No. 12. P. 1‒33.
Thompson J. O., Moulin M., Aslanian D., de Clarens P., Guillocheau F. New starting point for the Indian Ocean: Second phase of breakup for Gondwana // Earth-Science Rev. 2019. Vol. 191. P. 26‒56.
Torsvik T.H., Rousse S., Labails C., Smethurst M.A. A new scheme for the opening of the South Atlantic Ocean and the dissection of an Aptian salt basin // Geophys. J. Int. 2009. Vol. 177. No. 3. P. 1315‒1333.
Tucholke B.E., Houtz R.E., Barrett D.M. Continental crust beneath the Agulhas Plateau, Southwest Indian Ocean // J. Geophys. Res.1981. Vol. 86. P. 3791‒3806.
Vérard C., Flores K., Stampfli G. Geodynamic reconstructions of the South America–Antarctica plate system // J. Geodynamics. 2012. Vol. 53. P. 43‒60.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.


